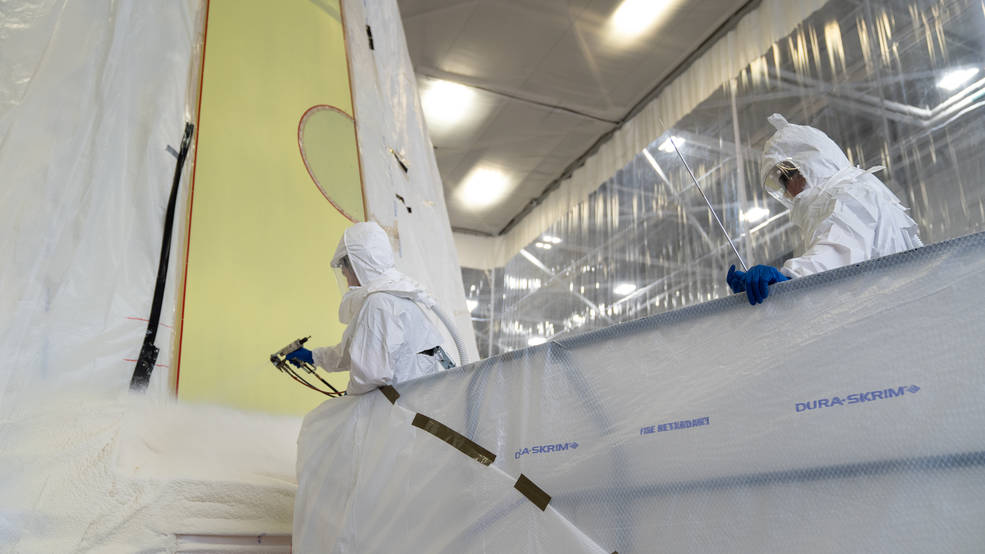
Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, apply the first round of spray foam as part of the thermal protection system to the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis III. The cone-shaped element connects the rocket’s core stage to its upper stage called the interim cryogenic propulsion stage and partially encloses it.
Spray-on foam insulation, along with other traditional insulation materials such as cork, provide thermal protection for every part – no matter how small or large – of the SLS rocket. The insulation is flexible enough to move with the rocket but rigid enough to handle the extreme pressures and temperatures as SLS accelerates from 0 to 17,400 mph and soars to more than 100 miles above Earth in just eight minutes.
The thermal protection system for the LVSA is applied entirely by hand using a tool similar to a spray gun. It is the largest piece of SLS hardware to be hand-sprayed. During each session, two technicians take turns applying the foam across the 20 individual “stripes,” or spray lanes, that make up the LVSA. It takes about two weeks to spray all 20 stripes, and technicians will apply another coat of thermal insulation later this summer. The LVSA is fully manufactured at Marshall by NASA and lead contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering.
NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. Artemis III will land astronauts on the Moon to advance long-term lunar exploration and scientific discovery and inspire the Artemis Generation.
Image credit: NASA/Brandon Hancock