Stone’s remarkable tenure on NASA’s longest-operating mission spans decades of historic discoveries and firsts.
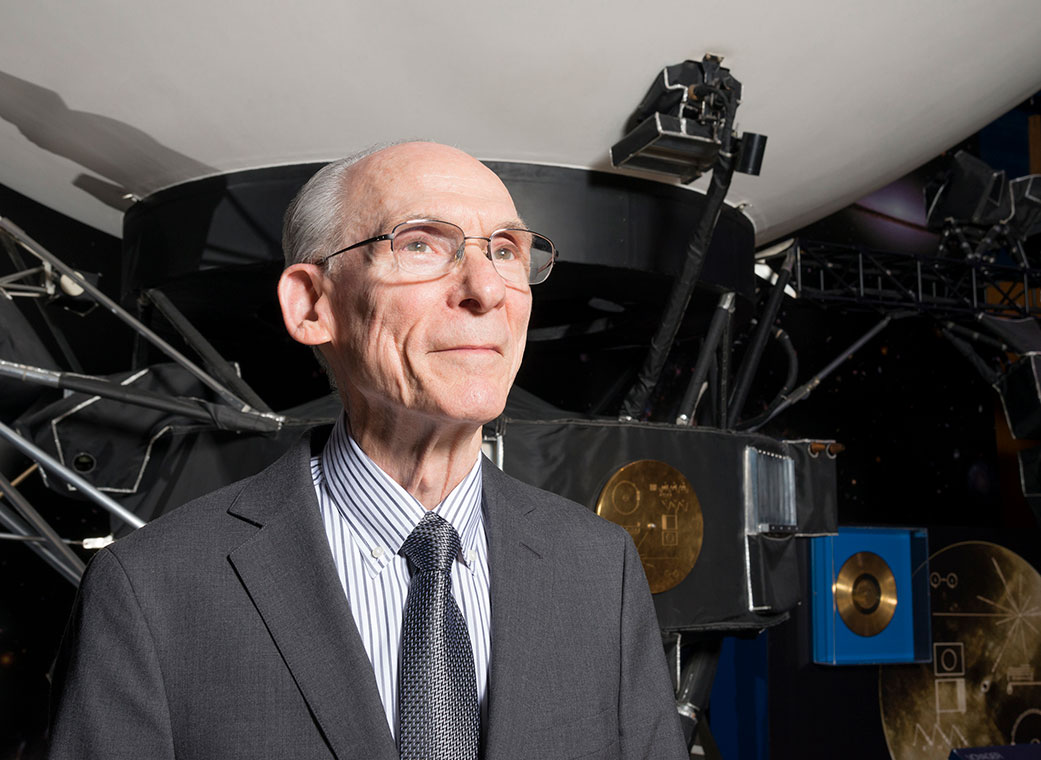
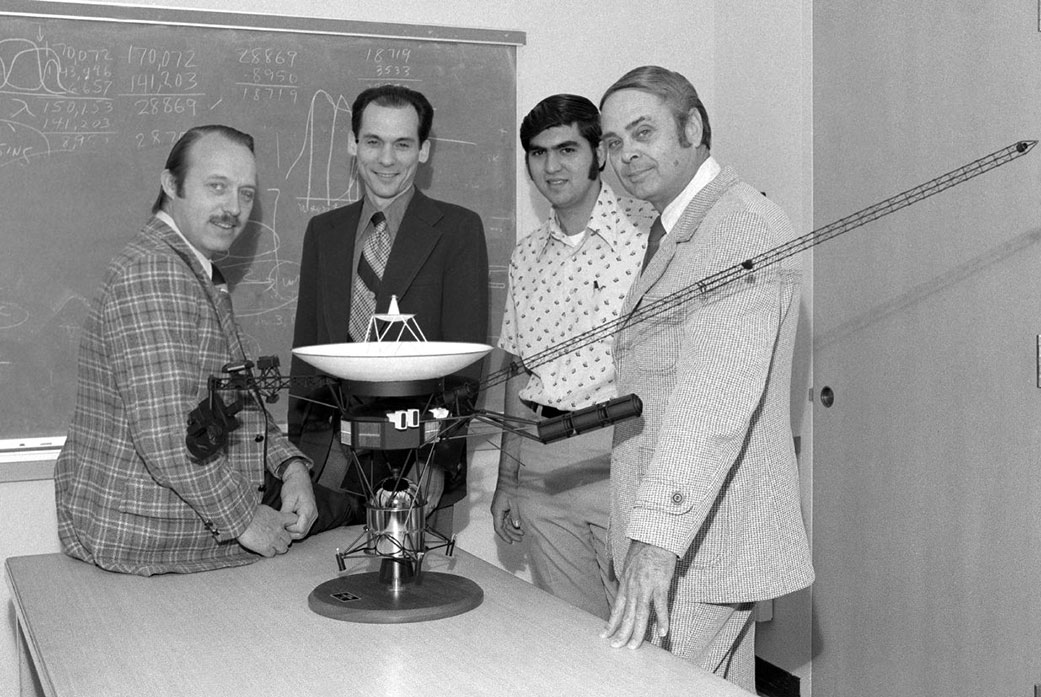
Edward Stone has retired as the project scientist for NASA’s Voyager mission a half-century after taking on the role. Stone accepted scientific leadership of the historic mission in 1972, five years before the launch of its two spacecraft, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2. Under his guidance, the Voyagers explored the four giant planets and became the first human-made objects to reach interstellar space, the region between the stars containing material generated by the death of nearby stars.
Until now, Stone was the only person to have served as project scientist for Voyager, maintaining his position even while serving as director of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California from 1991 to 2001. JPL manages the Voyager mission for NASA. Stone retired from JPL in 2001 but continued to serve as the mission’s project scientist.
“It has been an honor and a joy to serve as the Voyager project scientist for 50 years,” Stone said. “The spacecraft have succeeded beyond expectation, and I have cherished the opportunity to work with so many talented and dedicated people on this mission. It has been a remarkable journey, and I’m thankful to everyone around the world who has followed Voyager and joined us on this adventure.”
Linda Spilker will succeed Stone as Voyager’s project scientist as the twin probes continue to explore interstellar space. Spilker was a member of the Voyager science team during the mission’s flybys of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. She later became project scientist for NASA’s now-retired Cassini mission to Saturn, and rejoined Voyager as deputy project scientist in 2021.
Jamie Rankin, a research scientist at Princeton University and a member of the Voyager science steering group, has been appointed deputy project scientist for the mission. Rankin received her Ph.D. in 2018 from Caltech, where Stone served as her advisor. Her research combines data from Voyager and other missions in NASA’s heliophysics fleet.
The twin Voyager spacecraft launched in 1977, on a mission to explore Jupiter and Saturn, ultimately revealing never-before-seen features of those planets and their moons. Voyager 1 continued its journey out of the solar system, while Voyager 2 continued on to Uranus and Neptune – and remains the only spacecraft to have visited the ice giants.
Explore the Voyager mission’s 45-year journey with NASA’s interactive Eyes on the Solar System. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Following this “grand tour” of the outer planets, the Voyager Interstellar Mission began. The goal was to exit the heliosphere – a protective bubble created by the Sun’s magnetic field and outward flow of solar wind (charged particles from the Sun). Voyager 1 crossed the boundary of the heliosphere and entered interstellar space in 2012, followed by Voyager 2 (traveling slower and in a different direction) in 2018. Today, as part of NASA’s longest-running mission, both spacecraft continue to illuminate the interplay between our Sun, and the particles and magnetic fields in interstellar space.
“Ed likes to say that Voyager is a mission of discovery, and it certainly is,” said Suzanne Dodd, Voyager project manager. “From the flybys of the outer planets in the 1970s and ’80s, to the heliopause crossing and current travels through interstellar space, Voyager never ceases to surprise and amaze us. All those milestones and successes are due to Ed’s exceptional scientific leadership and his keen ability to share his excitement about these discoveries to the world.”
Among the many honors bestowed on him, Stone has been a member of the National Academy of Sciences since 1984. He was awarded the National Medal of Science from President George H.W. Bush in 1991. When Stone was interviewed on the late-night TV show “The Colbert Report” in 2013, NASA arranged for host Stephen Colbert to present him with the NASA Distinguished Public Service Medal, the agency’s highest honor for a nongovernment individual. In 2019, he received the Shaw Prize in Astronomy from the Shaw Foundation in Hong Kong for his work on the Voyager mission.
More About the Mission
A division of Caltech in Pasadena, JPL built and operates the Voyager spacecraft. The Voyager missions are a part of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate in Washington.
For more information about the Voyager spacecraft, visit:
Calla Cofield
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
626-808-2469
calla.e.cofield@jpl.nasa.gov
2022-161