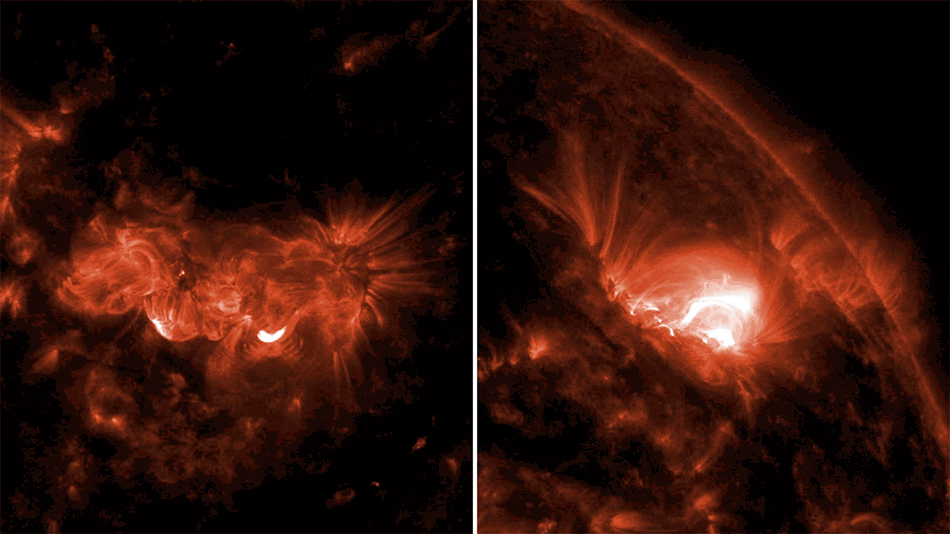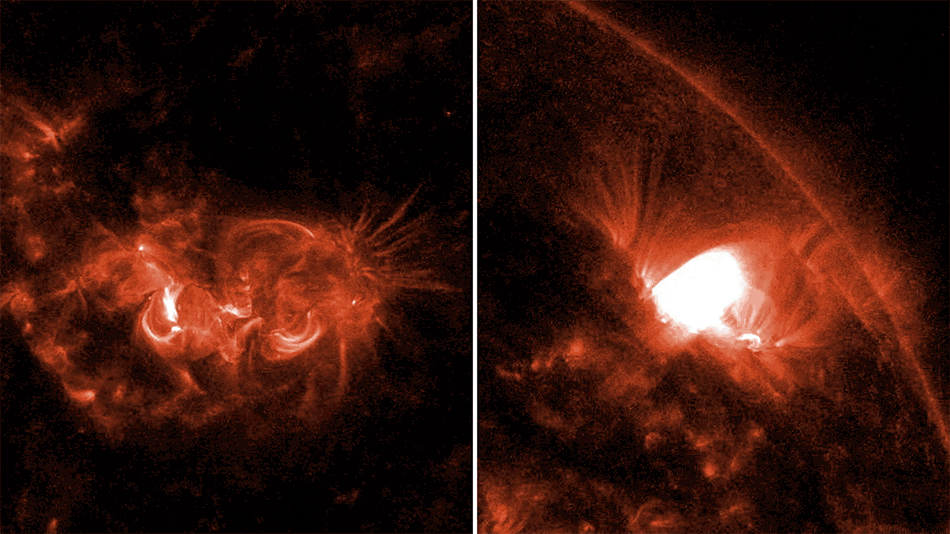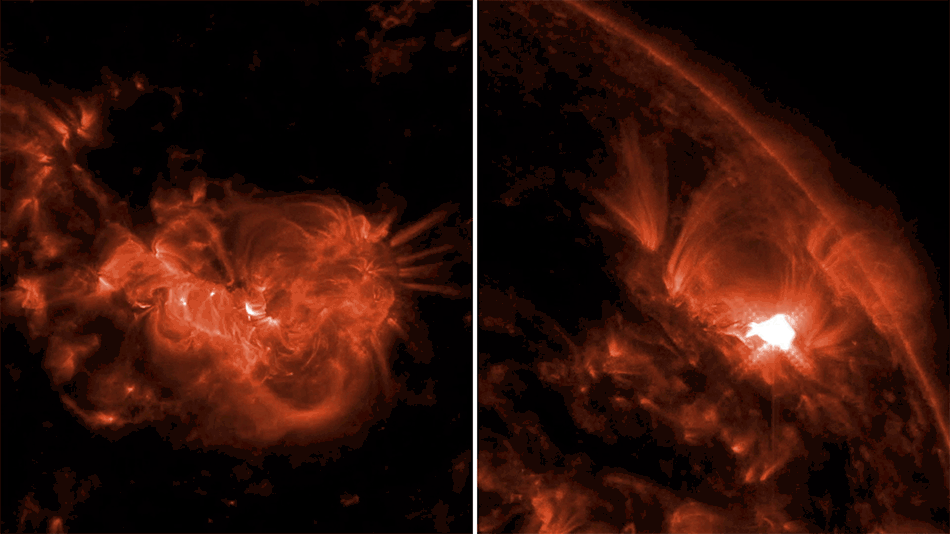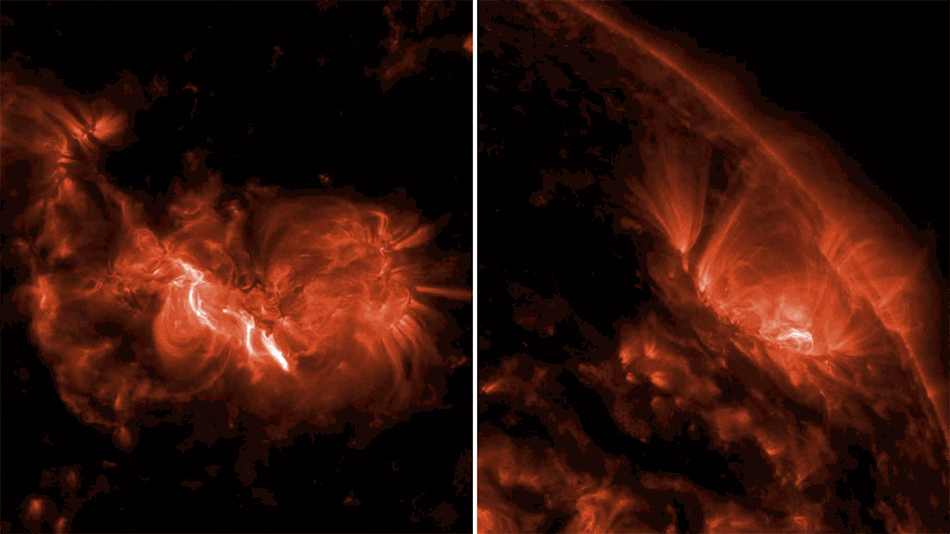
![Near the outskirts of the Small Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy roughly 200 000 light-years from Earth, lies the young star cluster NGC 602, which is featured in this new image from the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope. This image includes data from Webb’s NIRCam (Near-InfraRed Camera) and MIRI (Mid-InfraRed Instrument). The local environment of this cluster is a close analogue of what existed in the early Universe, with very low abundances of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium. The existence of dark clouds of dense dust and the fact that the cluster is rich in ionised gas also suggest the presence of ongoing star formation processes. This cluster provides a valuable opportunity to examine star formation scenarios under dramatically different conditions from those in the solar neighbourhood. [Image description: A star cluster is shown inside a large nebula of many-coloured gas and dust. The material forms dark ridges and peaks of gas and dust surrounding the cluster, lit on the inner side, while layers of diffuse, translucent clouds blanket over them. Around and within the gas, a huge number of distant galaxies can be seen, some quite large, as well as a few stars nearer to us which are very large and bright.]](https://www.nasa.gov/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/ngc602.jpg)
NASA Missions Spot Cosmic ‘Wreath’ Displaying Stellar Circle of Life
NGC 602 is a star cluster that lies on the outskirts of the Small Magellanic Cloud, one of the closest galaxies to the Milky Way. This image combines X-rays from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and infrared data from NASA's James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The dark ring-like structure in the JWST data is made up of dense clouds of dust. Chandra’s X-rays show young, massive stars that are illuminating the dust clouds, sending high-energy light into interstellar space. These X-rays are powered by winds flowing from the young, massive stars that are sprinkled throughout the cluster.
Image Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC; Infrared: ESA/Webb, NASA & CSA, P. Zeilder, E.Sabbi, A. Nota, M. Zamani; Image Processing: NASA/CXC/SAO/L. Frattare and K. Arcand
- X
https://www.nasa.gov/image-detail/ngc-602-webb-image/
TakenOctober 23, 2024
Image CreditX-ray: NASA/CXC; Infrared: ESA/Webb, NASA & CSA, P. Zeilder, E.Sabbi, A. Nota, M. Zamani; Image Processing: NASA/CXC/SAO/L. Frattare and K. Arcand
Size5332x4622px