Airborne Science Instruments at Ames
active projects
5
subject matter experts
4
NASA Ames poc
Matthew Fladeland
Spectrometer for Sky-Scanning, Sun-Tracking Atmospheric Research (4STAR)
4STAR is a spectrometer designed to fly on the P-3 Orion, C-130H, Convair 580 NRC, Gulfstream G-1, and DC-8, measuring NO2, O3, H2O, Spectral Aerosol Optical Depth, Aerosol Extinction Angstrom Exponent, Aerosol Single Scattering Albedo, Aerosol Asymmetry Parameter, Aerosol Scattering phase function, Aerosol Size Distribution, Aerosol Complex Refractive Index, Cloud Optical Depth, Cloud droplet effective radius, Cloud Thermodynamic Phase, and Cloud Liquid Water Content.
Click Here to Learn More About 4STAR about Spectrometer for Sky-Scanning, Sun-Tracking Atmospheric Research (4STAR)
Cloud Absorption Radiometer (CAR)
CAR is a radiometer designed to fly on the J-31, P-3 Orion, Convair 580 NRC, and C-131A, measuring solar flux and imagery.
Click Here to Learn More About CAR about Cloud Absorption Radiometer (CAR)
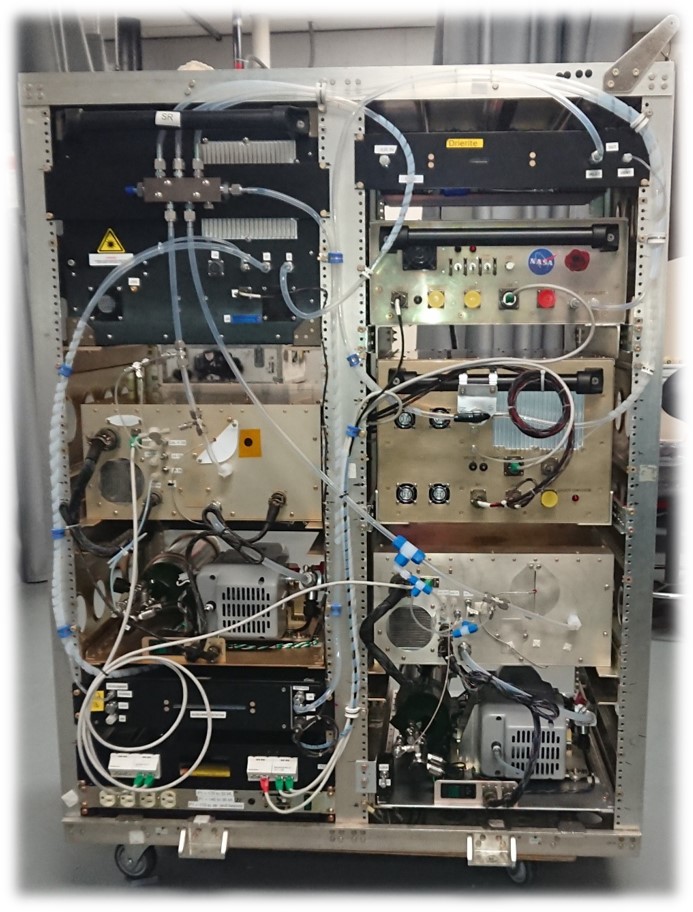
Carbon monOxide Measurement from Ames (COMA)
COMA is a laser absorption instrument designed to fly on the P-3 Orion and WB-57, measuring CO, N2O, and H2O.
Click Here to Learn More About COMA about Carbon monOxide Measurement from Ames (COMA)
Enhanced MODIS Airborne Simulator (eMAS)
eMAS is a multispectral VNIR/SWIR/LWIR imager flying on the ER-2 to acquire 50-meter spatial resolution imagery in 38 spectral bands of cloud and surface features.
Click Here to Learn More About eMAS about Enhanced MODIS Airborne Simulator (eMAS)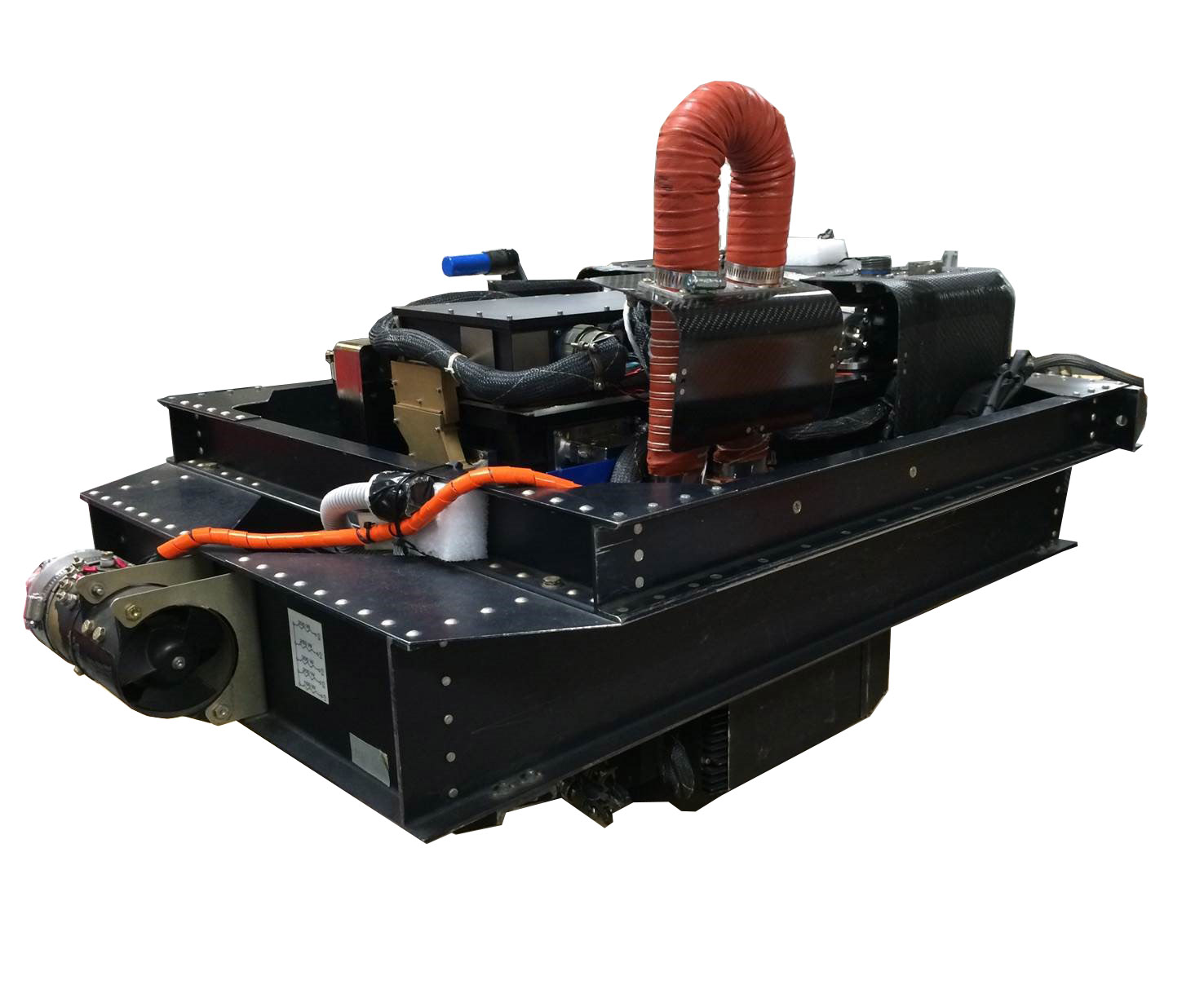
MODIS/ASTER Airborne Simulator (MASTER)
MASTER is a multispectral VNIR/SWIR/LWIR imager flying on the B-200, DC-8, ER-2, WB-57, and P-3 Orion to study geologic and other Earth surface properties.
Click Here to Learn More About MASTER about MODIS/ASTER Airborne Simulator (MASTER)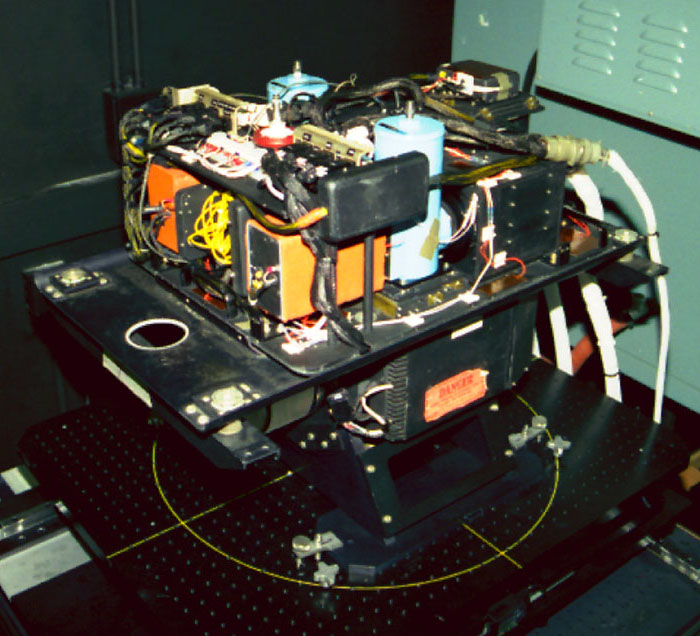
Meteorological Measurement System (MMS)
MMS is designed to measure 3D Wind, Turbulence, Temperature, Position, Velocities, Attitudes, True-Airspeed, and Potential Temperature on the Alpha Jet, Sierra UAV, DC-8, ER-2, Global Hawk, and WB-57.
Click Here to Learn More About MMS about Meteorological Measurement System (MMS)
Pushbroom Imager for Cloud and Aerosol Research and Development (PICARD)
PICARD is an instrument intended to fly on the ER-2 to simulate existing satellite imager products (MODIS/VIIRS,) and to validate radiances and geophysical retrievals, with an emphasis on cloud and aerosol science.
Click Here to Learn More About PICARD about Pushbroom Imager for Cloud and Aerosol Research and Development (PICARD)
Rapid Ozone Experiment (ROZE)
ROZE is an in-situ instrument designed to fly on the DC-8 and ER-2, measuring O3.
Click Here to Learn More About ROZE about Rapid Ozone Experiment (ROZE)