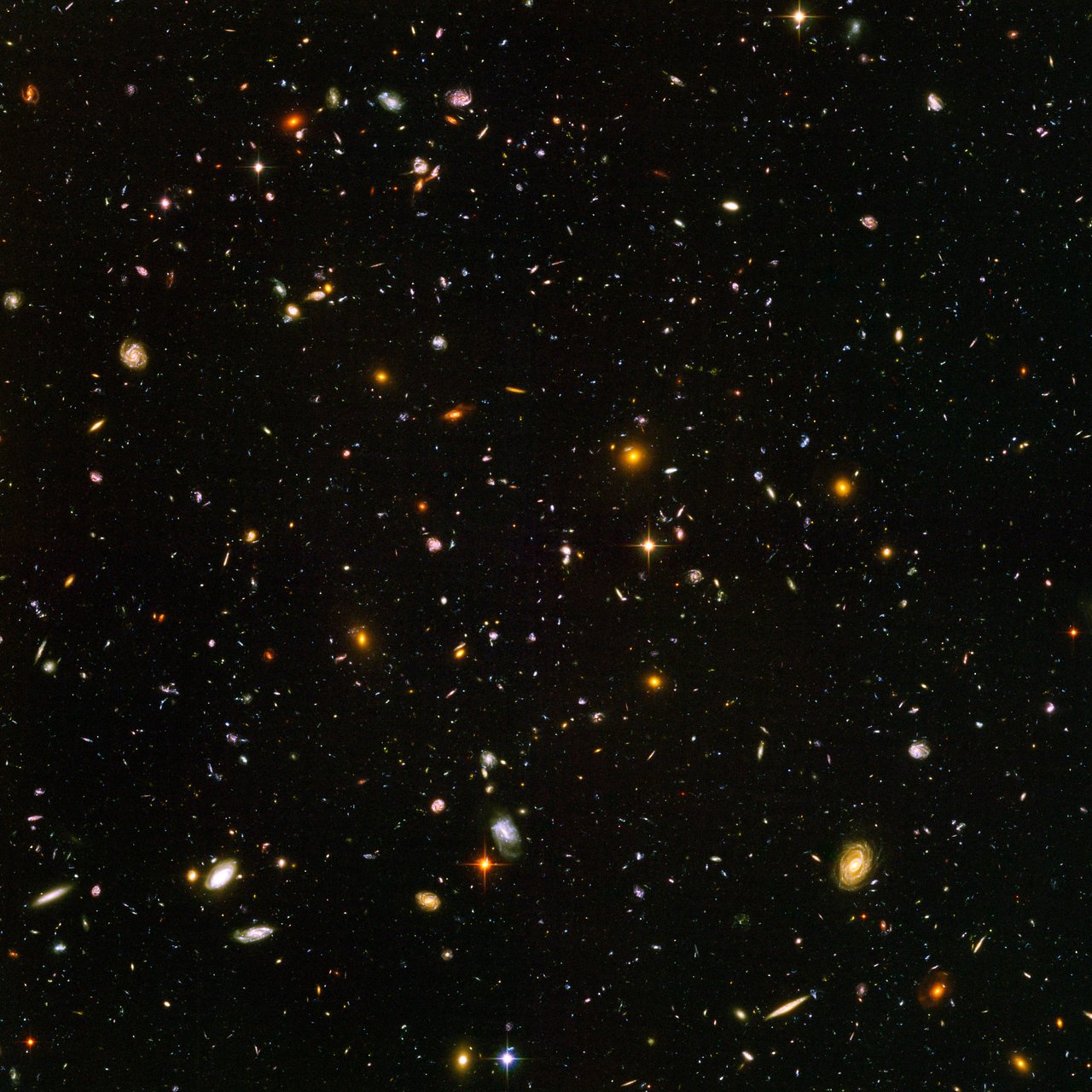
Scientists will use NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to study sections of the sky previously observed by NASA’s Great Observatories, including the Hubble Space Telescope and the Spitzer Space Telescope, to understand the creation of the universe’s first galaxies and stars.
After it launches and is fully commissioned, scientists plan to focus Webb telescope on sections of the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF) and the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey (GOODS). These sections of sky are among Webb’s list of targets chosen by guaranteed time observers, scientists who helped develop the telescope and thus get to be among the first to use it to observe the universe. The group of scientists will primarily use Webb’s mid-infrared instrument (MIRI) to examine a section of HUDF, and Webb’s near infrared camera (NIRCam) to image part of GOODS.
“By mixing [the data from] these instruments, we’ll get information about the current star formation rate, but we’ll also get information about the star formation history,” explained Hans Ulrik Nørgaard-Nielsen, an astronomer at the Danish Space Research Institute in Denmark and the principal investigator for the proposed observations.
Pablo Pérez-González, an astrophysics professor at the Complutense University of Madrid in Spain and one of several co-investigators on Nørgaard-Nielsen’s proposed observation, said they will use Webb to observe about 40 percent of the HUDF area with MIRI, in roughly the same location that ground-based telescopes like the Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA) and the Very Large Telescope array (VLT) obtained ultra-deep field data.
The iconic HUDF image shows about 10,000 galaxies in a tiny section of the sky, equivalent to the amount of sky you would see with your naked eye if you looked at it through a soda straw. Many of these galaxies are very faint, more than 1 billion times fainter than what the naked human eye can see, marking them as some of the oldest galaxies within the visible universe.
With its powerful spectrographic instruments, Webb will see much more detail than imaging alone can provide. Spectroscopy measures the spectrum of light, which scientists analyze to determine physical properties of what is being observed, including temperature, mass, and chemical composition. Pérez-González explained this will allow scientists to study how gases transformed into stars in the first galaxies, and to better understand the first phases in the formation of supermassive black holes, including how those black holes affect the formation of their home galaxy. Astronomers believe the center of nearly every galaxy contains a supermassive black hole, and that these black holes are related to galactic formation.
MIRI can observe in the infrared wavelength range of 5 to 28 microns. Pérez-González said they will use the instrument to observe a section of HUDF in 5.6 microns, which Spitzer is capable of, but that Webb will be able to see objects 250 times fainter and with eight times more spatial resolution. In this case, spatial resolution is the ability of an optical telescope, such as Webb, to see the smallest details of an object.
Pérez-González said in the area of HUDF they will observe, Hubble was able to see about 4,000 galaxies. He added that, with Webb, they “will detect around 2,000 to 2,500 galaxies, but in a completely different spectral band, so many galaxies will be quite different from the ones that [Hubble] detected.”
With NIRCam, the team will observe a piece of the GOODS region near their selected section of HUDF. The entire GOODS survey field includes observations from Hubble, Spitzer, and several other space observatories.
“These NIRCam images will be taken in three bands, and they will be the deepest obtained by any guaranteed time observation team,” explained Pérez-González.
NIRCam can observe in the infrared wavelength range of 0.6 to 5 microns. Pérez-González explained they will use it to observe a section of GOODS in the 1.15 micron band, which Hubble is capable of, but that Webb will be able to see objects 50 times fainter and with two times more spatial resolution. They will also use it to observe the 2.8 and 3.6 micron bands. Spitzer is able to do this as well, but Webb will be able to observe objects nearly 100 times fainter and with eight times greater spatial resolution.
Because the universe is expanding, light from distant objects in the universe is “redshifted,” meaning the light emitted by those objects is visible in the redder wavelengths by the time it reaches us. The objects farthest away from us, those with the highest redshifts, have their light shifted into the near- and mid-infrared part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The Webb telescope is specifically designed to observe the objects in that area of the spectrum, which makes it ideal for looking at the early universe.
“When you build an observatory with unprecedented capabilities, most probably the most interesting results will not be those that you can expect or predict, but those that no one can imagine,” said Pérez-González.
The James Webb Space Telescope, the scientific complement to NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, will be the most powerful space telescope ever built. Webb is an international project led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency).
MIRI was built by ESA, in partnership with the European Consortium, a group of scientists and engineers from European countries; a team from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California; and scientists from several U.S. institutions. NIRCam was built by Lockheed Martin and the University of Arizona in Tucson.
For more information about Webb telescope, visit: www.webb.nasa.gov or www.nasa.gov/webb
For more information about Hubble telescope, visit: www.nasa.gov/hubble
For more information about Spitzer telescope, visit: www.nasa.gov/spitzer