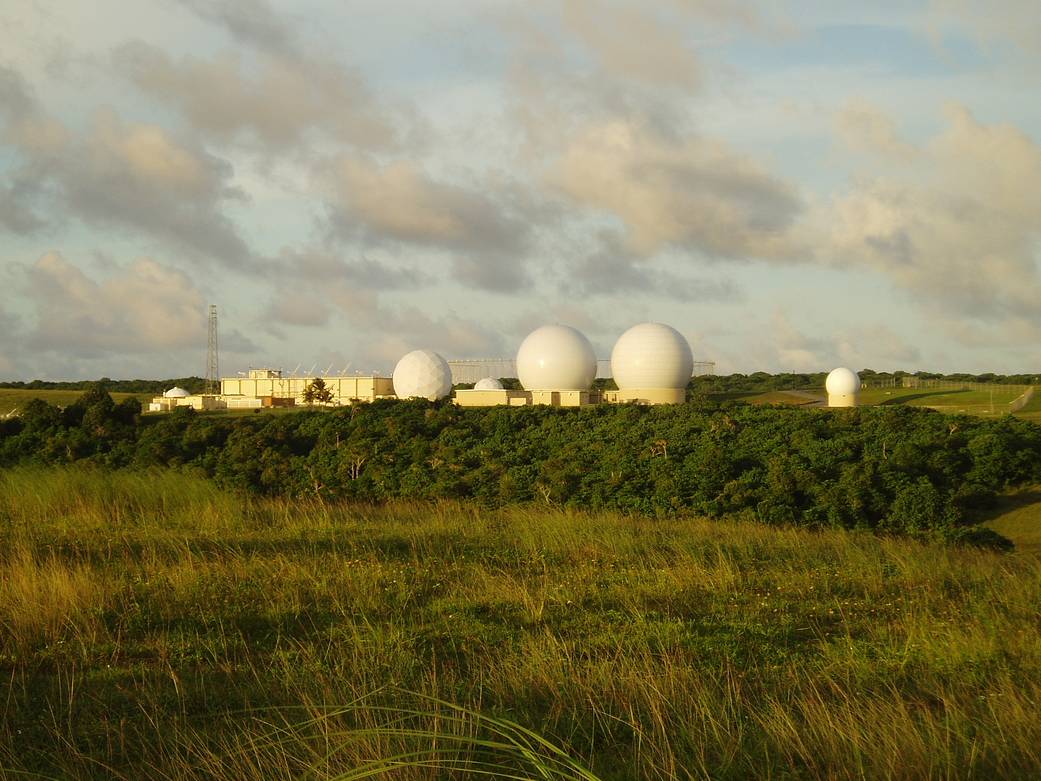
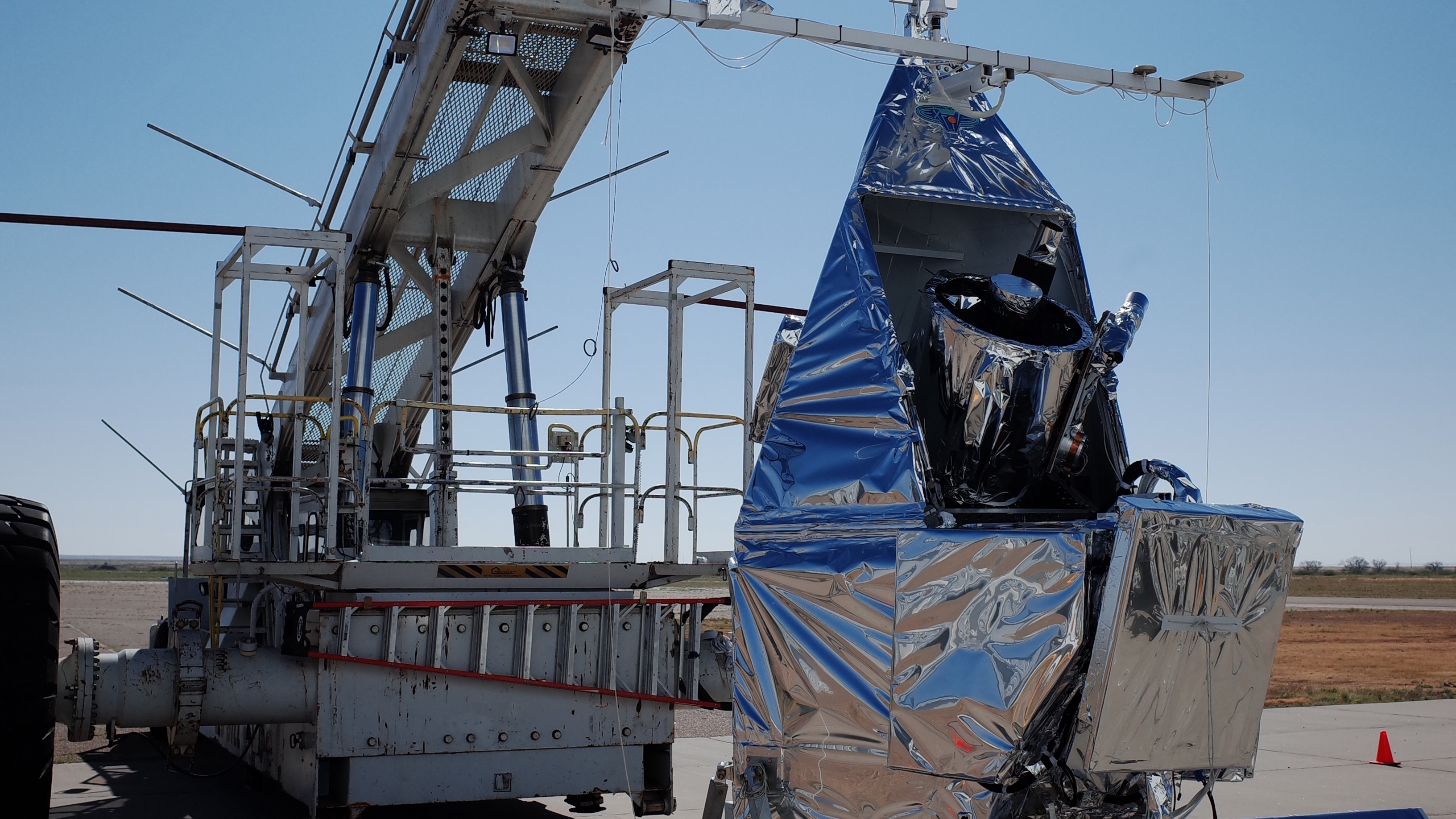
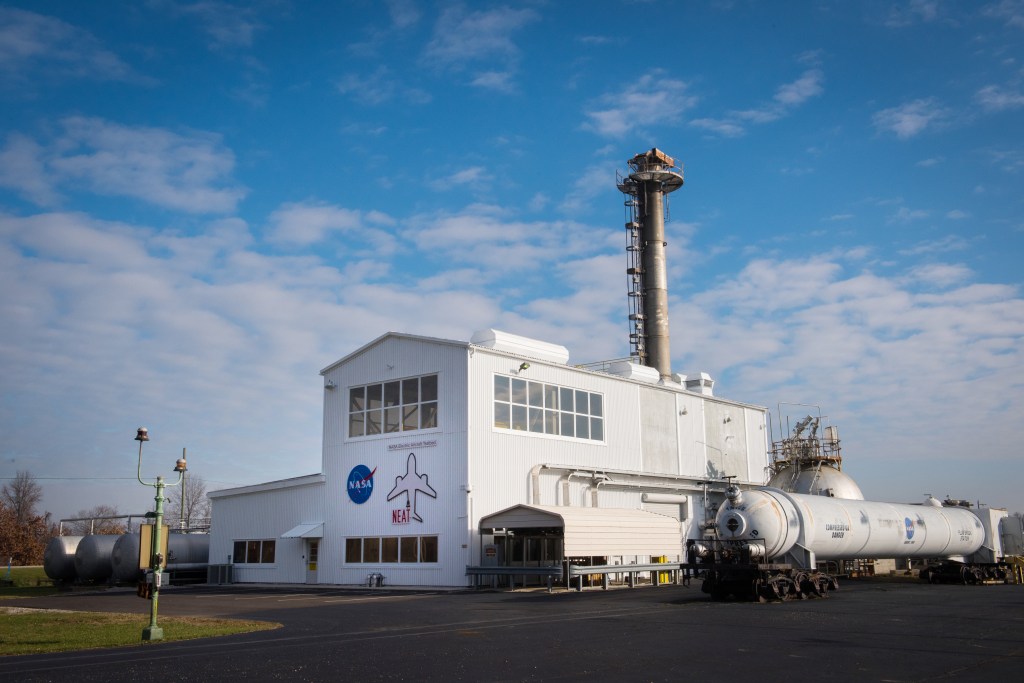
The Guam Remote Ground Terminal (GRGT) was constructed in the 1990s to close the gap in coverage, or Zone of Exclusion, over the Indian Ocean for the Near Space Network (NSN). GRGT allows Tracking and Data Relay Satellites (TDRS) to downlink and uplink data while not in line of sight of NASA's White Sands Ground Terminal (WSGT) in …
The Guam Remote Ground Terminal (GRGT) was constructed in the 1990s to close the gap in coverage, or Zone of Exclusion, over the Indian Ocean for the Near Space Network (NSN). GRGT allows Tracking and Data Relay Satellites (TDRS) to downlink and uplink data while not in line of sight of NASA’s White Sands Ground Terminal (WSGT) in Las Cruces, New Mexico. The antennas are protected by radomes as frequent rainy weather interferes with operations.