Pollinators play a crucial role in both human agriculture and ecosystems by supporting thousands of plant species and crops which feed humans and livestock. Unfortunately, habitat loss, disease, and pesticides contribute to the decline in pollinator biodiversity worldwide, which has led to a substantial reduction in native bee species, impacts to honeybees, and the decline of the iconic Monarch Butterfly. In their efforts to integrate sustainable design, several NASA centers have implemented measures promoting preservation of pollinator habitats though gardens, meadows, and other initiatives.
Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC)
In 2015, budget constraints resulted in the removal of plant beds to make way for low-maintenance turf grass. This prompted the Center’s Environmental Management team to propose a more sustainable landscape option resulting in the 0.1-acre Meadow Demonstration Project. With support from the University of Maryland Extension Service and Maryland Master Gardeners, the meadow became a certified Monarch Waystation. As the meadow flourished under the diligent efforts of staff and volunteers, an increasing number of pollinators were observed.
Due to the success of the initial meadow, GSFC partnered with USDA/Natural Resources Conservation Service to convert additional areas around the center with the goal of perfecting restoration methods. GSFC’s grounds provided an ideal environment to test various approaches. The latest addition is a 1.3-acre plot cultivated this year. GSFC partnered with the NRCS to display this project and participate in the Patuxent Wildlife Refuge Festival in May and the Pollinator Day Festival in June at the USDA HQ to showcase their project.
You can learn more about ongoing and upcoming events at the Meadow Demonstration Project blog.
Johnson Space Center (JSC)
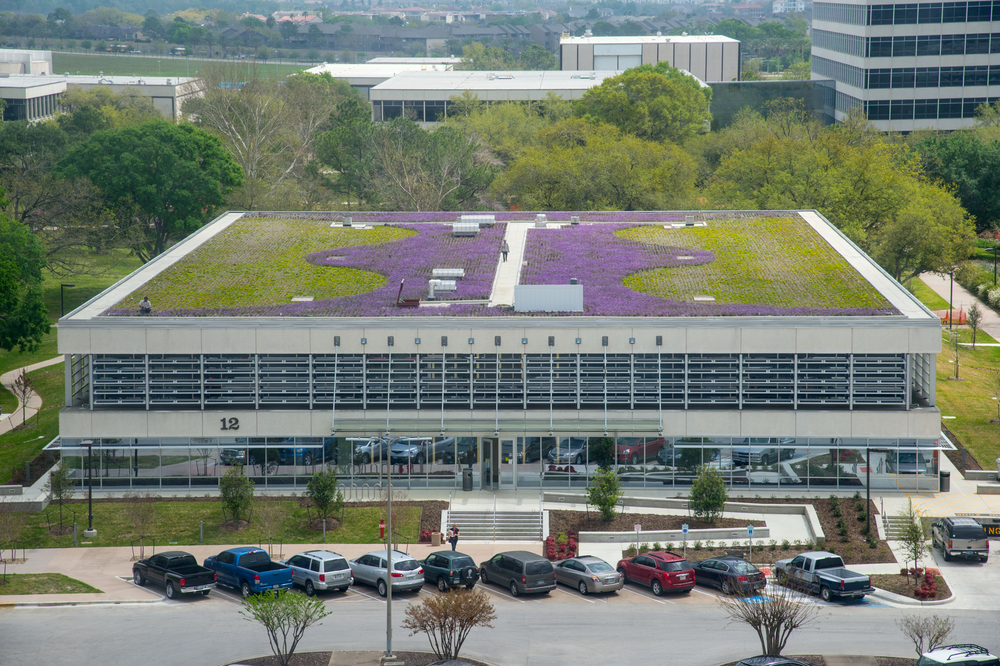
The Center is embedded in an urban landscape once dominated by Texas coastal prairies. To support resiliency of coastal prairie remnants on site, an altered mowing schedule promoting wildflower growth is implemented. JSC participates in a Houston Zoo program called the Prairie Pollinator Pathway to restore or recreate green pathways for pollinator movement through an otherwise highly fragmented urban environment. In 2012, a 30,000 square foot green roof was created on Building 12. Initially planted with non-native species that struggled in the Houston heat, the garden was replanted in 2022 with native grasses and flowers. To further protect pollinators, JSC employs alternative management techniques such as relocating honeybee swarms to minimize pesticide use wherever possible. Additionally, JSC continues to raise awareness about the importance of their prairies and pollinators.
Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)
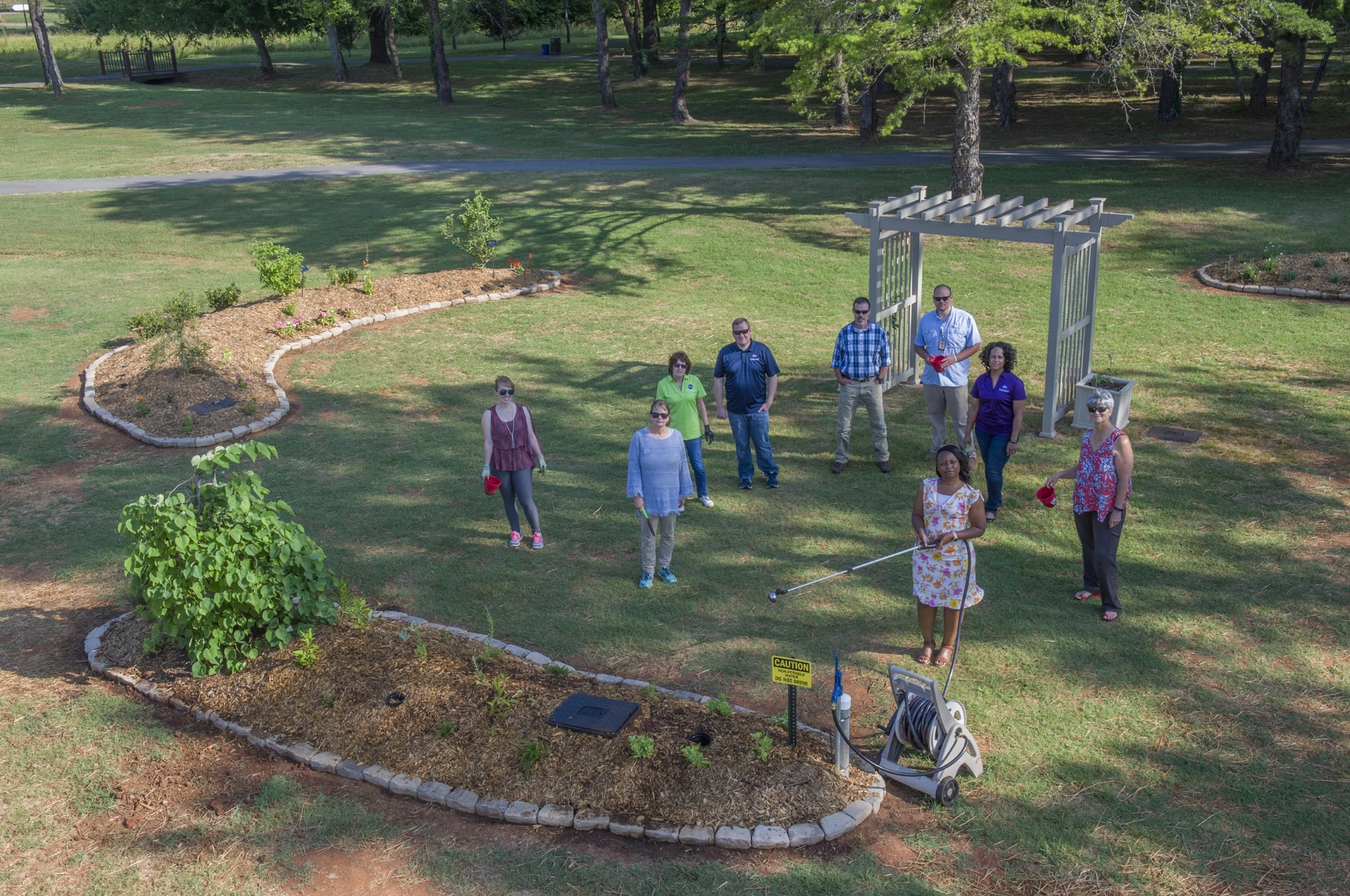
Several groups work to enhance pollinator habitat and the understanding of pollinator species around the center. Two pollinator focused project have been completed at MSFC: the pollinator garden and the pollinator meadow. The pollinator garden was constructed by the MSFC Green Team in collaboration with the Northern Alabama Master Gardeners. Garden consists of five beds located just behind the MSFC Wellness Center on the south end of the Walking Trail and is certified with the North American Butterfly Association and a registered Monarch Waystation. In the fall of 2023, maintenance of the pollinator garden was handed over to the Pollinator Club. In the spring of 2023, a roughly 2-acre pollinator meadow was planted. The meadow includes a mix of native flowering plants and is mowed once each year.
In addition to the pollinator focused projects, MSFC also has a garden club, which maintains individual and club garden plots that attract pollinators to the Center. The MSFC Green Team and clubs hold regular education and outreach events to increase knowledge of pollinators, their importance, and threats to their survival.
Langley Research Center (LaRC)
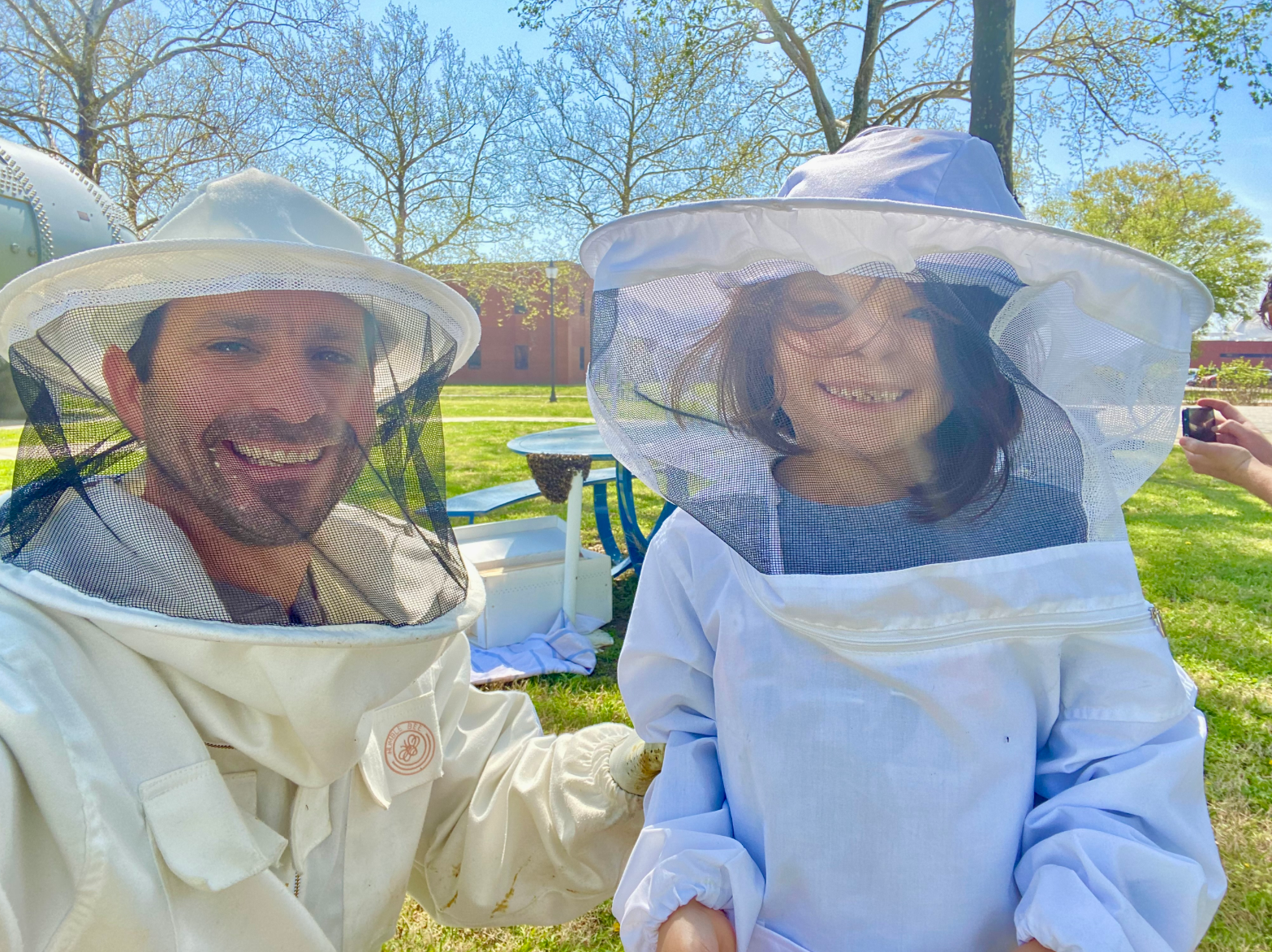
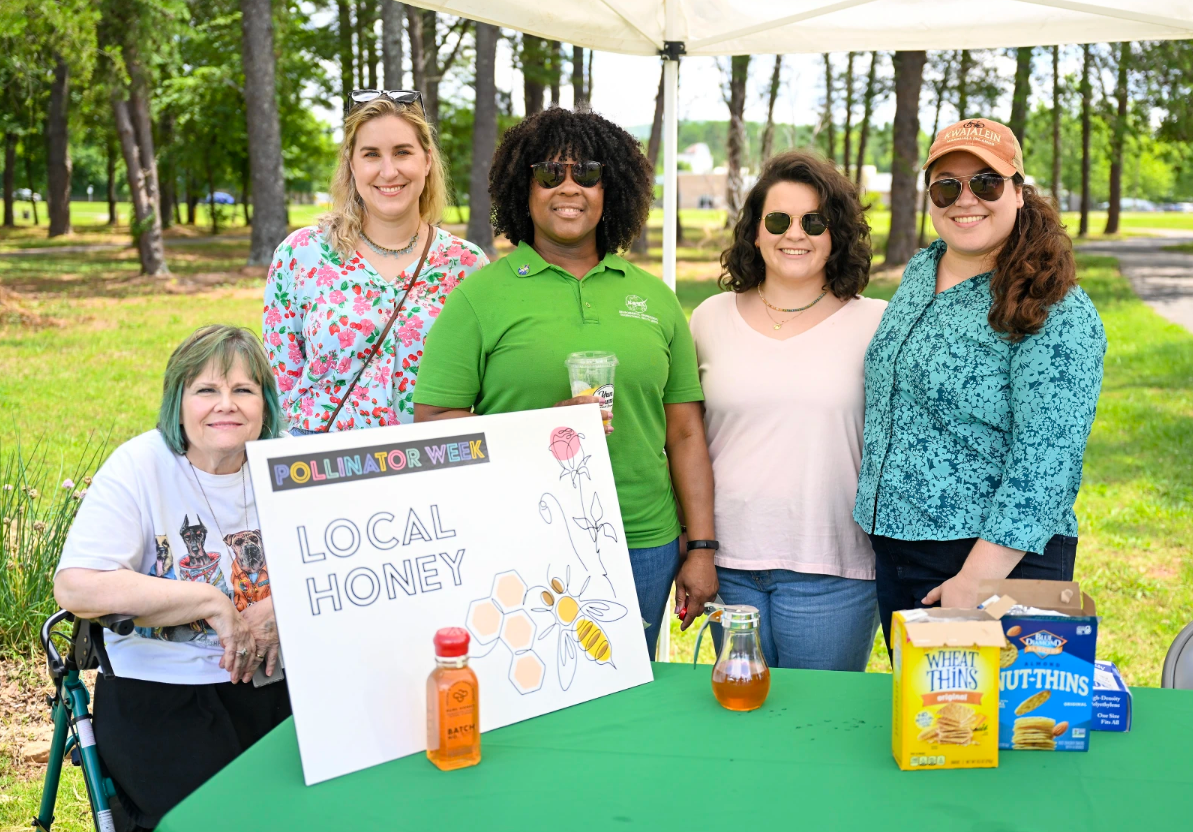
In addition to a registered Monarch Waystation, Langley Research Center (LaRC) is home to beehive colonies following two rescue missions on center. The first occurred in April of 2023, when a swarm of honeybees was discovered under a picnic table near the cafeteria. To relocate this colony, the center enlisted the help of LaRC personnel Dr. Jeremy Pinier, a member of the Colonial Beekeepers Association, along with his 6-year-old daughter Olivia, his apprentice beekeeper. The bees were relocated to a habitat near the community garden, which hosts 16 year-round and 24 seasonal plots rented by active members of the LaRC Garden Club. The second hive was relocated in April 2024 from a service vehicle’s truck bed. The bees are flourishing and have earned the nickname “The Artemis Colony,” coined by Dr. Pinier. Center personnel have enjoyed the colony’s honey and remain committed to nurturing its bee population and preserving the garden for the future.
White Sands Test Facility (WSTF)
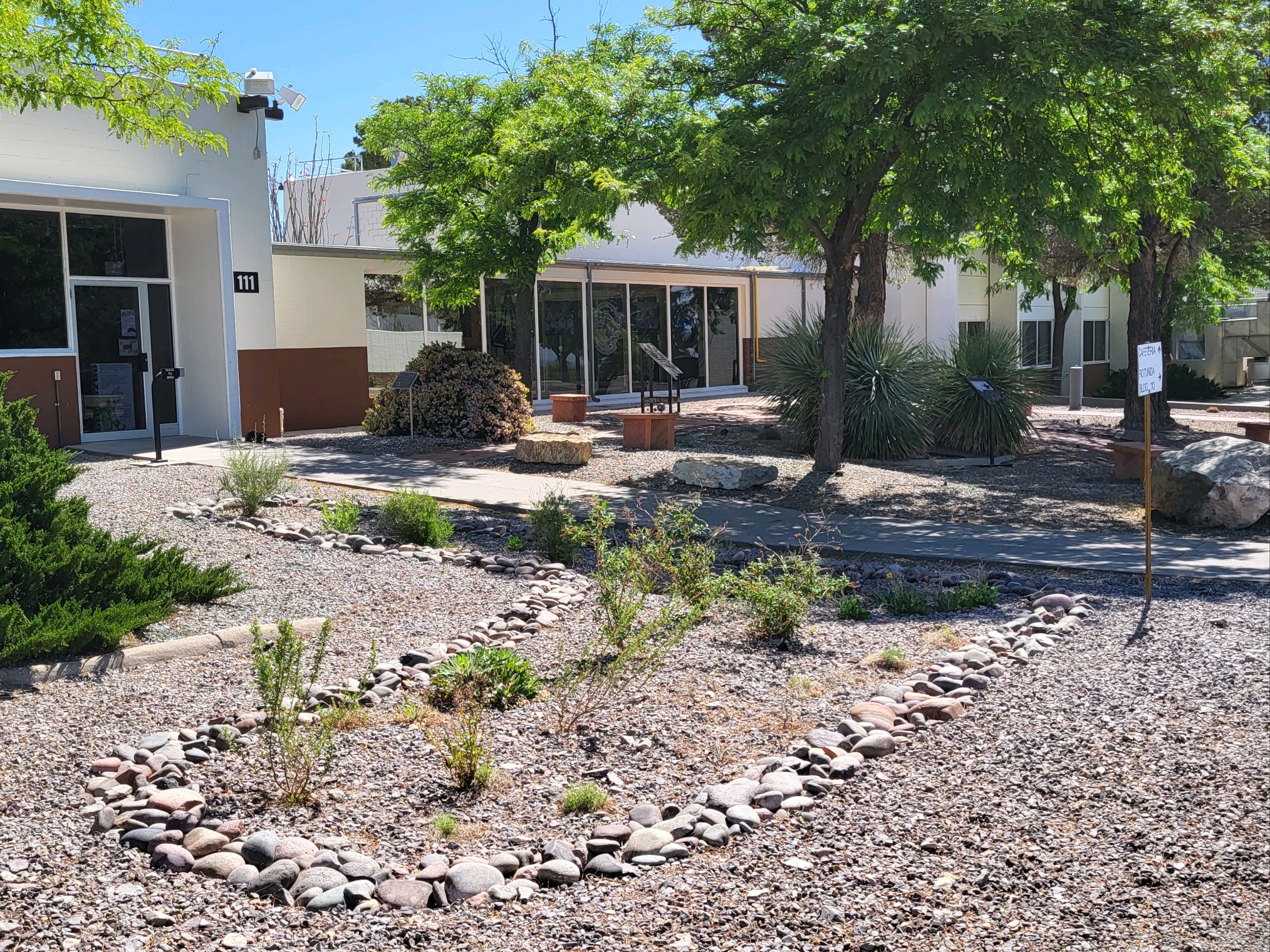
To enhance New Mexico’s natural beauty, four pollinator gardens were planted in 2022 on the south sides of B100 and B101 and at the main entrances to the cafeteria and rotunda. They were created to mitigate some function of the natural landscape that was offset to build the Center. These gardens also help to educate visitors on the beauty and names of surrounding desert flora and provide a peaceful place to sit and view the garden, the Jornada del Muerto, and mountains in the distance.
The native plants are drought resistant, hardy, and attract bees, butterflies, hummingbirds, and other pollinators. There are plans to install a trail camera at one of the garden sites to identify some of the visiting pollinator species. The Center also wants to register the gardens as wildlife habitats through the National Wildlife Federation and Monarch Waystations.
Conclusion
In addition to the great work already underway across NASA Centers, other sites such as Kennedy Space Center are developing plans for their own programs supporting local pollinators. Keep up to date with agency-wide education efforts and new developments in Pollinator Programs at EMD’s NRM Program EMD’s NRM Program Website.