When people and equipment travel to the International Space Station, microbes like bacteria and fungi also come along for the ride. While some are harmless or even beneficial, some hitchhiking microbes could cause problems on the station. Even sparse populations of microbes that are normally benign on Earth could impact crew health if given a chance to multiply. Other bacteria, if grown unchecked on station surfaces, can potentially degrade critical life support, research, and electronic systems.
To ensure crew safety, NASA scientists carefully monitor the microbiome of the space station. They have two main goals: to map and keep track of microbes present through time, and to discover any patterns of microbial growth that could potentially affect the crew’s health and safety. They’re seeking to puzzle out whether the station itself creates conditions that spur microbial growth.
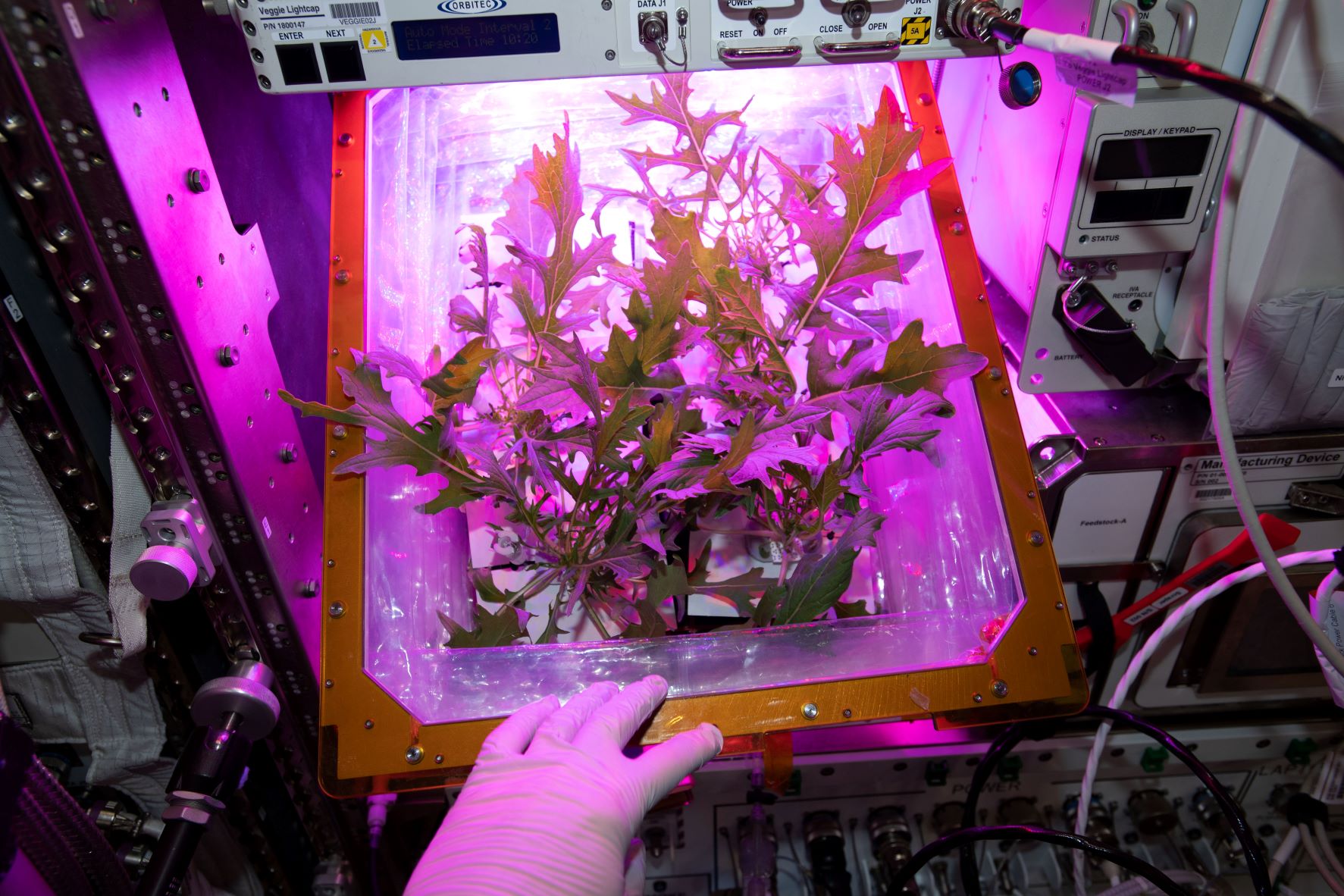
A group of NASA scientists are paying particular attention to monitoring the Vegetable Production System, or Veggie, the hardware used for growing plants aboard the space station. Led by Dr. Cherie Oubre, a senior scientist at NASA’s Johnson Space Center Microbiology Laboratory in Houston, this group is on a multiyear effort to characterize and monitor the microbes present on Veggie.
“NASA is going to the Moon and will someday head to Mars. These long missions will need systems like Veggie,” explains Oubre. “But if the crew consumes food contaminated with pathogenic organisms, they could become ill. Or, if plant growth systems become contaminated with plant pathogens, the crops could be compromised or fail. To prepare, we must assess Veggie’s vulnerabilities and carefully monitor it for microbial growth.”
With its root-mat to provide water to the plants and plant “pillows” that contain fertilizer and seed, Veggie creates added pockets for possible microbes to thrive. Oubre’s team wants to know: What kind of microbes are actually growing there, and are they different from those on Earth?
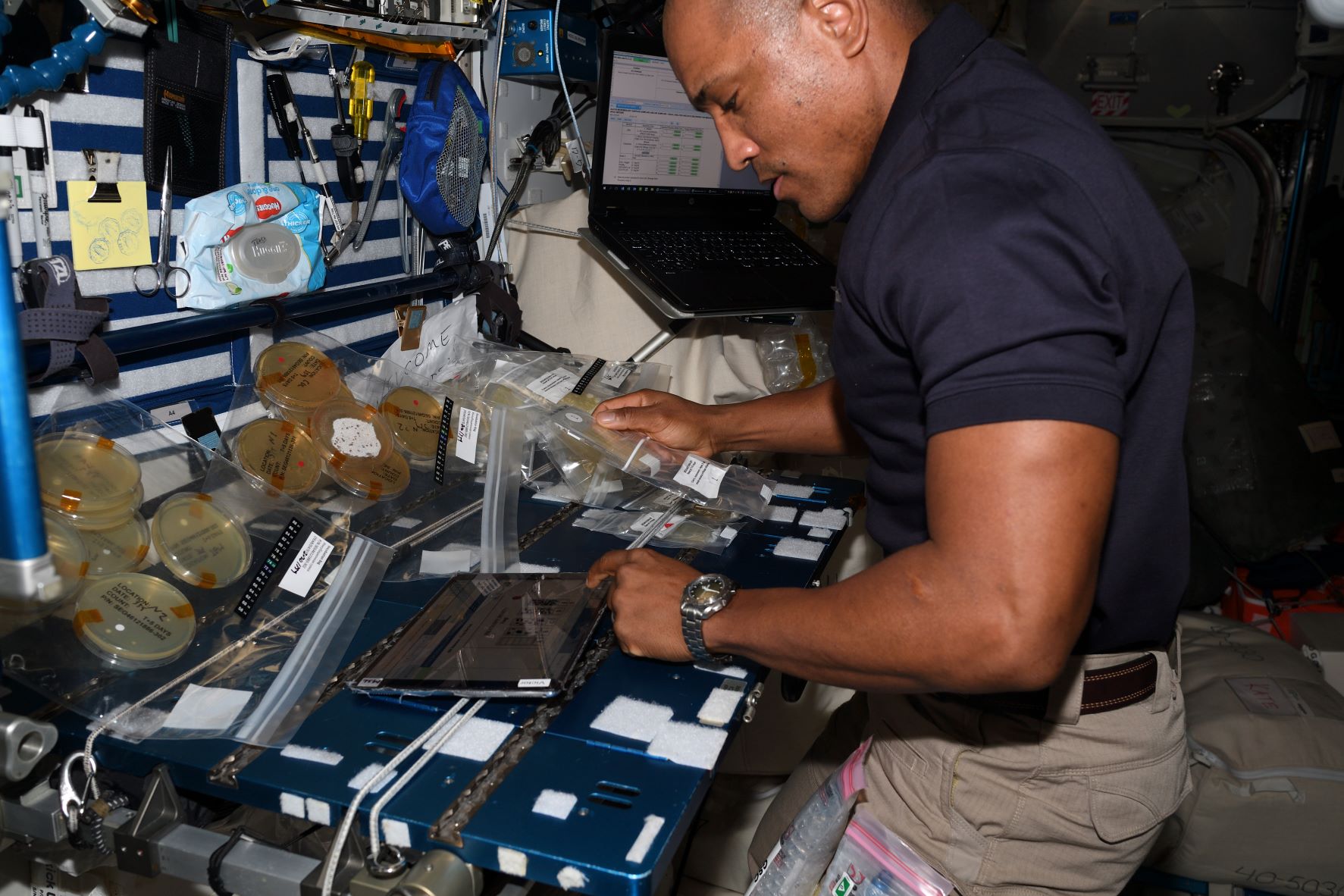
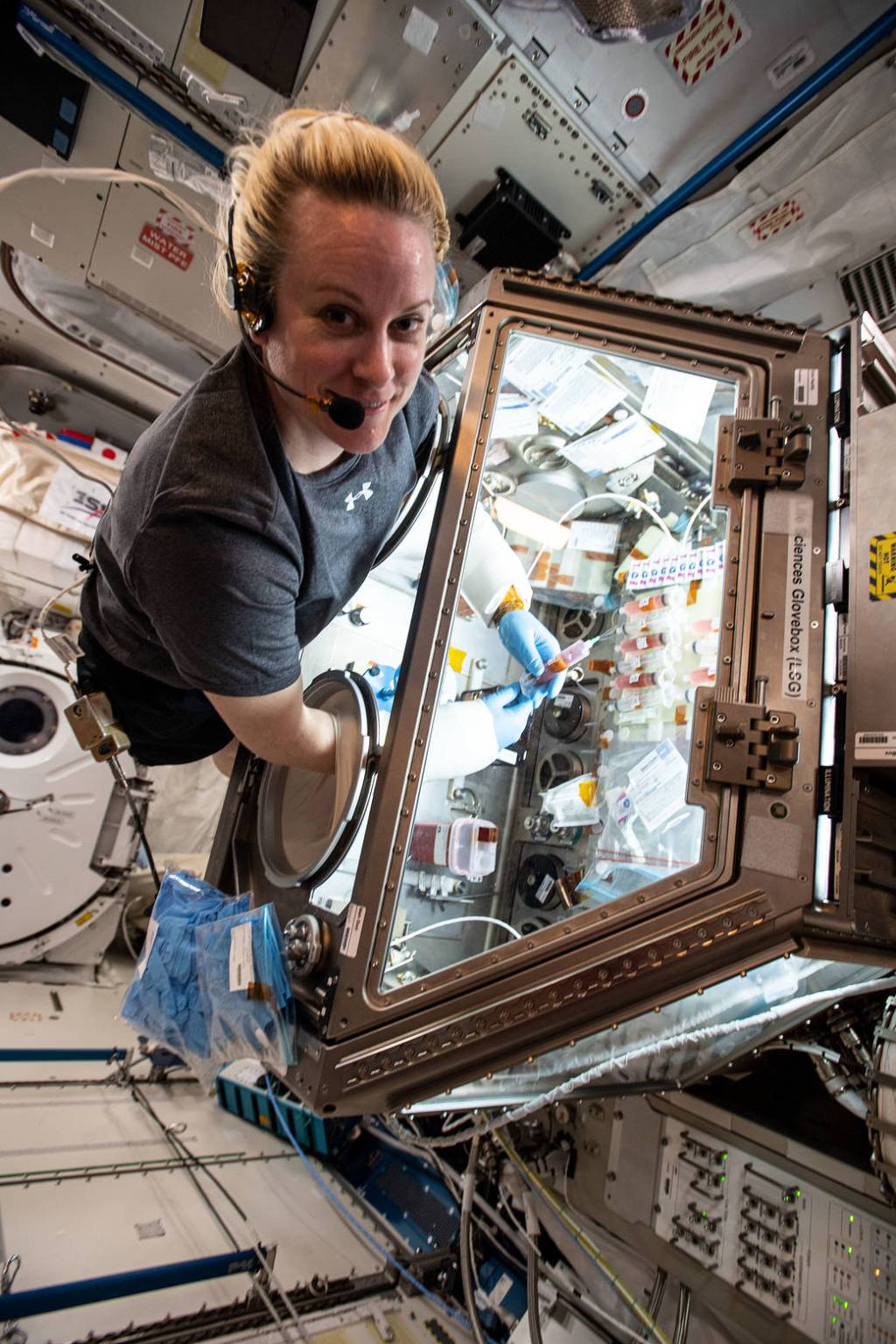
To help find out, astronauts on the station swab exterior components of the Veggie system such as the vent screen and control panel. They also take water samples from the station’s drinking water supply. Swabbing and sample collection occurs about every four months.
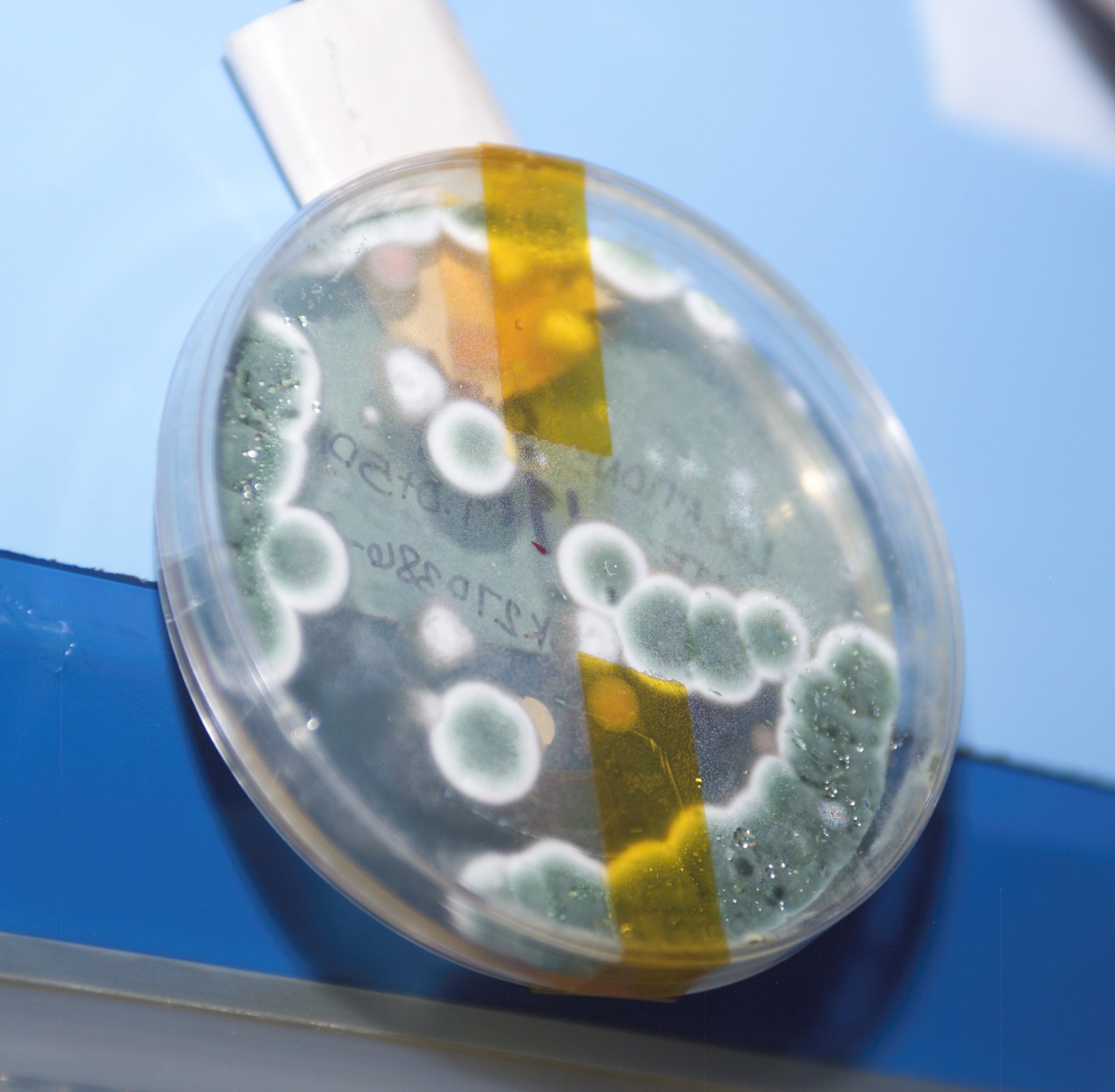
These swabs and samples are then transferred to growth media slides (microbe “food”) and incubated at ambient temperature, to allow the microbes to grow for several days until colonies of organisms are visible. After five days of incubation, crew members analyze the slides and record the density of the colonies. Finally, samples are stowed and returned to Earth when a mission ends.
At that point, the work of Oubre’s team begins. They identify each distinct microbial species on the slides, which involves carefully scrutinizing microbes under a microscope. They whittle down possible species classifications based on how different microbes react in the presence of nutrients and other biochemicals, and sequence the microbes’ DNA.
Once different samples have been analyzed over four to five years, the team will try to assess patterns in microbial growth through time. With this information, scientists can also see how growth patterns on Veggie fit with data on the full microbial map of the station through time.
Samples have been collected, returned to Earth, and analyzed from four space station expeditions: 58, 59, 61, and 62. Sampling began in 2019. Oubre anticipates that samples need to be collected for at least two more years to obtain the necessary information.
Victoria Castro, a microbiologist on Oubre’s team, notes that thus far, microbes found on Veggie align with what the team expects to find. The team found, for instance, species of Penicillium fungi, commonly found on bread, and Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteria, often found on human skin.
“Such microbial growth alone is not always enough to cause concern or even warrant any immediate action,” says Castro. “Continued surveillance is important to capture patterns or trends that indicate issues. And if known pathogens are ever isolated, we’re on hand to step the crew through how to remove them, and the crew will assist us in resampling to make sure the pathogens stay gone.”
Results from this study will help researchers design a better plant production system, and ensure the crew’s safety and fresh food security during Artemis missions, on Gateway, and eventually on Mars. On Earth, the same principles can be applied to improve food production in remote environments.
______
NASA’s Human Research Program, or HRP, pursues the best methods and technologies to support safe, productive human space travel. Through science conducted in laboratories, ground-based analogs, and the International Space Station, HRP scrutinizes how spaceflight affects human bodies and behaviors. Such research drives HRP’s quest to innovate ways that keep astronauts healthy and mission-ready as space travel expands to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.