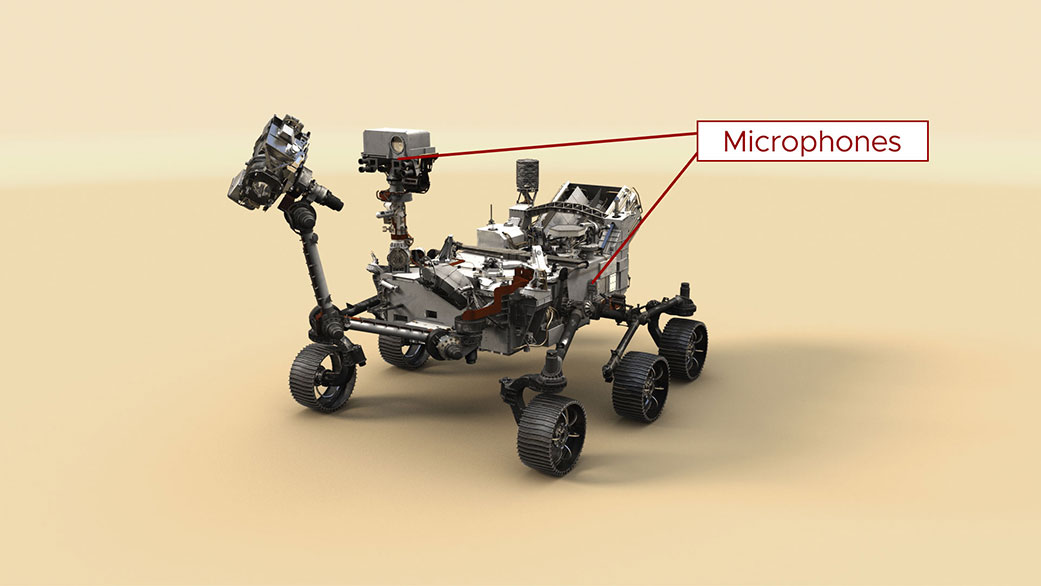
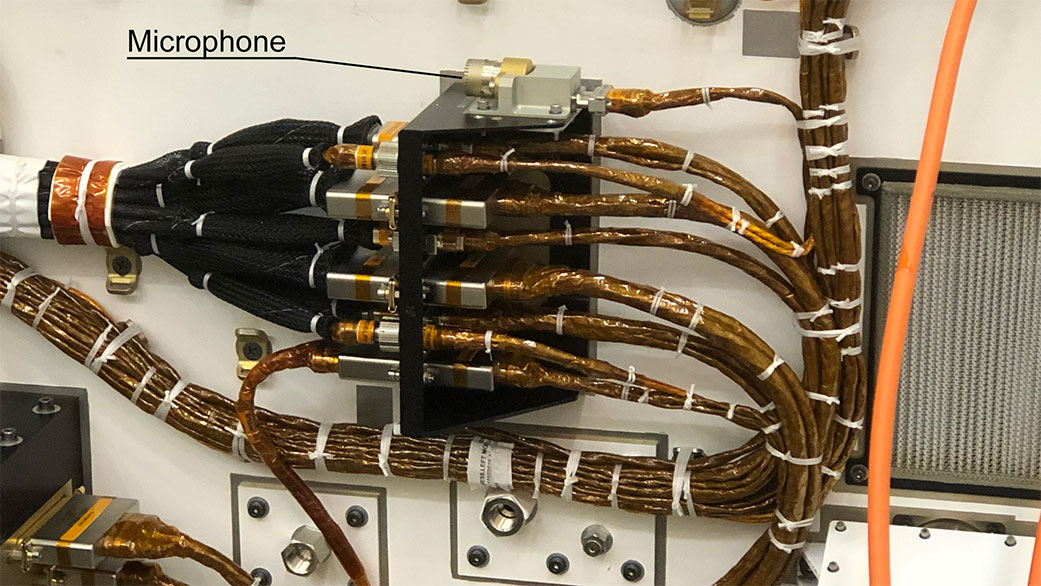
Two microphones aboard the six-wheeled spacecraft add a new dimension to the way scientists and engineers explore the Red Planet.
Thanks to two microphones aboard NASA’s Perseverance rover, the mission has recorded nearly five hours of Martian wind gusts, rover wheels crunching over gravel, and motors whirring as the spacecraft moves its arm. These sounds allow scientists and engineers to experience the Red Planet in new ways – and everyone is invited to listen in.
“It’s like you’re really standing there,” said Baptiste Chide, a planetary scientist who studies data from the microphones at L’Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie in France. “Martian sounds have strong bass vibrations, so when you put on headphones, you can really feel it. I think microphones will be an important asset to future Mars and solar system science.”
Perseverance is the first spacecraft to record the sound of the Red Planet using dedicated microphones – both of which were commercially available, off-the-shelf devices. One rides on the side of the rover’s chassis. The second mic sits on Perseverance’s mast as a complement to the SuperCam laser instrument’s investigations of rocks and the atmosphere.
The body mic was provided by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, while the SuperCam instrument and its microphone were provided by the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) in New Mexico and a consortium of French research laboratories under the auspices of the Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES).
The Era of Space Microphones
SuperCam studies rocks and soil by zapping them with a laser, then analyzing the resulting vapor with a camera. Because the laser pulses up to hundreds of times per target, opportunities to capture the sound of those zaps quickly add up: the microphone has already recorded more than 25,000 laser shots.
Some of those recordings are teaching scientists about changes in the planet’s atmosphere. After all, sound travels through vibrations in the air. From its perch on Perseverance’s mast, the SuperCam mic is ideally located for monitoring “microturbulence” – minute shifts in the air – and complements the rover’s dedicated wind sensors, which are part of a suite of atmospheric tools called MEDA, short for the Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer.
MEDA’s sensors sample the wind’s speed, pressure, and temperature one to two times per second for up to two hours at a time. SuperCam’s microphone, on the other hand, can provide similar information at a rate of 20,000 times per second over several minutes.
“It’s kind of like comparing a magnifying glass to a microscope with 100 times magnification,” said MEDA’s principal investigator, Jose Rodriguez-Manfredi of the Centro de Astrobiología (CAB) at the Instituto Nacional de Tecnica Aeroespacial in Madrid. “From the weather scientist’s point of view, each perspective – detail and context – complements one another.”
The microphone also allows for research on how sound propagates on Mars. Because the planet’s atmosphere is much less dense than Earth’s, scientists knew higher-pitched sounds in particular would be hard to hear. In fact, a few scientists – unsure if they’d hear anything at all – were surprised when the microphone picked up the Ingenuity helicopter’s buzzing rotors during its fourth flight, on April 30, from a distance of 262 feet (80 meters).
Information from the helicopter audio enabled researchers to eliminate two of three models developed to anticipate how sound propagates on Mars.
“Sound on Mars carries much farther than we thought,” said Nina Lanza, a SuperCam scientist who works with the microphone data at LANL. “It shows you just how important it is to do field science.”
Sound Check
There’s another aspect of space exploration that could benefit from an audio dimension: spacecraft maintenance. Engineers use cameras to monitor the wheel wear on Curiosity rover and dust accumulating on InSight’s solar panels. With microphones, they could also check a spacecraft’s performance the way mechanics might listen to a car engine.
The Perseverance team is amassing loads of recordings from the rover’s chassis mic, which is well-positioned to listen to its wheels and other internal systems. While there aren’t enough recordings yet to detect any changes, over time, engineers may be able to pore over that data and discern subtle differences, like additional electric current going to a particular wheel. This would add to the ways they already monitor the spacecraft’s health.
“We would love to listen to these sounds regularly,” said Vandi Verma, Perseverance’s chief engineer for robotic operations at JPL. “We routinely listen for changes in sound patterns on our test rover here on Earth, which can indicate there’s an issue that needs attention.”
More About the Mission
A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust).
Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis.
The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA’s Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet.
JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, California, built and manages operations of the Perseverance rover.
For more about Perseverance:
mars.nasa.gov/mars2020/
and
nasa.gov/perseverance
Andrew Good
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
818-393-2433
andrew.c.good@jpl.nasa.gov
Karen Fox / Alana Johnson
NASA Headquarters, Washington
301-286-6284 / 202-358-1501
karen.c.fox@nasa.gov / alana.r.johnson@nasa.gov
2021-211