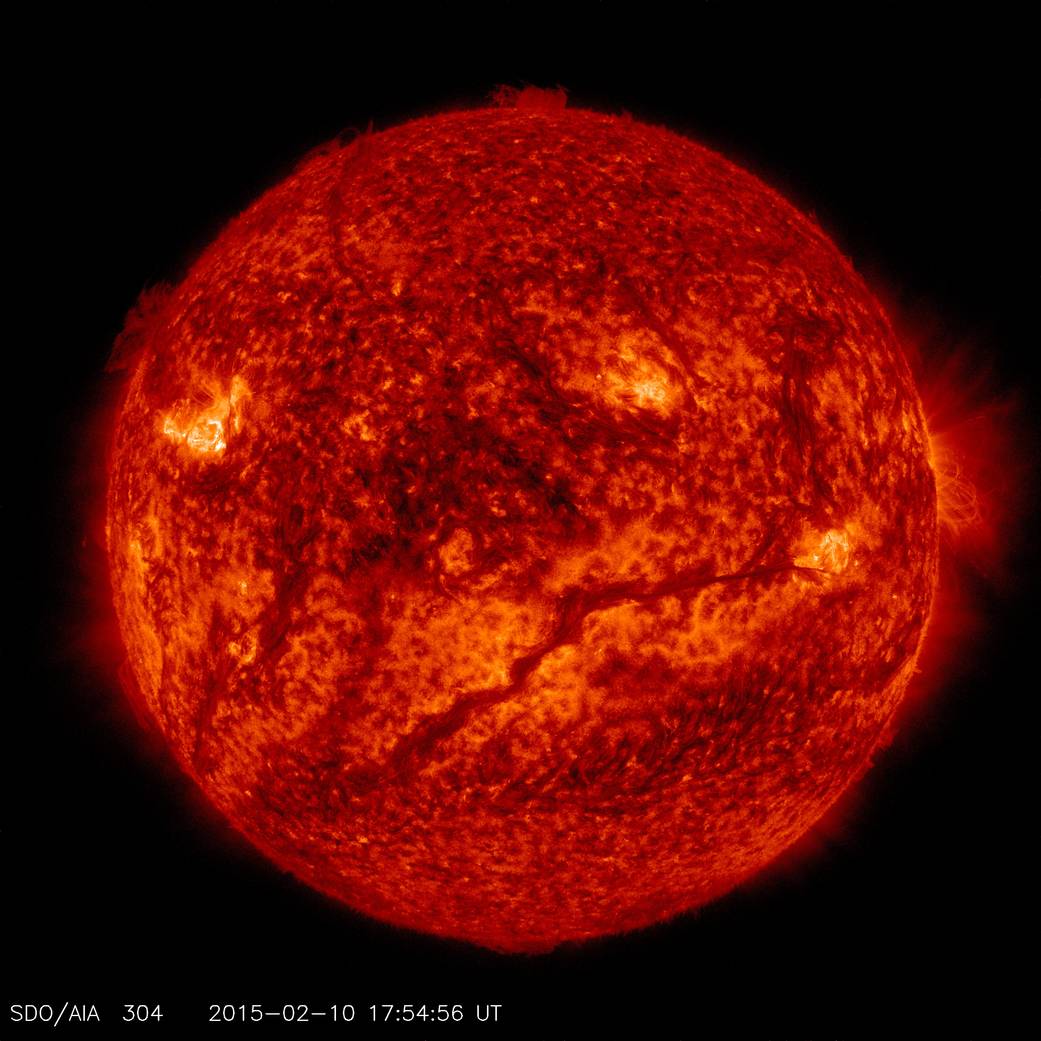
A dark, snaking line across the lower half of the sun in this Feb. 10, 2015, image from NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) shows a filament of solar material hovering above the sun’s surface. SDO shows colder material as dark and hotter material as light, so the line is, in fact, an enormous swatch of colder material hovering in the sun’s atmosphere, the corona. Stretched out, that line – or solar filament as scientists call it – would be more than 533,000 miles long. That is longer than 67 Earths lined up in a row. Filaments can float sedately for days before disappearing. Sometimes they also erupt out into space, releasing solar material in a shower that either rains back down or escapes out into space, becoming a moving cloud known as a coronal mass ejection, or CME. SDO captured images of the filament in numerous wavelengths, each of which helps highlight material of different temperatures on the sun. By looking at such features in different wavelengths and temperatures, scientists learn more about what causes these structures, as well as what catalyzes their occasional eruptions.
Launched on Feb. 11, 2010 aboard a ULA Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory is designed to study the causes of solar variability and its impacts on Earth. The spacecraft’s long-term measurements give solar scientists in-depth information to help characterize the interior of the sun, the sun’s magnetic field, the hot plasma of the solar corona, and the density of radiation that creates the ionosphere of the planets. The information is used to create better forecasts of space weather needed to protect aircraft, satellites and astronauts living and working in space.
Image Credit: NASA/SDO