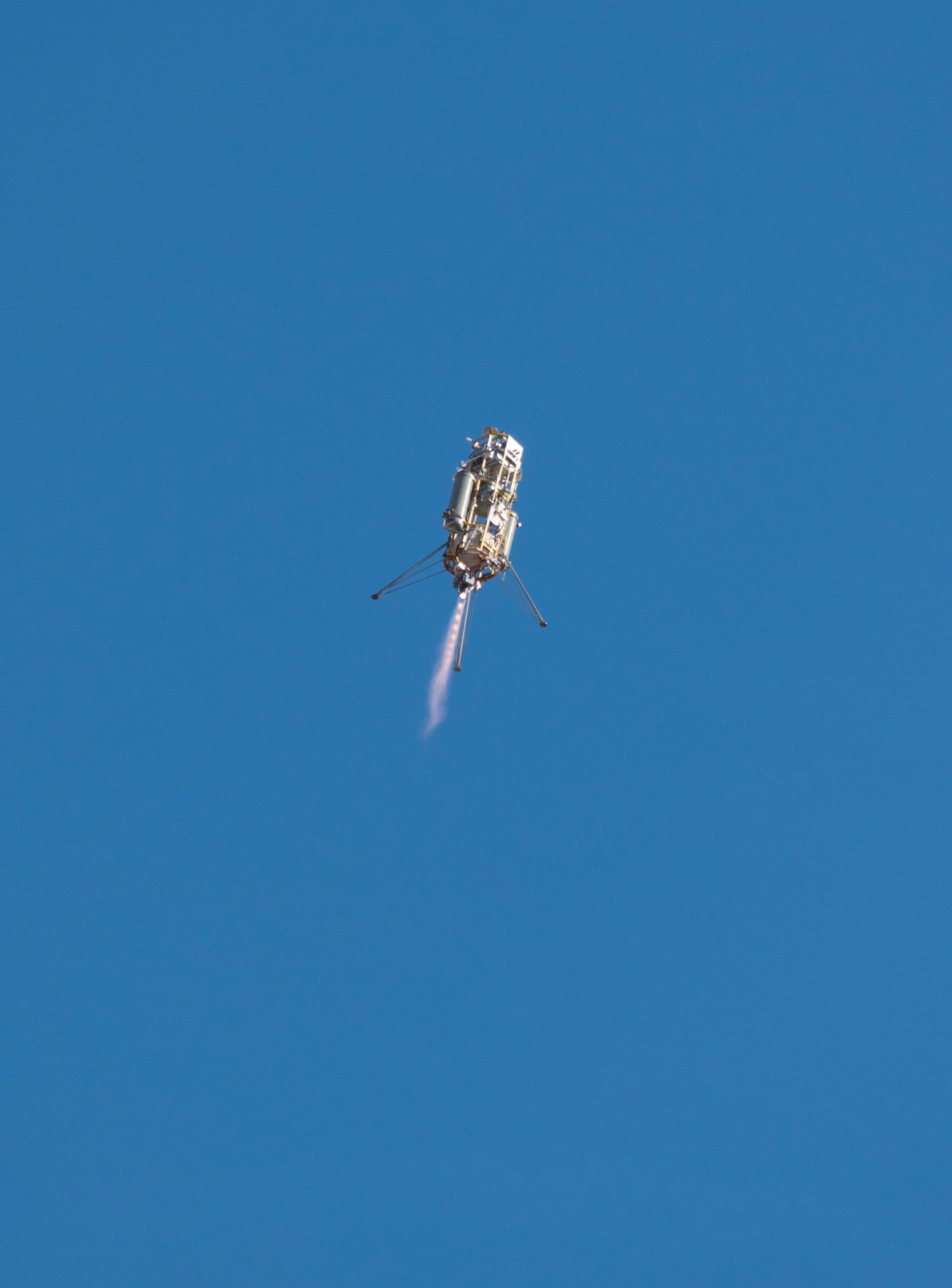
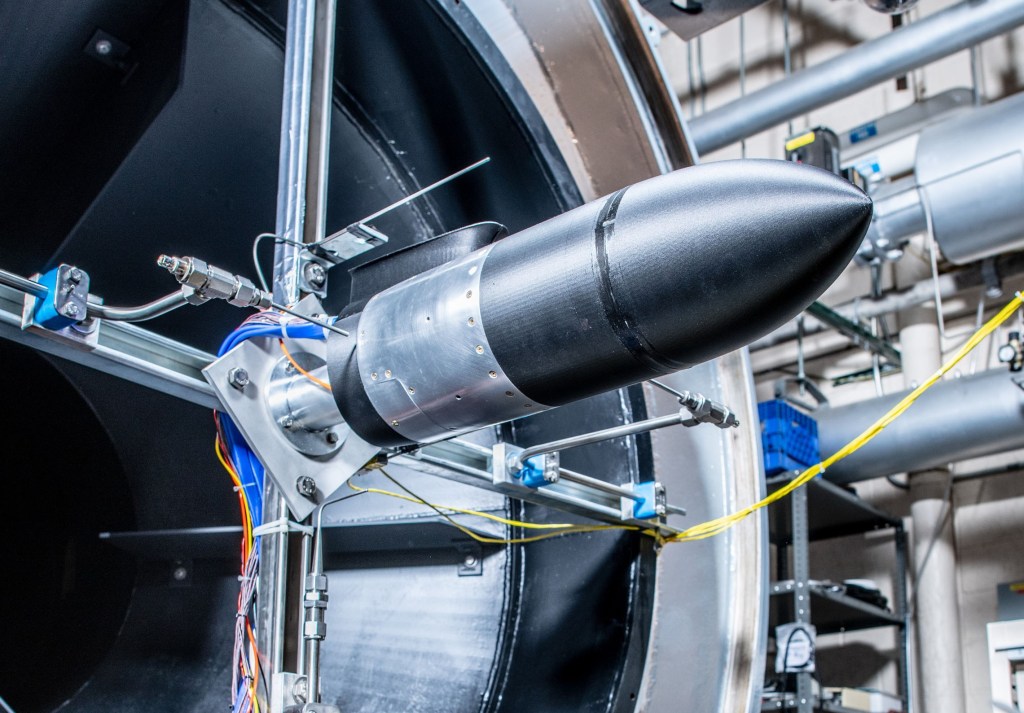
NASA tested new “eyes” for its next Mars rover mission on a rocket built by Masten Space Systems in Mojave, California, in 2014, thanks in part to NASA’s Flight Opportunities Program, or FO program.
The agency’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, is leading development of the Mars 2020 rover’s Lander Vision System, or LVS. The prototype vision system launched 1,066 feet into the air aboard Masten’s rocket-powered “Xombie” test platform and helped guide the rocket to a precise landing at a predesignated target. LVS flew as part of a larger system of experimental landing technologies called the Autonomous Descent and Ascent Powered-flight Testbed, or ADAPT.
LVS, a camera-based navigation system, photographs the terrain beneath a descending spacecraft and matches it with onboard maps allowing the craft to detect its location relative to landing hazards such as boulders and outcroppings.
The system can then direct the craft toward a safe landing at its primary target site or divert touchdown toward better terrain if there are hazards in the approaching target area. Imaging matching is aided by an inertial measurement unit that monitors orientation.
FO program funded the Masten flight tests under the Space Technology Mission Directorate. The program obtains commercial suborbital space launch services to pursue science, technology and engineering to mature technology relevant to NASA’s pursuit of space exploration. The program nurtures the emerging suborbital space industry and allows NASA to focus on deep space.
Andrew Johnson, principal investigator in the Lander Vision System development, said the tests built confidence that the vision system will enable Mars 2020 to land safely.
“By providing funding for flight tests, FOP motivated us to build guidance, navigation and control payloads for testing on Xombie,” Johnson said. “In the end we showed a closed loop pinpoint landing demo that eliminated any technical concerns with flying the Lander Vision System on Mars 2020.”
According to “Lander Vision System for Safe and Precise Entry Descent and Landing,” a 2012 abstract co-authored by Johnson for a Mars exploration workshop, LVS enables a broad range of potential landing sites for Mars missions.
Typically, Mars landers have lacked the ability to analyze and react to hazards, the abstract says. To avoid hazards, mission planners selected wide-open landing sites with mostly flat terrain. As a result, landers and rovers were limited to areas with relatively limited geological features, and were unable to access many sites of high scientific interest with more complex and hazardous surface morphology. LVS will enable safe landing at these scientifically compelling Mars landing sites.
An LVS-equipped mission allows for opportunities to land within more challenging environments and pursue new discoveries about Mars. With LVS baselined for inclusion on Mars 2020, the researchers are now focused on building the flight system ahead of its eventual role on the red planet.
To learn more about NASA’s Flight Opportunities program, visit: https://www.nasa.gov/directorates/spacetech/flightopportunities/index.html
To read more about NASA’s Mars 2020 rover, visit: http://mars.nasa.gov/mars2020/