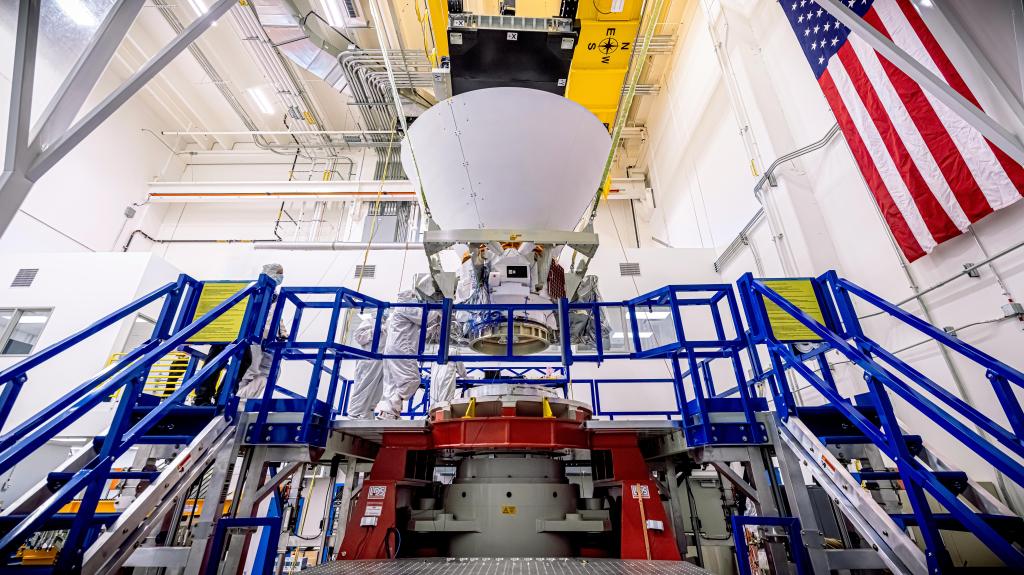
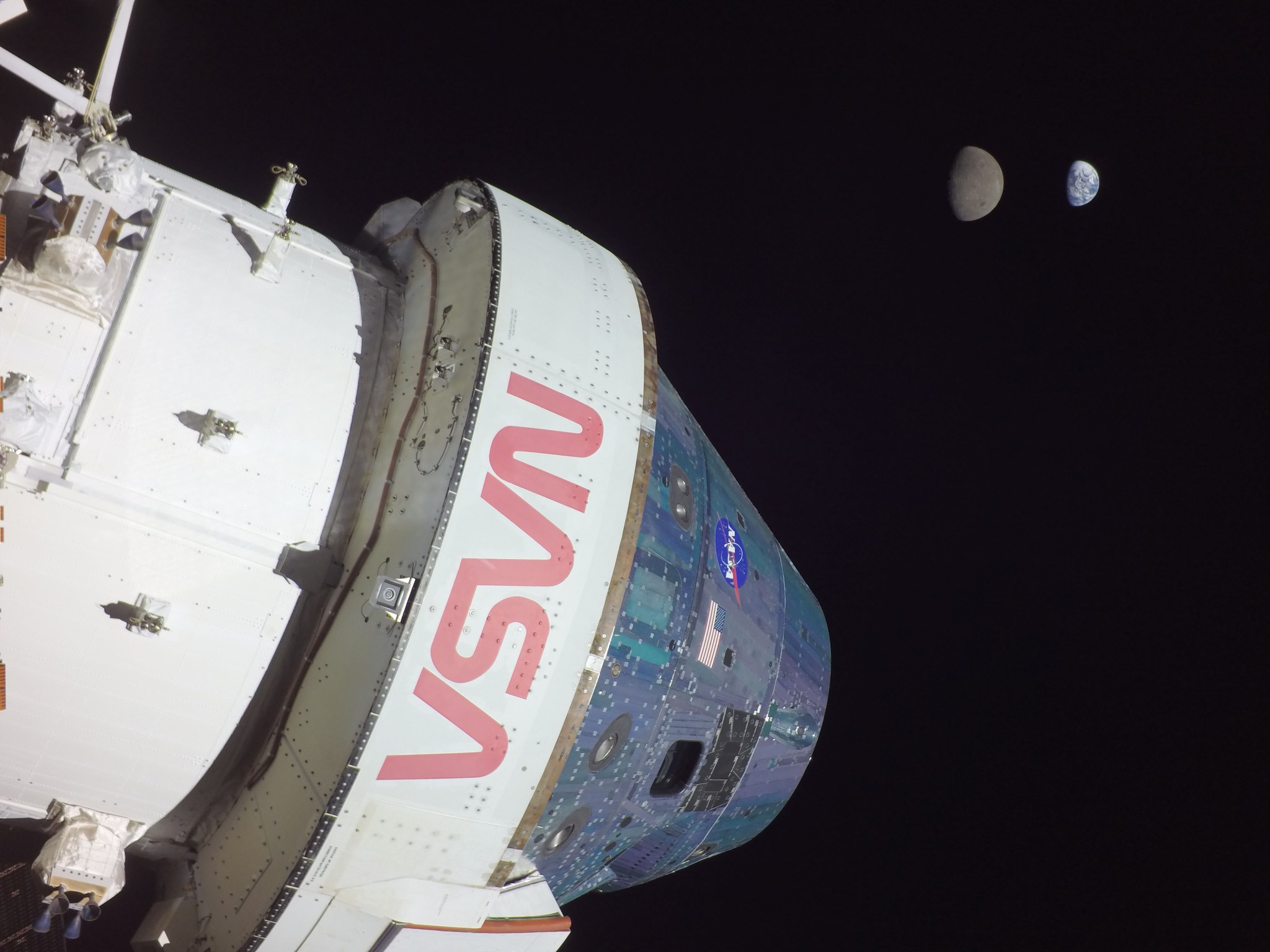
The Artemis II test flight will be NASA’s first mission with crew under the Artemis campaign and will pave the way to land astronauts on the Moon on Artemis III and future missions. The crew of four aboard the agency’s Orion spacecraft will travel around the Moon and back to confirm the spacecraft’s systems operate as designed with crew aboard in the actual environment of deep space. Through Artemis, NASA will send astronauts – including the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut – to explore the Moon for scientific discovery, economic benefits, and to build the foundation for crewed missions to Mars.
On Dec. 5, NASA updated its timelines for the missions and shared the results of an investigation into the Orion heat shield after it experienced an unexpected loss of charred material during re-entry of the Artemis I uncrewed test flight in late 2022.
Here are some frequently asked questions about Artemis II, NASA’s recent updates, and the agency’s path to the Moon and Mars.
What is Orion?
NASA’s Orion spacecraft is where our crew live while traveling to and from deep space. Orion is built to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before. On Artemis missions, Orion will carry crews of four astronauts from Earth to space, provide emergency abort capability, sustain them as they venture to the Moon, and safely return them to Earth from deep space speeds and temperatures.
What is a heat shield and why is it important?
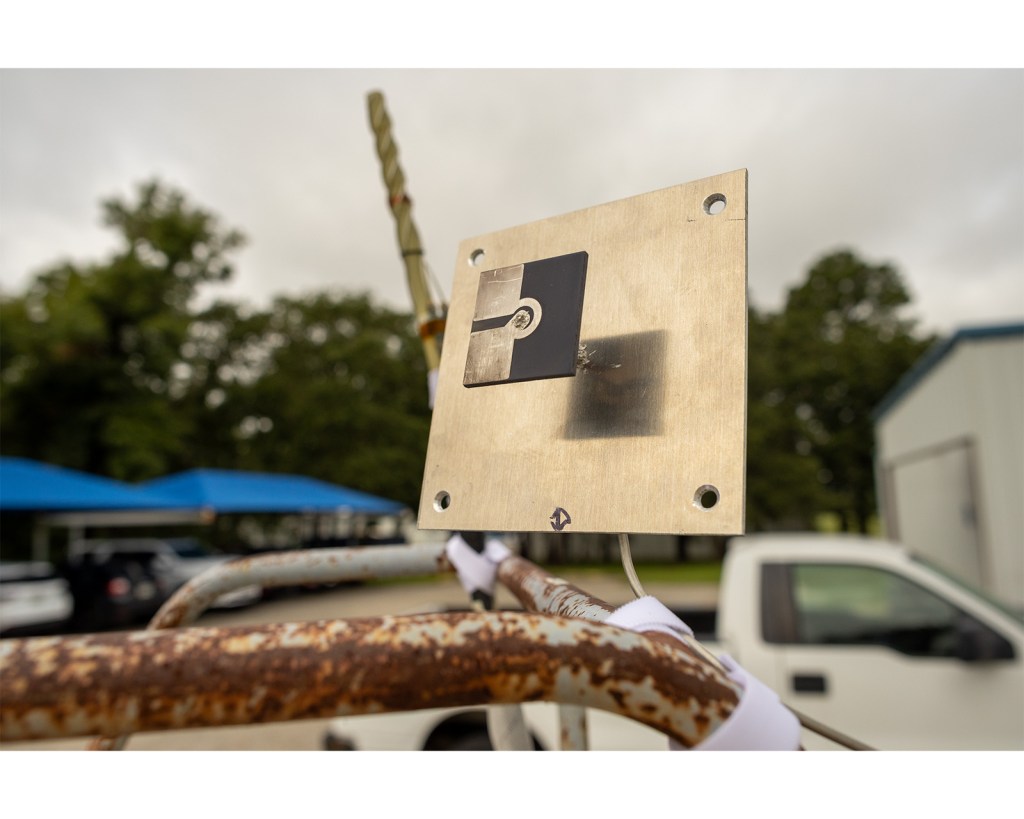
When Orion travels back from deep space, its journey through Earth’s atmosphere generates intense temperatures of up to 5,000 degrees Fahrenheit on parts of the spacecraft. The 16-foot diameter protective heat shield on the bottom of the capsule is designed to dissipate that heat and keep the crew inside safe. Orion’s heat shield is primarily composed of Avcoat, a material designed to wear away as it heats up.
What abnormal behavior did you see on the Artemis I heat shield?
NASA flew the uncrewed Artemis I mission in late 2022 to test Orion, the agency’s SLS rocket, and the ground systems needed to launch them, testing these elements together for the first time to ensure engineers understand everything about the systems before flights with astronauts. The successful test flight sent Orion past the Moon and provided valuable data to ensure our deep space spacecraft and other systems are ready for crewed missions. When Orion returned to Earth, engineers saw variations across Orion’s heat shield they did not expect. Some of the charred material had broken off. If a crew had been aboard the flight, they would have remained safe, but understanding the phenomenon has been the subject of an extensive investigation since the test flight.
What did NASA find as the cause of the issue?
Engineers determined that as Orion was returning from its uncrewed mission around the Moon, gases generated inside the heat shield’s ablative outer material called Avcoat were not able to vent and dissipate as expected. This allowed pressure to build up and horizontal cracking to occur near the surface of the charred layer, causing some charred material to break off in several locations.
For Artemis II, engineers will limit how long Orion spends in the temperature range in which the Artemis I heat shield phenomenon occurred by modifying how far Orion can fly between when it enters Earth atmosphere and lands. Engineers already are assembling and integrating the Orion spacecraft for Artemis III based on lessons learned from Artemis I and implementing enhancements to how heat shields for crewed returns from lunar landing missions are manufactured to achieve uniformity and consistent permeability. A more detailed description is here.
Why did NASA decide to use the current heat shield?
Extensive data from the investigation has given engineers confidence the heat shield for Artemis II can be used to safely fly the mission’s crew around the Moon and back. NASA will modify the trajectory by shortening how far Orion can fly between when it enters Earth’s atmosphere and splashes down in the Pacific Ocean. This will limit how long Orion spends in the temperature range in which the Artemis I heat shield phenomenon occurred. The heat shield for the test flight is already attached to Orion.
When will Artemis II take place?
The Artemis II test flight will be NASA’s first mission with crew aboard the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft and will pave the way to land astronauts on the Moon on Artemis III. Artemis II builds on the success of the uncrewed Artemis I mission and will demonstrate a broad range of capabilities needed on lunar missions. The 10-day flight will help to confirm all of the spacecraft’s systems operate as designed with crew aboard in the actual environment of deep space. The mission is targeted for April 2026.
The updated timeline for the Artemis II flight is informed by technical issues engineers are troubleshooting including with an Orion battery issue and its environmental control system. The heat shield was installed in June 2023 and the root cause investigation took place in parallel to other assembly and testing activities to preserve as much schedule as possible.
What are the astronauts doing during the mission delay?
NASA astronauts Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, Christina Koch, and Canadian Space Agency (CSA) astronaut Jeremy Hansen will continue training for the mission. More intensive training will begin about six months before launch.
About the Artemis Campaign
What is Artemis?
NASA is establishing a long-term presence at the Moon for scientific exploration and discovery with our commercial and international partners, learning how to live and work far from home, and preparing for future human exploration of Mars – we call this endeavor Artemis. Under Artemis, NASA will land the first woman, first person of color, and first international partner astronaut on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
Why is NASA going back to the Moon?
NASA is going back to the Moon for scientific discovery, economic benefits, and inspiration for a new generation of explorers: the Artemis Generation. Artemis is a new approach to America’s space exploration efforts — it is the most technically challenging, collaborative, international endeavor humanity has ever set out to do. What we learn from expanding scientific knowledge and developing new technologies will be applied to improve life on Earth. Samples from the lunar South Pole could tell us more about the formation of our planet and origins of our solar system. We are meeting this challenge by investing in American ingenuity and leadership to advance our understanding of the universe for the benefit of all.
What makes Artemis different from Apollo?
The Apollo Program successfully landed 12 men near the equator of the Moon in the 1960s and 1970s. Under Artemis, NASA is going to the lunar South Pole region, where no humans have ever set foot, in new ways with commercial and international partners. The agency is leading the largest international coalition in space to push humanity farther than ever before for the benefit of all, developing capabilities for astronauts to live and work on the Moon before our next giant leap – human exploration of Mars.
What happens after Artemis II?
Artemis III will build on the crewed Artemis II flight test, adding new capabilities with the human landing system and advanced spacesuits to send the first humans to explore the lunar South Pole region. Over the course of about 30 days a crew of four will launch atop the Space Launch System rocket in Orion and travel to a special lunar orbit where they will dock with SpaceX’s Starship human landing system. Two Artemis crew members will transfer from Orion to Starship and descend to the lunar surface. There, they will collect samples, perform science experiments, and observe the Moon’s environment before returning in Starship to Orion waiting in lunar orbit. The mission is planned for mid-2027.
NASA is also working with SpaceX to further develop the company’s Starship lander requirements for Artemis IV. These requirements include landing more mass on the Moon and docking with the agency’s Gateway lunar space station for crew transfer. NASA will use Blue Origin’s human landing system for Artemis V.