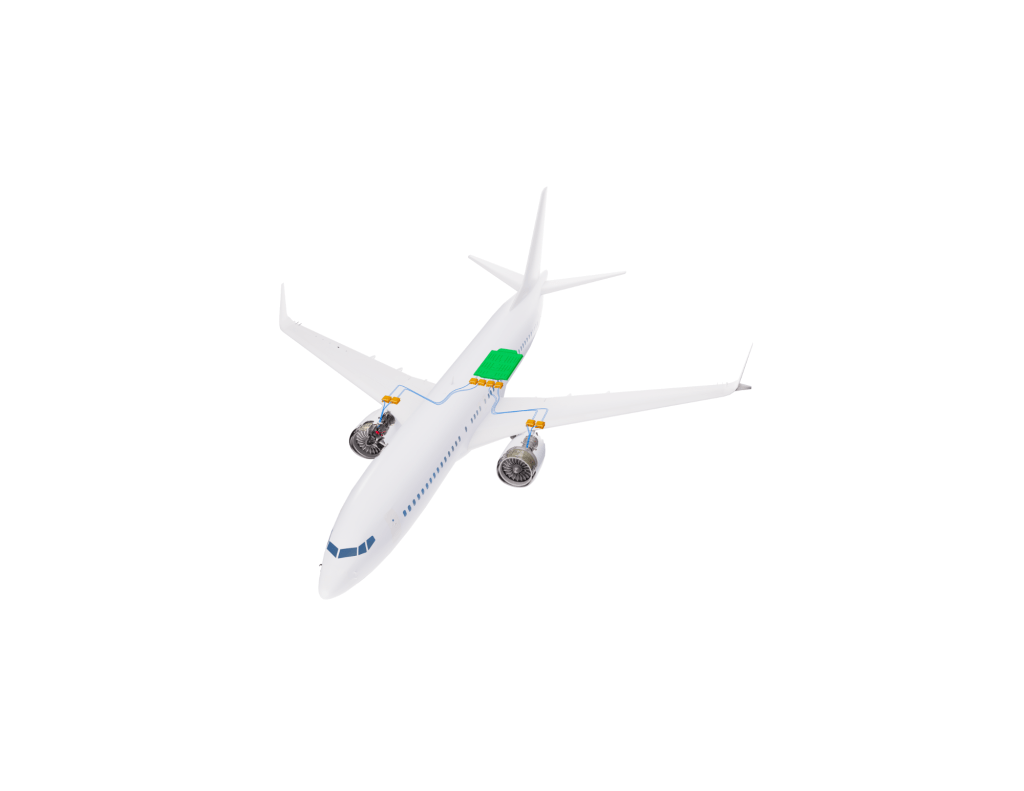
Aircraft Configurations
Electrified aircraft concepts use electricity from battery-powered motors for propulsion. They can either be the sole source of energy or be combined with traditional fuel-based engines. NASA and its industry partners are exploring six different propulsion system architectures for future electrified aircraft, including an all-electric system configuration, three hybrid electric configurations, and two turboelectric configurations.
All-electric
Fully electric aircraft systems use electricity from batteries as the sole source of power for propulsion.
Hybrid Electric
Hybrid electric aircraft systems use traditional fuel-based engines for propulsion and to charge onboard batteries that can also be used as an energy source during flight.
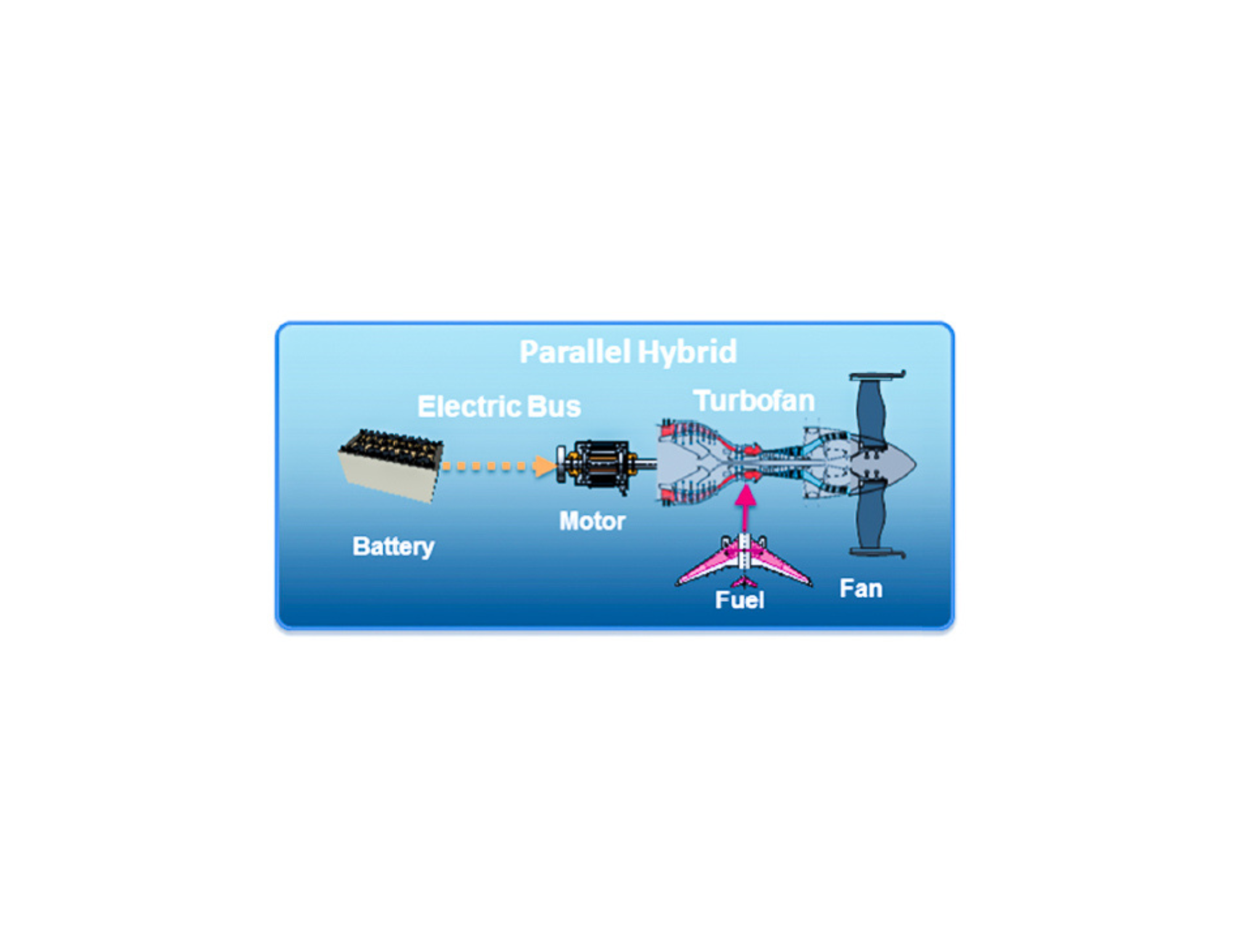
Parallel Hybrid
In a parallel hybrid system, a battery-powered motor and a traditional fuel-based engines are both mounted on a shaft that drives fan, so either one or both can provide propulsion at any given time.
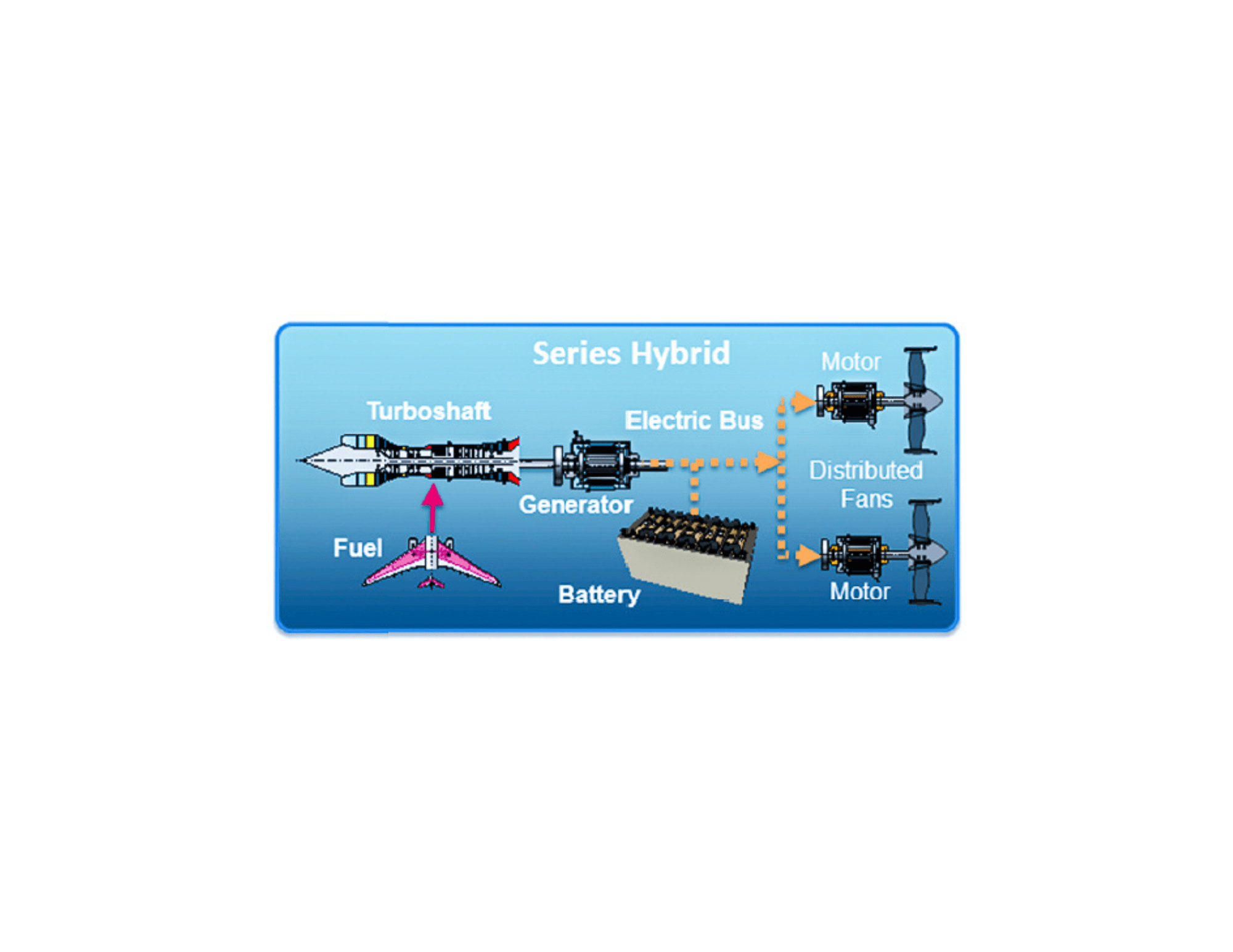
Series Hybrid
In a series hybrid system, only the electric motors are connected to the fans, and the traditional engines are used to drive an electrical generator that drives the motors and/or charges the batteries.
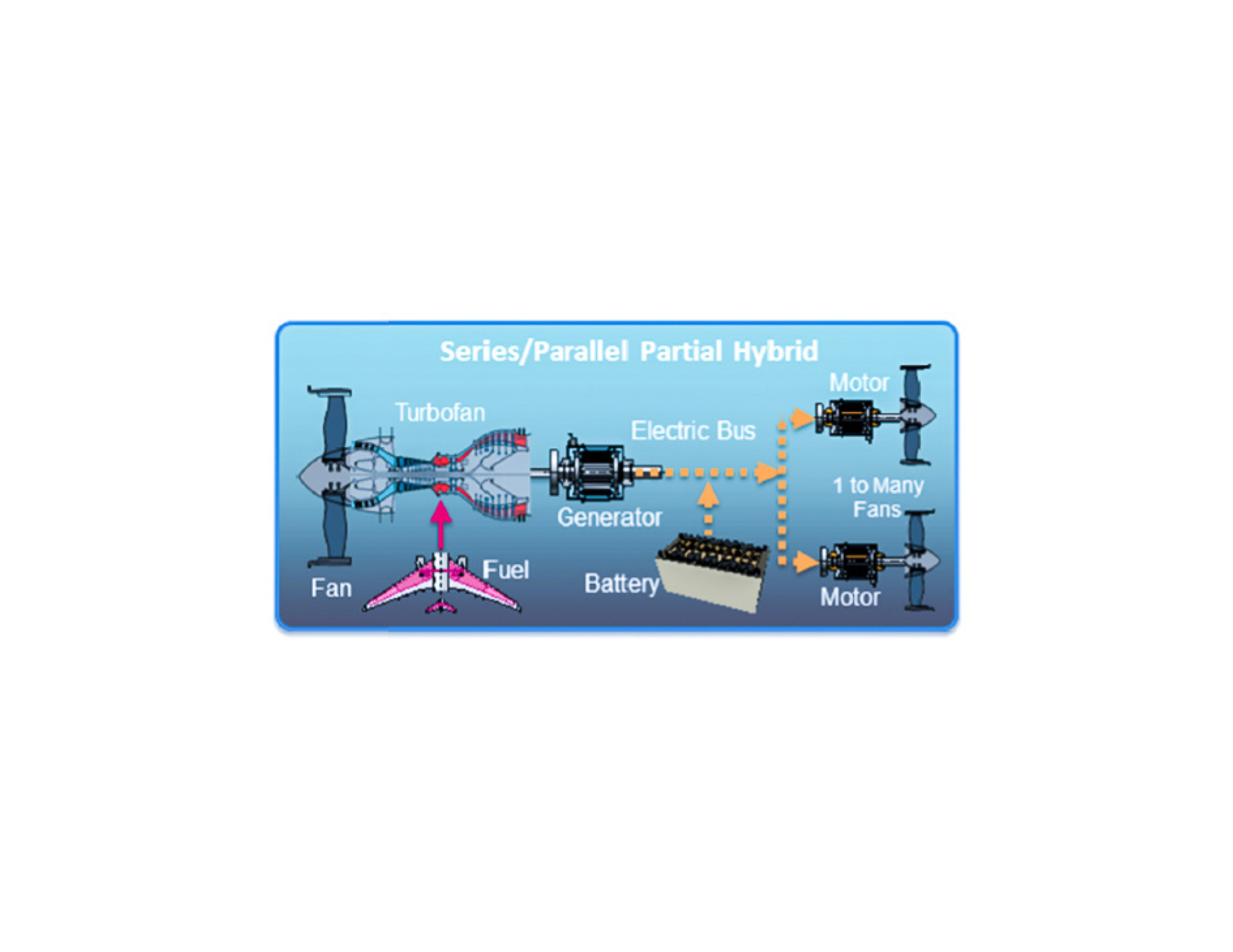
Series/Parallel Partial Hybrid
In a series/parallel partial hybrid system, there are one or more fans that can be driven directly by a traditional fuel-based engine and additional fans that are driven exclusively by electrical motors that can be powered by a battery or a turbine-driven generator.
Turboelectric
Turboelectric aircraft systems rely on traditional fuel-based engines to drive electric generators that power inverters and motors that power individual distributed electric fans. These systems do not directly use batteries as an energy source during flight.
Partially Turboelectric
A partially turboelectric system uses electric propulsion to provide part of the propulsive power, with the rest provided by a turbofan driven by a traditional fuel-based engine.
Fully turboelectric
A fully turboelectric system relies fully on traditional fuel-based engines to drive electric generators that then power inverters and motors to drive disturbed fans.
Reference
The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, Commercial Aircraft Propulsion and Energy Systems Research: Reducing Global Carbon Emissions, The National Academies Press, Washington, DC, 2016, Chap. 4.
















![In Memoriam: Jeff Dozier [1944–2024]](https://assets.science.nasa.gov/dynamicimage/assets/science/esd/earth-observer/2025/2025-in-memoriam/InMemoriam-Dozier1.jpg)
![In Memoriam: Berrien Moore III [1941–2024]](https://assets.science.nasa.gov/dynamicimage/assets/science/esd/earth-observer/2025/2025-in-memoriam/InMemoriam-Moore..jpg)