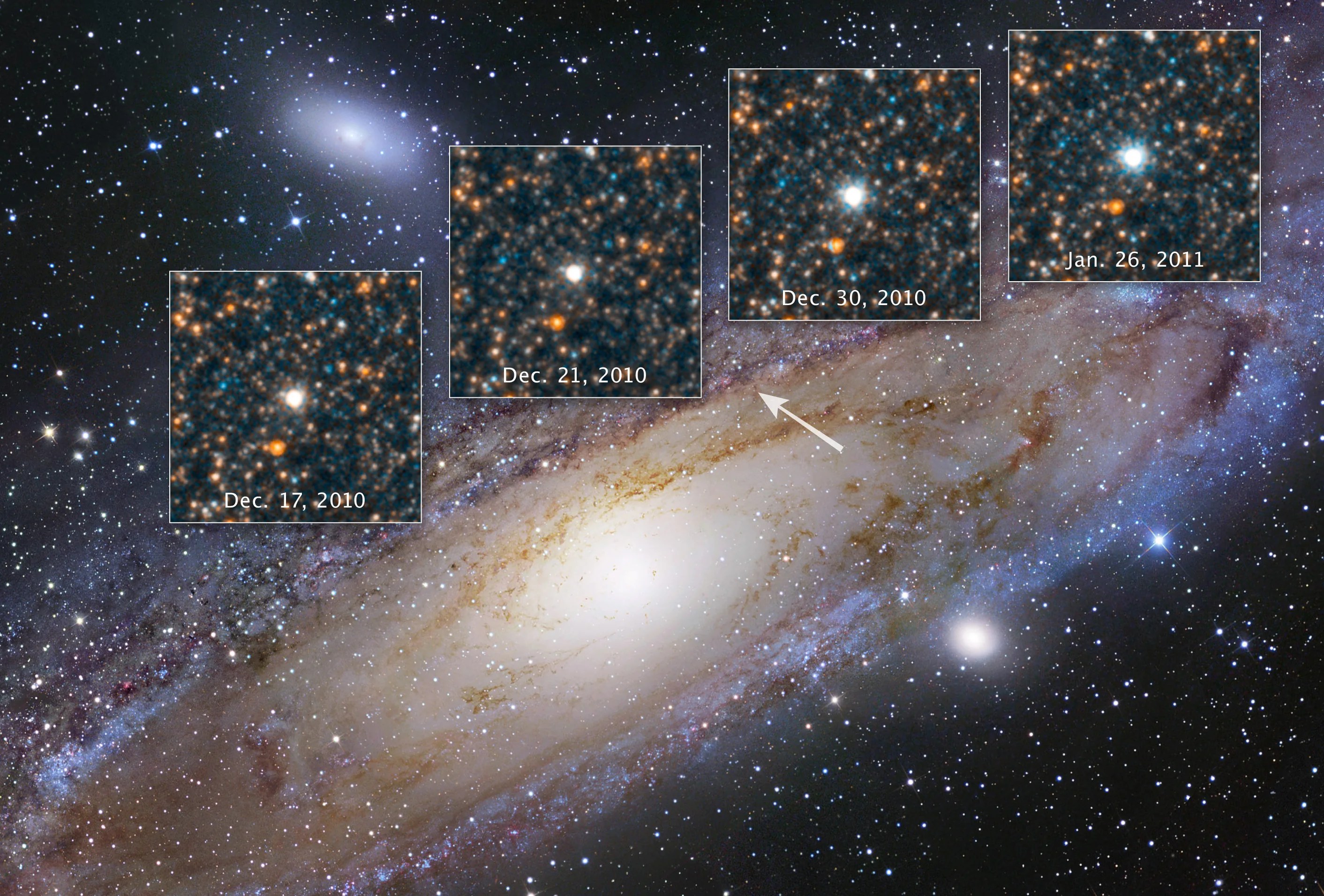
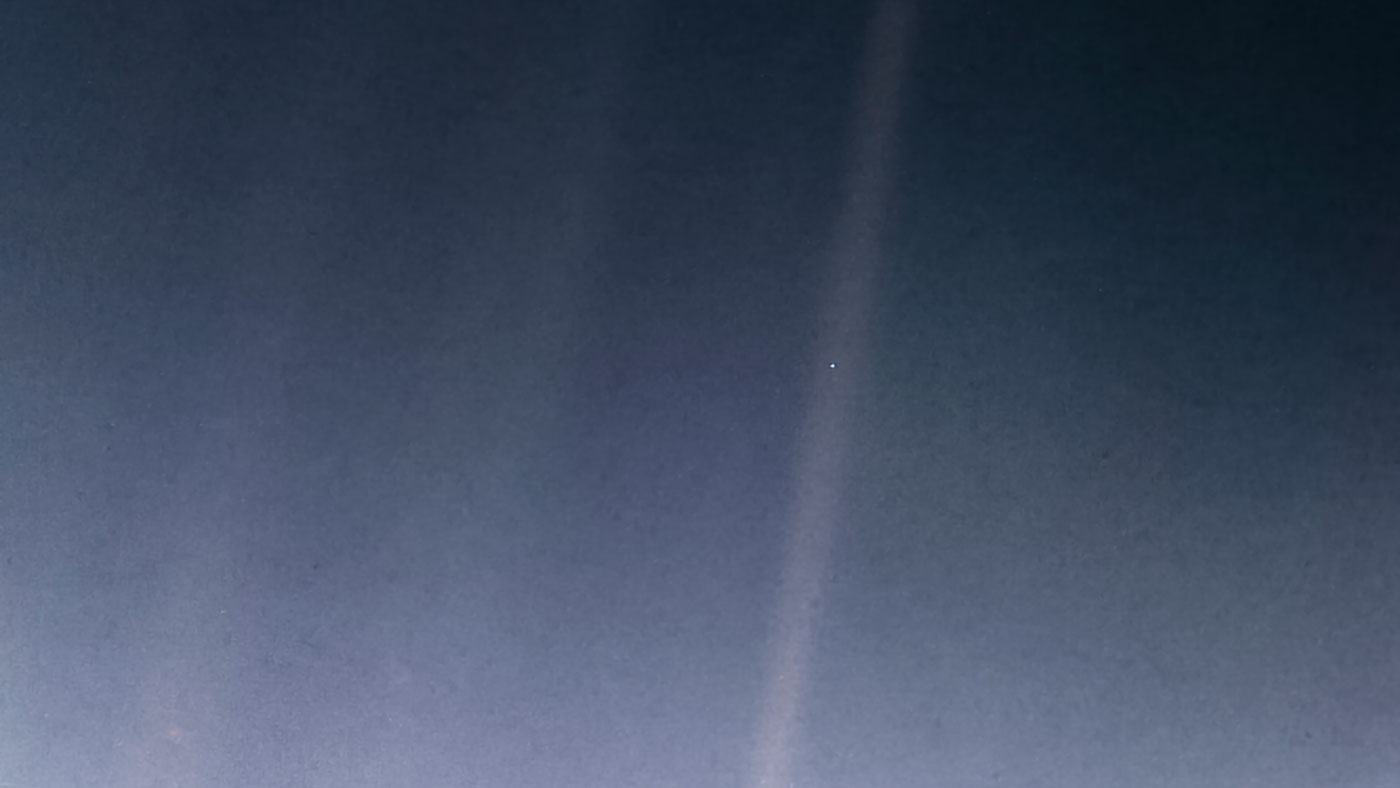
For the 30th anniversary of one of the most iconic views from the Voyager mission, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, is publishing a new version of the image known as the “Pale Blue Dot.”
The updated image uses modern image-processing software and techniques while respecting the intent of those who planned the image. Like the original, the new color view shows Planet Earth as a single, bright blue pixel in the vastness of space. Rays of sunlight scattered within the camera optics stretch across the scene, one of which happens to have intersected dramatically with Earth.
The view was obtained on Feb. 14, 1990, just minutes before Voyager 1’s cameras were intentionally powered off to conserve power and because the probe — along with its sibling, Voyager 2 — would not make close flybys of any other objects during their lifetimes. Shutting down instruments and other systems on the two Voyager spacecraft has been a gradual and ongoing process that has helped enable their longevity.
This celebrated Voyager 1 view was part of a series of 60 images designed to produce what the mission called the “Family Portrait of the Solar System.” This sequence of camera-pointing commands returned images of six of the solar system’s planets, as well as the Sun. The Pale Blue Dot view was created using the color images Voyager took of Earth.
The popular name of this view is traced to the title of the 1994 book by Voyager imaging scientist Carl Sagan, who originated the idea of using Voyager’s cameras to image the distant Earth and played a critical role in enabling the family portrait images to be taken.
Additional information about the Pale Blue Dot image is available at:
https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/resources/536/voyager-1s-pale-blue-dot/
The original Pale Blue Dot and Family Portrait images are available at:
https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/spaceimages/details.php?id=PIA00452
https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/spaceimages/details.php?id=PIA00451
The Voyager spacecraft were built by JPL, which continues to operate both. JPL is a division of Caltech in Pasadena. The Voyager missions are a part of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate in Washington. For more information about the Voyager spacecraft, visit:
Calla Cofield
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
626-808-2469
calla.e.cofield@jpl.nasa.gov
Written by Preston Dyches
2020-030