In 1967, while much attention was focused on landing humans on the Moon before the end of the decade, NASA also managed an active planetary exploration program at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California,, targeting Earth’s closest neighbors Venus and Mars.
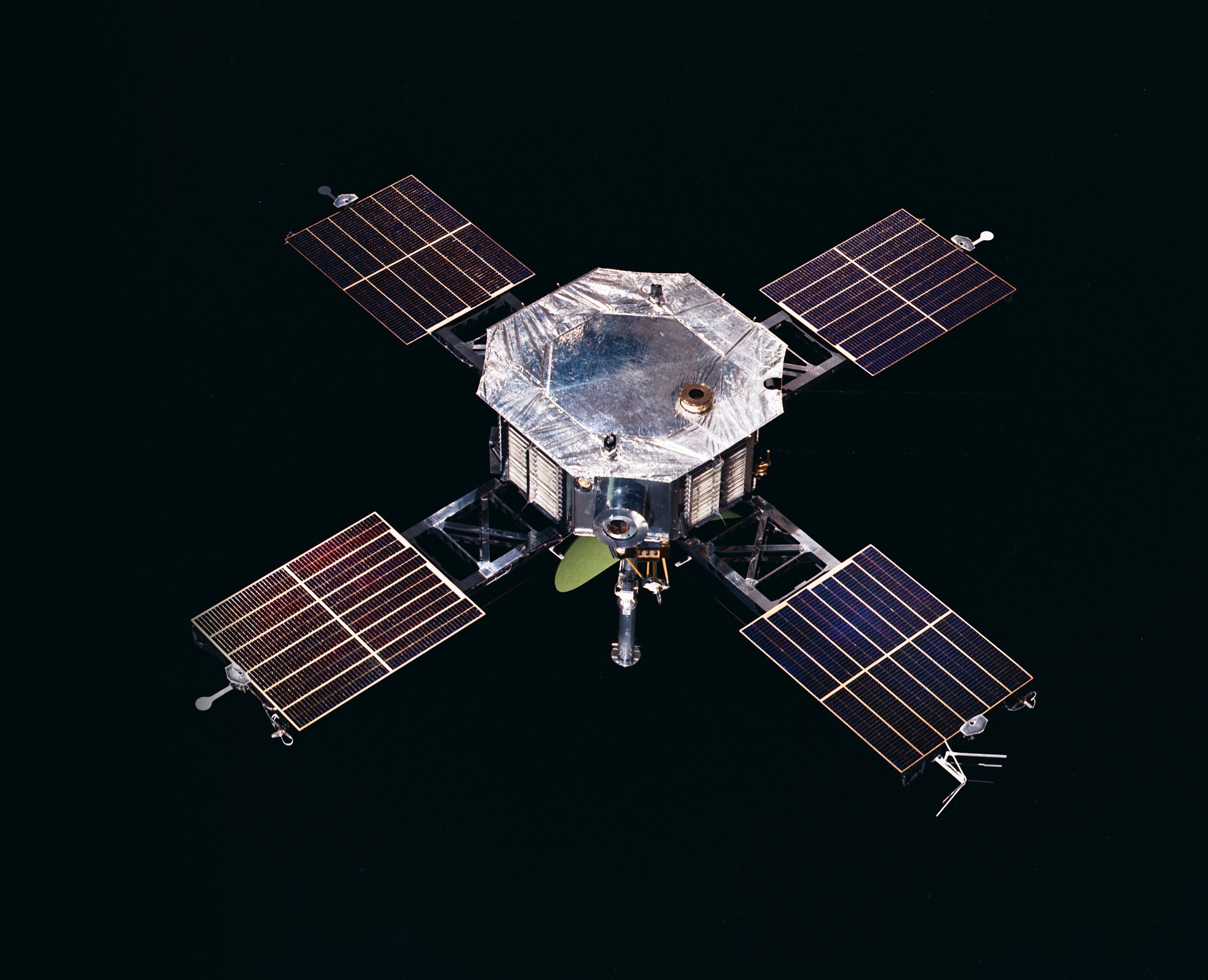
On June 14, 1967, Mariner 5 launched on an Atlas-Agena rocket from Cape Canaveral, Florida. As a cost-saving measure, the Mariner 5 spacecraft, originally built as a backup for the successful Mariner 4 mission to Mars in 1965, was reconfigured to explore Venus. Since Mariner 5 would be travelling closer to the Sun, the required modifications included the addition of a sunshield to keep the spacecraft cool and facing the solar arrays in the opposite direction of those on Mariner 4.
On October 19, after a 127-day flight from Earth, Mariner 5 flew within 3,990 km of Venus, becoming only the second successful Venus exploration mission in history. The spacecraft provided detailed information about the planet’s atmospheric pressure (75-100 atmospheres) and temperature (527oC), and found no trapped radiation belts around Venus as its magnetic field was only 1% as strong as Earth’s. So despite Venus’ similarity to Earth in terms of size, the spacecraft found a much different world, dispelling visions of Venus as a planet potentially hospitable to life.
Mariner 5 stopped transmitting on December 4, 1967, having completed its highly successful mission and significantly increasing our knowledge of Venus and its environment.
For more on Mariner 5, see https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1967-060A