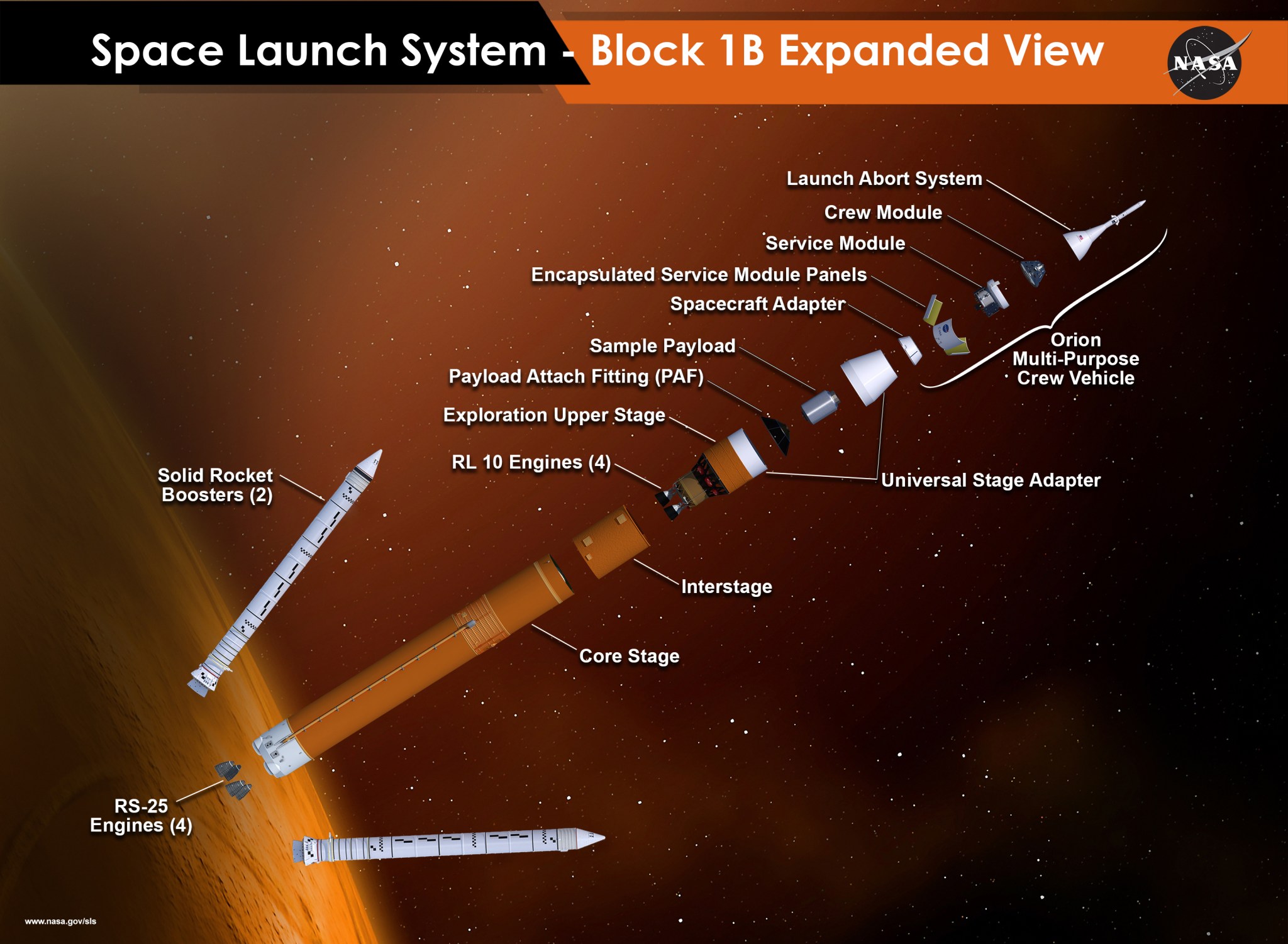
NASA has successfully completed the exploration upper stage (EUS) preliminary design review for the powerful Space Launch System rocket. The detailed assessment is a big step forward in being ready for more capable human and robotic missions to deep space, including the first crewed flight of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft in 2021.

“To send humans and even more cargo farther away from Earth than ever before, NASA decided to add a more powerful upper stage — the upper part of the rocket that continues to operate after launch and ascent,” said Kent Chojnacki, EUS team lead and preliminary design review manager.
“With the completion of this review, our teams will start developing components and materials for the EUS, and build up tooling,” he added. “Full-scale manufacturing will begin after the critical design phase is completed.” Critical design review is the next programmatic milestone that will provide a final look at the design and development of the EUS before beginning full-scale fabrication.
Starting with that first crewed mission, future configurations of SLS will include the larger exploration upper stage and use four RL10C-3 engines. The EUS will replace the interim cryogenic propulsion stage that will be used on the initial configuration of SLS for the first, uncrewed flight with Orion. The EUS will use an 8.4-meter diameter liquid hydrogen tank and a 5.5-meter diameter liquid oxygen tank. A new universal stage adapter will connect the EUS to the Orion spacecraft, and be capable of carrying large co-manifested payloads, such as a habitat.
The preliminary design review kicked off Nov. 30, 2016, with approximately 500 experts from across NASA and industry assessing more than 320 items on the EUS, including documents and data. This review had a new “techie” touch to it with the incorporation of virtual reality glasses, which gave teams enhanced visuals of how the EUS is put together and a broader perspective on the size of the hardware. The preliminary design review board was completed Jan. 19, with the board voting unanimously that the EUS is ready to move to the critical design phase.
“I couldn’t be prouder of the SLS Stages team completing this review,” said SLS Program Manager John Honeycutt. “We continue to make progress on hardware for SLS’s first flight, while also working on the next-generation rocket that will take astronauts to deep-space destinations, like Mars.”
The powerful stage will be built at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Massive welding machines, like the Vertical Assembly Center, currently building the SLS core stage, also will help build the EUS liquid hydrogen tank. New tooling and assembly areas will be put in place to manufacture the liquid oxygen tank.
Once built, the EUS structural test article will undergo qualification testing at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to ensure the hardware can withstand the incredible stresses of launch. “Green run” testing on the first flight article will be done at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. For the test, the EUS and RL10 engines will fire up together for the first time before being sent to Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the 2021 launch.
Kim Henry
Marshall Space Flight Center
Huntsville, Ala.
kimberly.m.henry@nasa.gov
256-684-6658
Tracy McMahan
Marshall Space Flight Center
Huntsville, Ala.
tracy.mcmahan@nasa.gov
256–682-5326