Lynn Rothschild
NASA Ames Research Center
Description
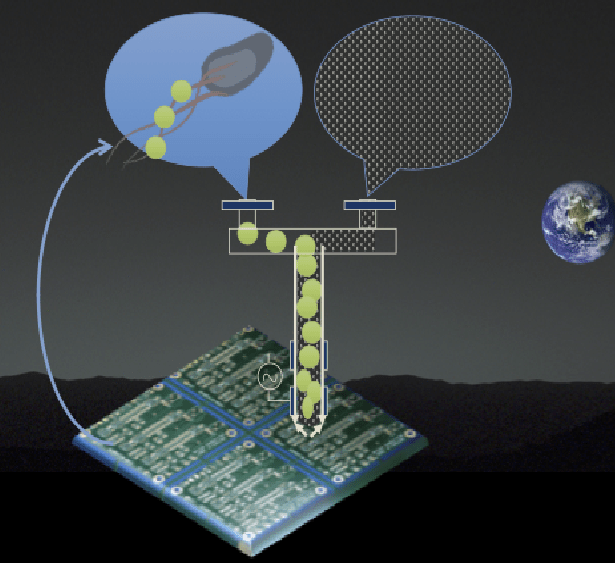
Space missions rely utterly on metallic components, from the spacecraft to electronics. Yet, metals add mass, and electronics have the additional problem of a limited lifespan. Thus, current mission architectures must compensate for replacement. In space, spent electronics are discarded; on earth, there is some recycling but current processes are toxic and environmentally hazardous. Imagine instead an end-to-end recycling of spent electronics at low mass, low cost, room temperature, and in a non-toxic manner. Here, we propose a solution that will not only enhance mission success by decreasing upmass and providing a fresh supply of electronics, but in addition has immediate applications to a serious environmental issue on the Earth. Spent electronics will be used as feedstock to make fresh electronic components, a process we will accomplish with so-called ‘urban biomining’ using synthetically enhanced microbes to bind metals with elemental specificity. To create new electronics, the microbes will be used as ‘bioink’ to print a new IC chip, using plasma jet electronics printing. The plasma jet electronics printing technology will have the potential to use martian atmospheric gas to print and to tailor the electronic and chemical properties of the materials. Our preliminary results have suggested that this process also serves as a purification step to enhance the proportion of metals in the ‘bioink’. The presence of electric field and plasma can ensure printing in microgravity environment while also providing material morphology and electronic structure tunabiity and thus optimization. Here we propose to increase the TRL level of the concept by engineering microbes to dissolve the siliceous matrix in the IC, extract copper from a mixture of metals, and use the microbes as feedstock to print interconnects using mars gas simulant. To assess the ability of this concept to influence mission architecture, we will do an analysis of the infrastructure required to execute this concept on Mars, and additional opportunities it could offer mission design from the biological and printing technologies. In addition, we will do an analysis of the impact of this technology for terrestrial applications addressing in particular environmental concerns and availability of metals.
2016 Phase I and Phase II Selections