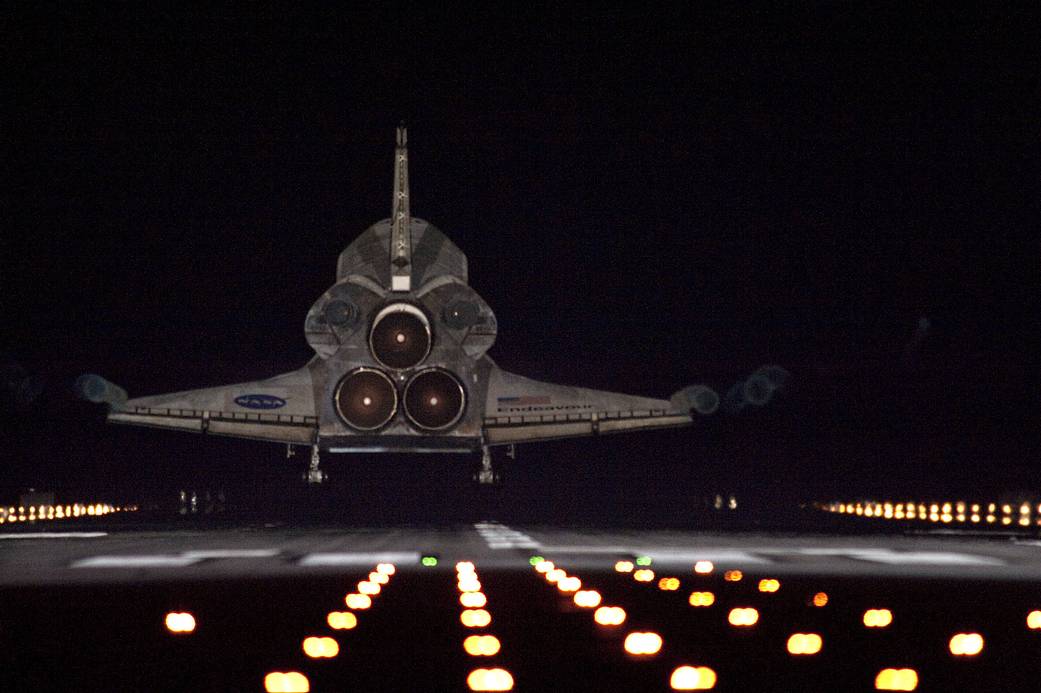
This week in 2011, space shuttle Endeavour, mission STS-134, landed at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. During its 16-day mission to the International Space Station, Endeavour delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer and spare parts, including two S-band communications antennas, a high-pressure gas tank, and additional parts for Dextre – the Canadian Space Agency’s robotic handyman. This was the 36th shuttle mission to the space station and the final flight for Endeavour. Today, the Payload Operations Integration Center at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center serves as “science central” for the space station, working 24/7, 365 days a year in support of the orbiting laboratory’s science experiments. After 20 years of continuous human presence, the space station remains the sole space-based proving ground and stepping stone toward achieving the goals of the Artemis program. The NASA History Program is responsible for generating, disseminating, and preserving NASA’s remarkable history and providing a comprehensive understanding of the institutional, cultural, social, political, economic, technological, and scientific aspects of NASA’s activities in aeronautics and space. For more pictures like this one and to connect to NASA’s history, visit the Marshall History Program’s webpage. (NASA)
1 min read