Retrieving an asteroid sample is no easy task. Doing the job blindfolded is even more challenging. That’s why scientists equipped the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft with a set of eyes to watch it all unfold.
NASA’s Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer (OSIRIS-REx) launched Sept. 8, 2016, and is travelling to a near-Earth asteroid known as Bennu, to harvest a sample of surface material, and return it to Earth for study. A trio of cameras will capture it all.
Download this video in HD formats from NASA Goddard’s Scientific Visualization Studio
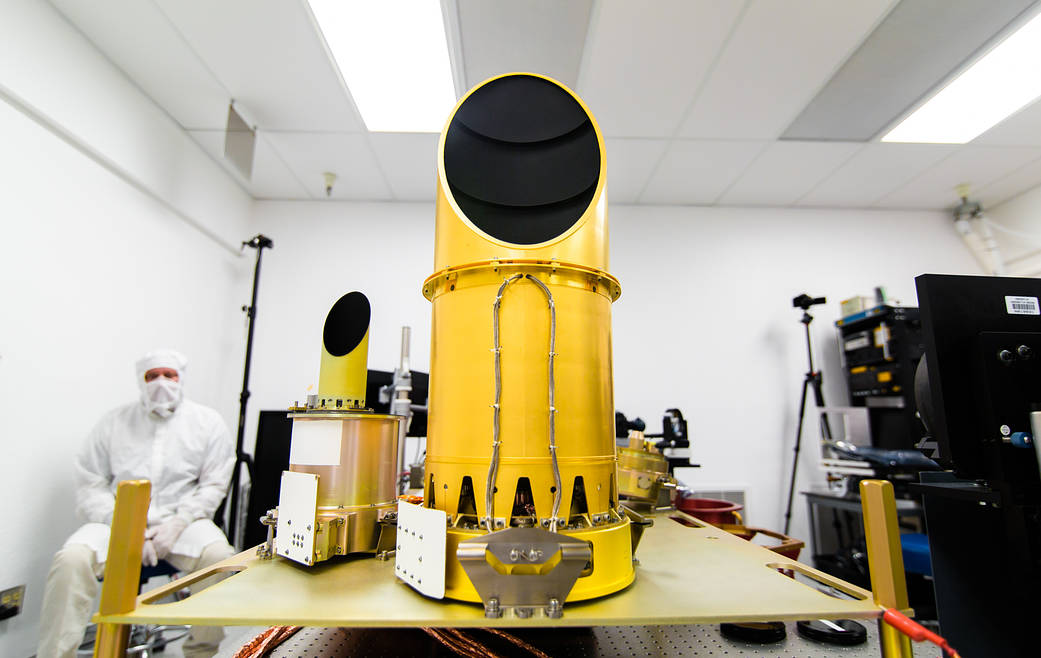
The OSIRIS-REx Camera Suite, or OCAMS, consists of three cameras. PolyCam is a high-resolution camera that will acquire the first images of Bennu and perform an initial mapping of the asteroid. MapCam is a medium-resolution camera that will map the asteroid in color and search for satellites and dust plumes. SamCam will document the sampling process. The spacecraft will store the images captured by OCAMS and send them to the OSIRIS-REx team every few days.
Scientists designed the camera suite to be functionally redundant, meaning that if one of the cameras fails during the mission, the other two cameras can stand in.
“When you have a critical mission like this, you want redundancy,” said Christian d’Aubigny, OCAMS deputy instrument scientist at the University of Arizona, Tucson. “The cameras have some amount of overlap in their capabilities. They’re not exact copies of each other, but if one fails, they can still get the job done.”
The first camera to see Bennu is called PolyCam. Similar to a polymath — a human that is skilled at doing several different things — PolyCam can perform a wide range of optical tasks.
PolyCam has a focus mechanism that allows it to refocus from infinity to about 500 feet (0.15 kilometers), which provides PolyCam with the ability to switch from detecting stars and asteroids from far away to resolving small pebbles on the surface of the asteroid.
PolyCam has better visual acuity, or sharpness of vision, than an eagle. Several eagle species can see small objects such as prey from as far as 2 miles away. But with its high resolution, PolyCam can acquire images of similarly sized objects on Bennu at a range of about 30 to 60 miles (48.2 to 96.5 kilometers) to determine its shape and figure out how the scientists can maneuver the spacecraft around the asteroid.
Once PolyCam performs an initial mapping of the asteroid, scientists will use the camera to identify a site where the spacecraft might collect a sample of Bennu’s surface that is as free of hazards as possible, such as boulders and dramatic slopes.
“Already, at about 2 miles (3.5 kilometers), we’re dividing the surface of the asteroid into ‘go’ and ‘no go’ places,” said Bashar Rizk, OCAMS instrument scientist at the University of Arizona. “If a place is covered with hazards, we’re just not going to go there because we don’t want to risk damaging the spacecraft.”
The second camera to get a glimpse of Bennu is called MapCam. This camera has a wider field of view than PolyCam and is equipped with a number of color filters in its filter wheel to help the scientists identify locations on the asteroid where specific minerals of interest may be present, particularly those that may have once been in contact with liquid water.
MapCam will also look for satellites and dust plumes, which may present a hazard to the spacecraft. There are a number of suspected mechanisms for plume formation, such as sublimation, in which a frozen substance transitions directly to a gas without first passing through the liquid phase, and electromagnetic levitation due to electrical charging from solar wind as the asteroid gets closer to the sun.
“Asteroids are exposed to a lot of solar radiation because they have no atmosphere,” Rizk said. “They’re just mercilessly tortured by the sun every time they go around it.”
Due to a lack of water on the surface, the scientists predict that Bennu’s regolith — a layer of loose material, including dust, soil and broken rock — is very dry, similar to the surface of the moon. The surface material can easily stick to things, increasing the risk of contaminating the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft during sampling.
Dust contamination is of particular concern to the spacecraft’s third camera — SamCam. This camera is a low-resolution, wide-angle camera designed to get up close and personal with the asteroid to document the sampling acquisition. When it comes time to retrieve a sample, SamCam will need to be able to retain its functionality for up to three attempts.
To combat this potential threat, the team at the University of Arizona furnished SamCam with multiple copies of the same filter, which are placed in front of the camera optics to act as a cover. The filters help ensure that the camera has a dust-free, unobstructed viewing of the sampling event in case sampling needs to be repeated.
The team also had to account for radiation from gamma rays and X-rays when designing OCAMS. Scientists housed the cameras in a suit of armor made from solid titanium and aluminum. These materials can block the radiation OSIRIS-REx will encounter during the mission. The lenses are made of materials, such as silicon dioxide, that are radiation resistant, as well as a number of other types of glass that are infused with cerium, which prevents the glass from turning opaque when exposed to high levels of radiation.
“We tried to think of everything that the spacecraft might be subjected to and account for that,” Rizk said. “It’s a multi-step process of simulations, testing and design to ensure that the cameras work properly and that we get the best images we can.”
A collaborative team of engineers and scientists at the University of Arizona’s Lunar and Planetary Laboratory and the College of Optical Sciences and the Utah State University’s Space Dynamics Laboratory spent four and a half years designing and building OCAMS.
“In the end, the University of Arizona OCAMS team did an excellent job designing, building and testing the camera suite,” said Brent Bos, OSIRIS-REx optics discipline lead at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
OSIRIS-REx’s eyes are a critical part of retrieving an asteroid sample, which will help scientists investigate how planets formed and how life began, as well as improve our understanding of asteroids that might impact Earth.
Goddard will provide overall mission management, systems engineering and safety and mission assurance for OSIRIS-REx. Dante Lauretta is the mission’s principal investigator at the University of Arizona. Lockheed Martin Space Systems in Denver will build the spacecraft. OSIRIS-REx is the third mission in NASA’s New Frontiers Program. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages New Frontiers for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington.
Related Link
By Sarah Schlieder
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.