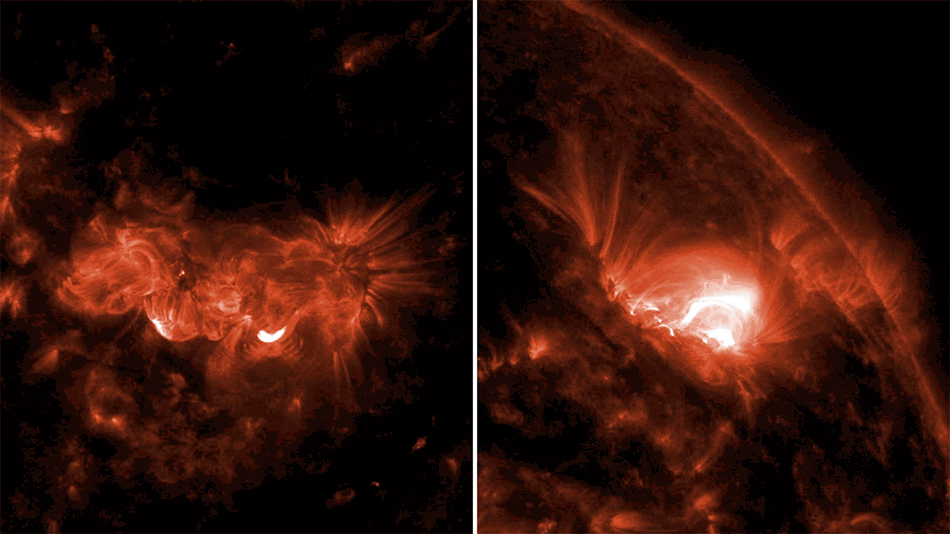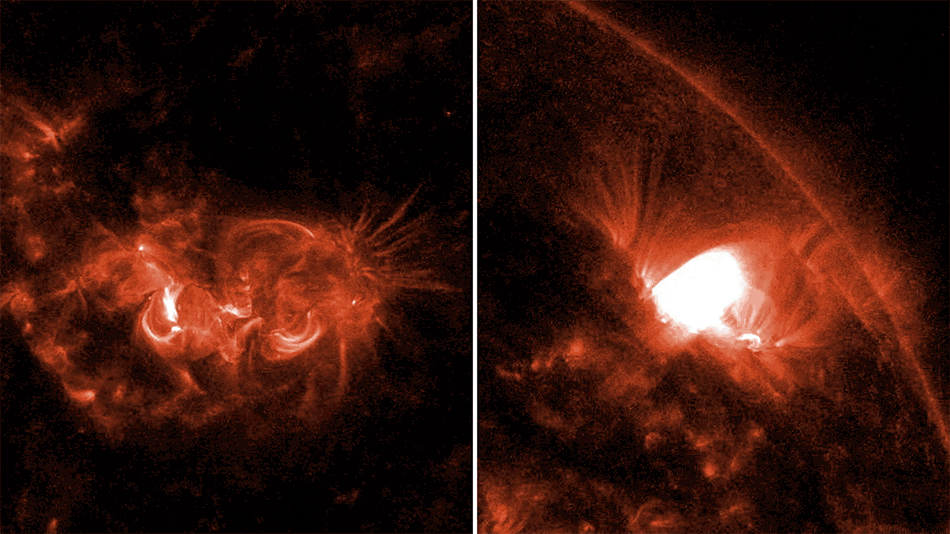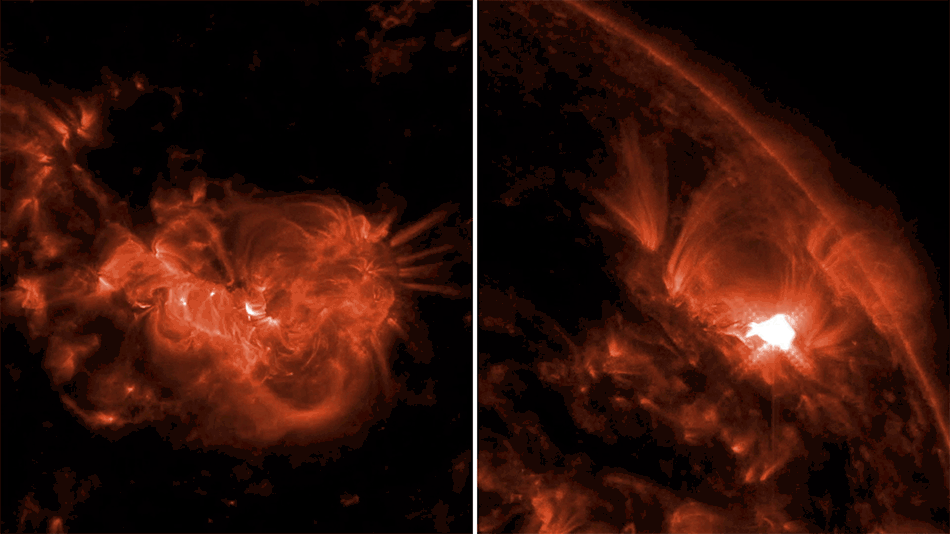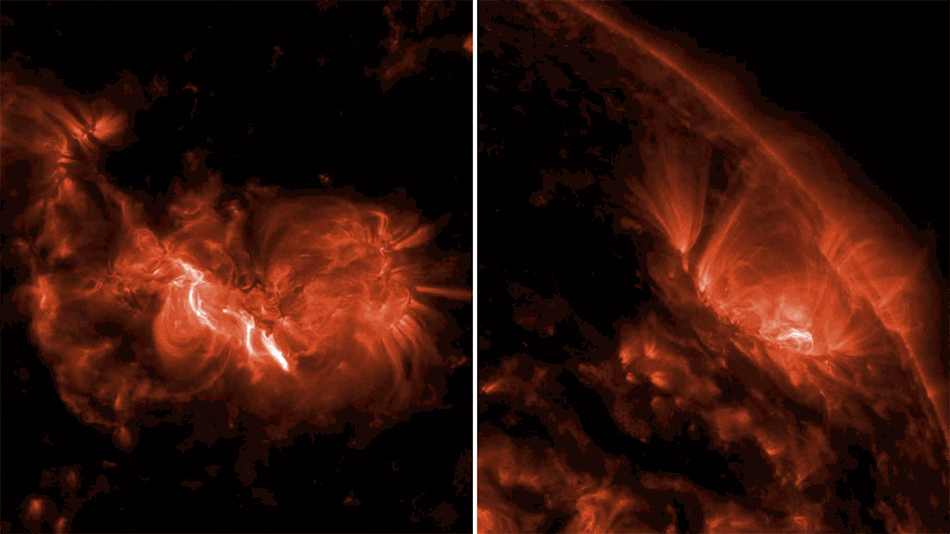
A motor designed by Aerojet Rocketdyne for the Launch Abort System (LAS) on NASA’s Orion spacecraft was successfully tested by engineers at the U.S. Army Redstone Test Center on Redstone Arsenal in Huntsville, Alabama. During the Orion Launch Abort System Jettison Motor Qualification Motor-1 Hot-Fire Test, the motor produced more than 40,000 pounds of thrust, enough to lift 26 elephants off the ground. The 1.5-second test was the first in a round of tests aimed at qualifying the LAS Jettison Motor for human spaceflight in preparation for Exploration Mission-2. The LAS is a safety mechanism for Orion that will launch atop NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS), which will carry crew to deep space missions. The Jettison Motor is a critical element for ensuring astronaut safety. The Launch Abort System will safely lift the Orion Crew Module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during ascent. Once Orion reaches a safe distance from the rocket, the Orion Jettison Motor would ignite to separate the LAS structure from the spacecraft, which could then deploy its parachutes for a safe landing. The Launch Abort System consists of three solid rocket motors: the Jettison Motor, the Abort Motor that pulls the Crew Module away from the launch vehicle, and the Attitude Control Motor used for steering to reorient the Crew Module’s position following an abort. A jettison motor will also be included in an upcoming test of the Launch Abort System, Ascent Abort 2 (AA-2). The Jettison Motor was built by Aerojet Rocketdyne in Sacramento, California, for the Lockheed Martin-built Orion spacecraft’s Launch Abort System. The LAS is led out of NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia in collaboration with NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama.
Video Credit: NASA
Caption Credit: Jonathan Deal, NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center