Members: Joe Roser
Objectives:
1. Measure mid-IR spectra of PAH neutrals, cations, and clusters to better constrain emitters of the Aromatic Infrared Bands, PAH-linked IR emission features seen throughout our Galaxy.
2. Measure optical constants of ammonia/water ices to provide fundamental data for reflectance modeling studies of outer Solar System bodies
Equipment:
Glass line: (10-8 Torr bkgd)
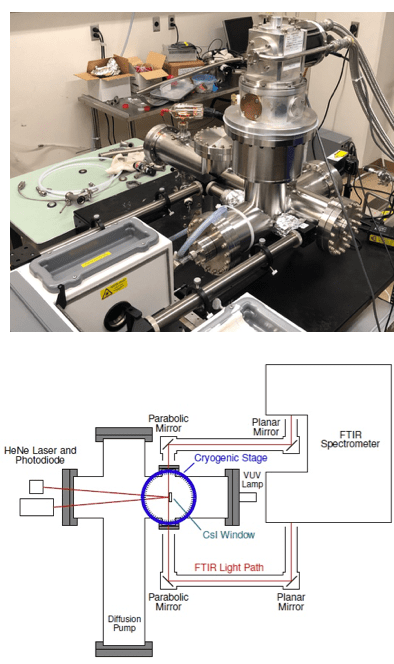
Matrix Isolation Chamber (Experiment)
- Rotatable cryogenic stage (Tmin = 4 K with heat shield)
- Crucible for evaporating molecules (Tmax = 750°C)
- FTIR spectrometer (~15000–400 cm-1 / 0.67–25 µm)
- H2 VUV discharge lamp (110–180 nm)
Associated Calculations
- Estimate of monomer fraction of matrix-isolated PAHs
- IR optical constants (Kramers-Kronig algorithm)
Objective 1. Measure mid-IR spectra of PAH neutrals, cations, and clusters to better constrain emitters of the Aromatic Infrared Bands, PAH-linked IR emission features seen throughout our Galaxy.
Methodology:
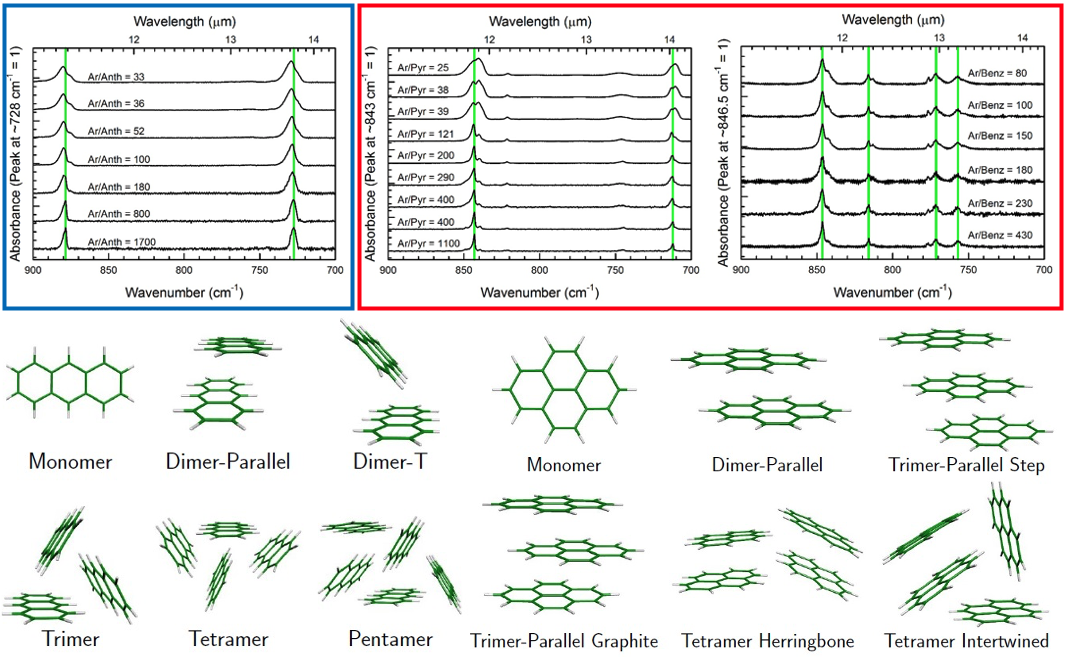
- Measure mid-IR spectra of PAH neutrals and clusters that are representative of the interstellar PAHs using IR Matrix Isolation Spectroscopy in argon matrix
- Deduce cluster structural patterns from spectral features measured as a function of PAH concentration
Future projects: Large (40+ C) PAHs
Objective 2. Measure optical constants of ammonia/water ices to provide fundamental data for reflectance modeling studies of outer Solar System bodies
Application: Ammonia ice is important in the outer Solar System as a surface ice component and as a driver of cryovolcanism, recently confirmed to be occurring on Pluto.
Methodology:
- measure IR transmission spectra in the laboratory
- derive optical constants from laboratory spectra using the well-known Kramers-Kronig algorithm in a Python code that utilizes an iterated optimization workflow to determine best-fit optical constants.
Future projects:
- Measure optical constants of other ices and ice mixtures to provide fundamental data for reflectance modeling studies of outer Solar System bodies.
- Determine optical constants of complex organic molecules (COM) of outer Solar System interest embedded in ices (nitrogen, methane, water)
Find our publications here.