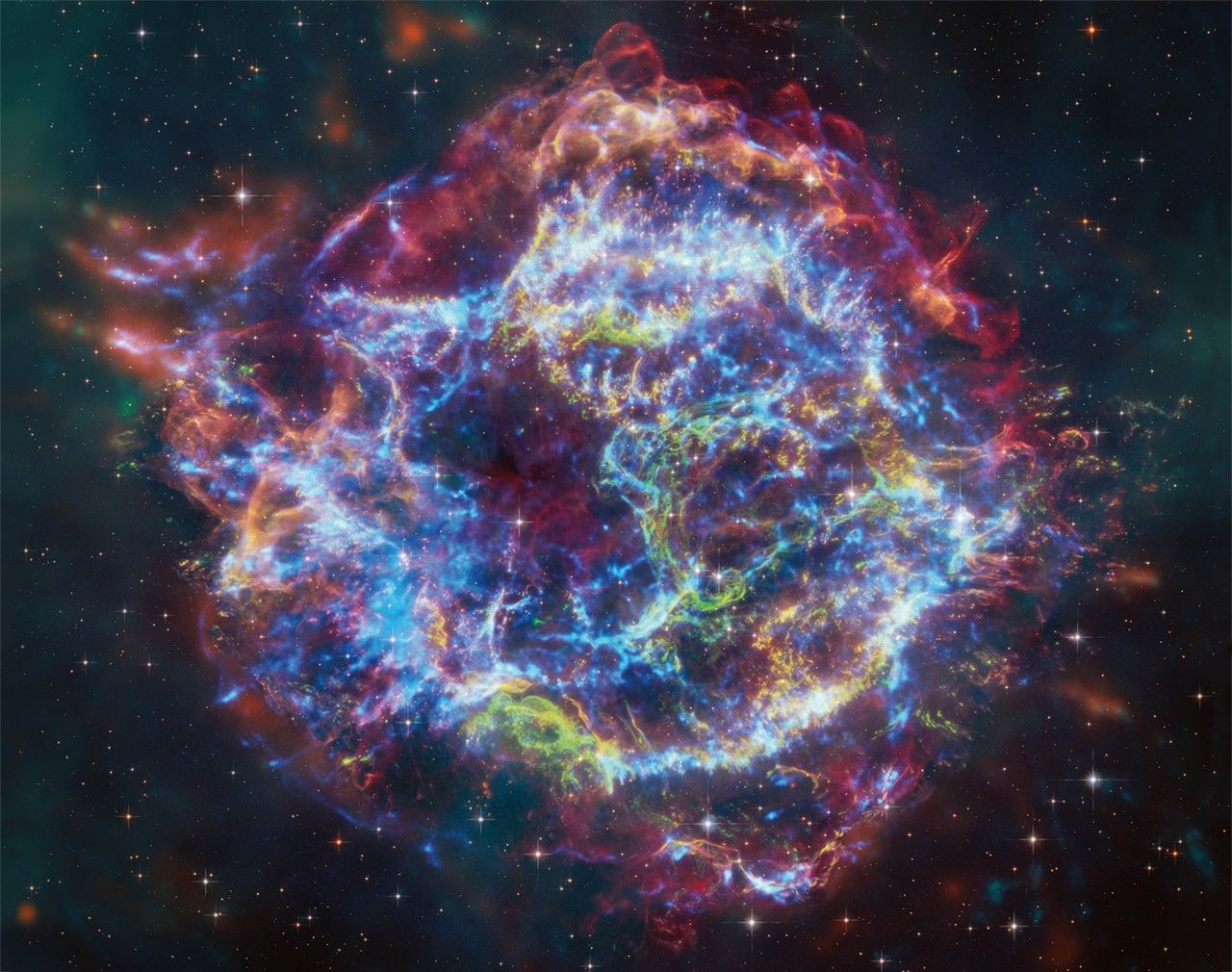
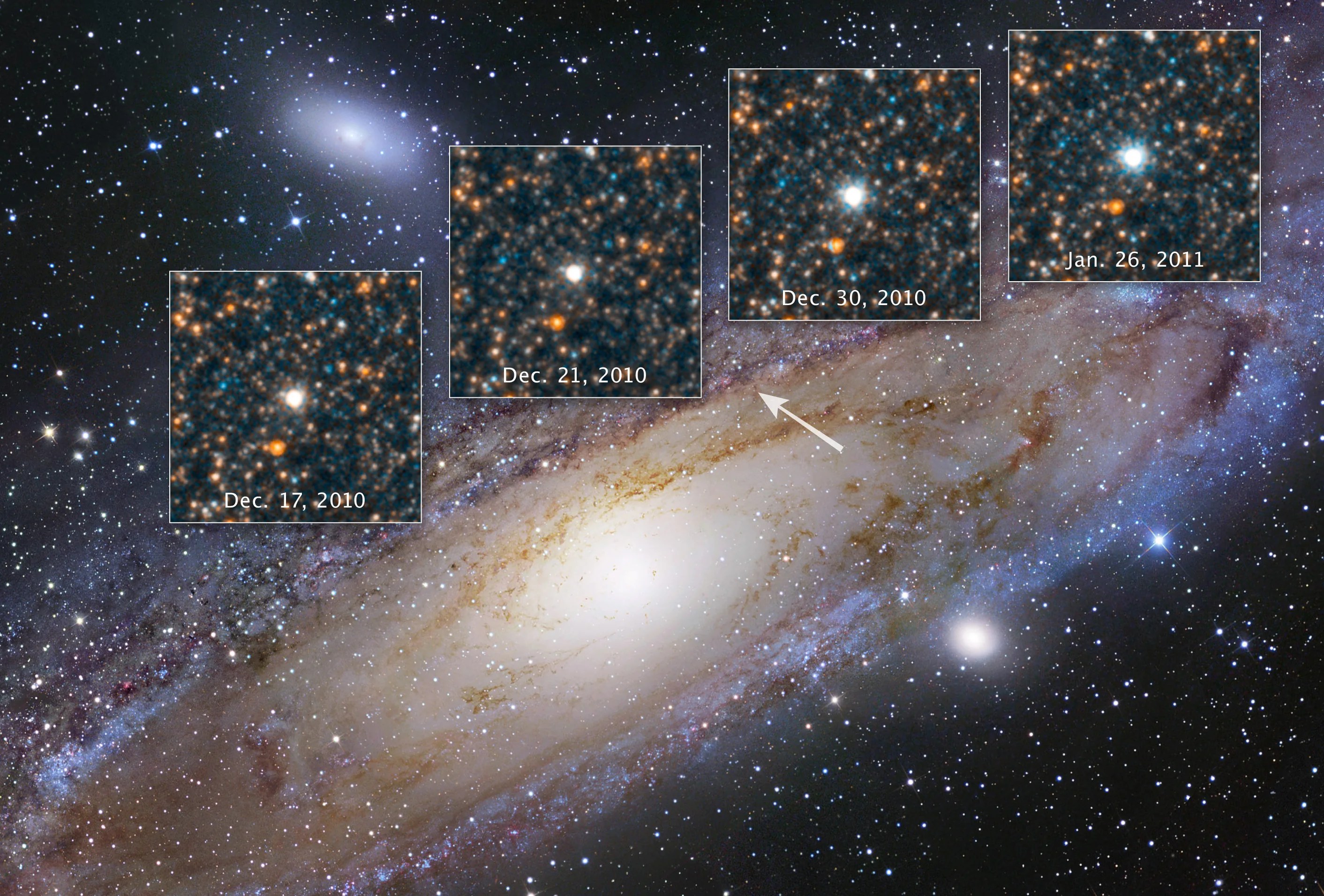
New data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory has provided stringent constraints on the environment around one of the closest supernovas discovered in decades. The Chandra results provide insight into possible cause of the explosion, as described in our press release.
On January 21, 2014, astronomers witnessed a supernova soon after it exploded in the Messier 82, or M82, galaxy. Telescopes across the globe and in space turned their attention to study this newly exploded star, including Chandra. Astronomers determined that this supernova, dubbed SN 2014J, belongs to a class of explosions called “Type Ia” supernovas. These supernovas are used as cosmic distance-markers and played a key role in the discovery of the Universe’s accelerated expansion, which has been attributed to the effects of dark energy. Scientists think that all Type Ia supernovas involve the detonation of a white dwarf. One important question is whether the fuse on the explosion is lit when the white dwarf pulls too much material from a companion star like the Sun, or when two white dwarf stars merge.
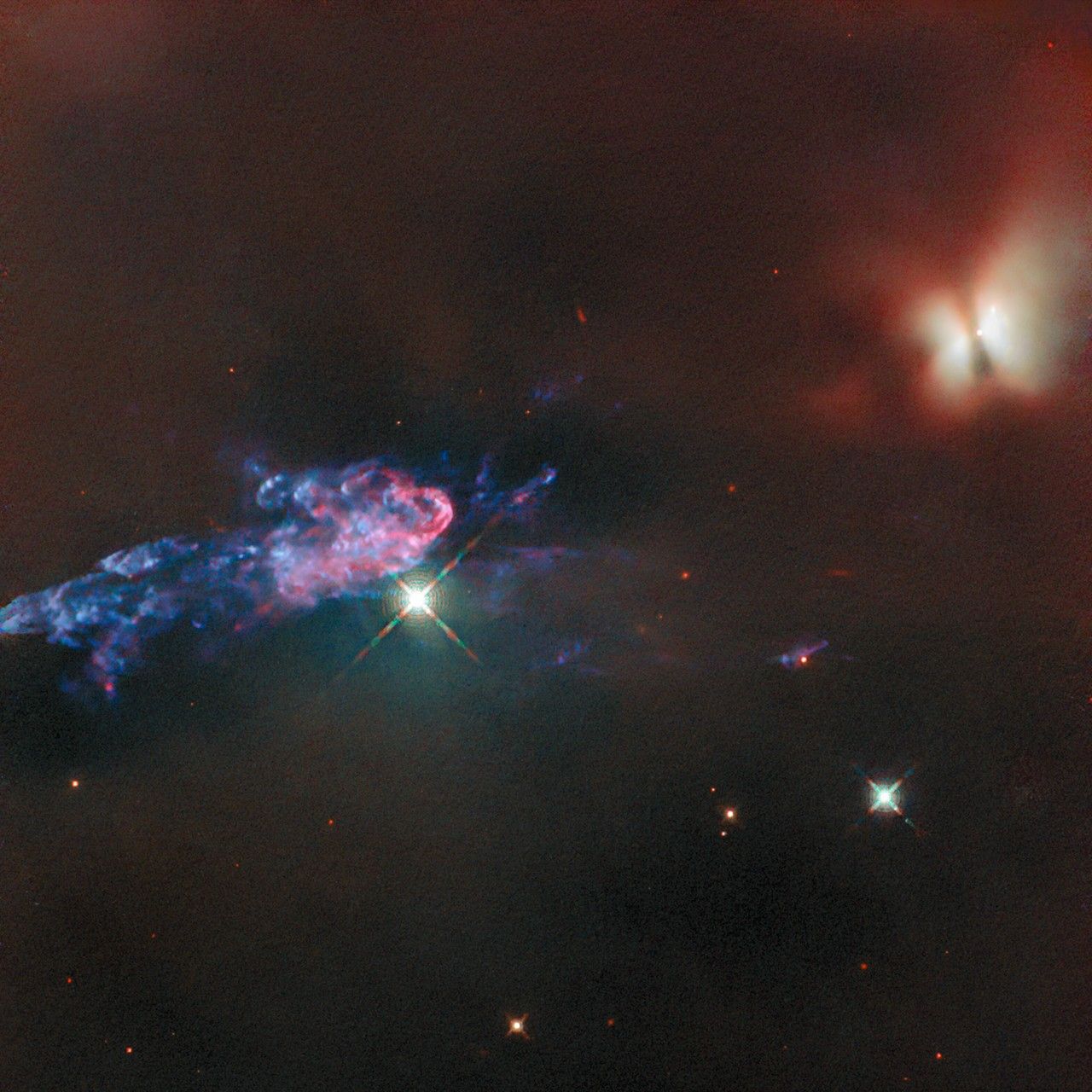
This image contains Chandra data, where low, medium, and high-energy X-rays are red, green, and blue respectively. The boxes in the bottom of the image show close-up views of the region around the supernova in data taken prior to the explosion (left), as well as data gathered on February 3, 2014, after the supernova went off (right). The lack of the detection of X-rays detected by Chandra is an important clue for astronomers looking for the exact mechanism of how this star exploded.
The non-detection of X-rays reveals that the region around the site of the supernova explosion is relatively devoid of material. This finding is a critical clue to the origin of the explosion. Astronomers expect that if a white dwarf exploded because it had been steadily collecting matter from a companion star prior to exploding, the mass transfer process would not be 100% efficient, and the white dwarf would be immersed in a cloud of gas.
If a significant amount of material were surrounding the doomed star, the blast wave generated by the supernova would have struck it by the time of the Chandra observation, producing a bright X-ray source. Since they do not detect any X-rays, the researchers determined that the region around SN 2014J is exceptionally clean.
A viable candidate for the cause of SN 2014J must explain the relatively gas-free environment around the star prior to the explosion. One possibility is the merger of two white dwarf stars, in which case there might have been little mass transfer and pollution of the environment before the explosion. Another is that several smaller eruptions on the surface of the white dwarf cleared the region prior to the supernova. Further observations a few hundred days after the explosion could shed light on the amount of gas in a larger volume, and help decide between these and other scenarios.
A paper describing these results was published in the July 20 issue of The Astrophysical Journal and is available online. The first author is Raffaella Margutti from the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA) in Cambridge, MA, and the co-authors are Jerod Parrent (CfA), Atish Kamble (CfA), Alicia Soderberg (CfA), Ryan Foley (University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign), Dan Milisavljevic (CfA), Maria Drout (CfA), and Robert Kirshner (CfA).
Image Credit: NASA/CXC/SAO/R.Margutti et al