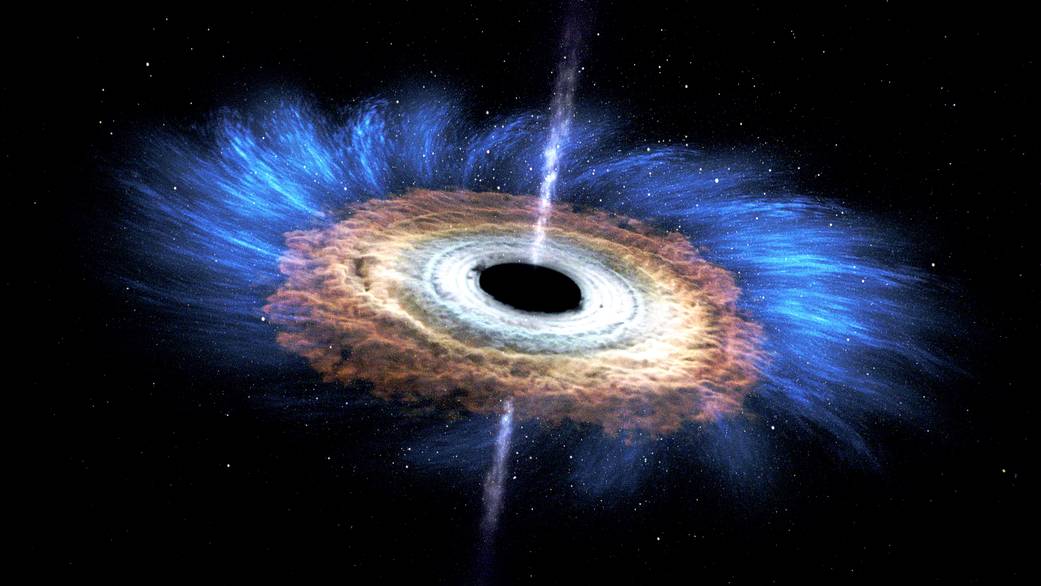
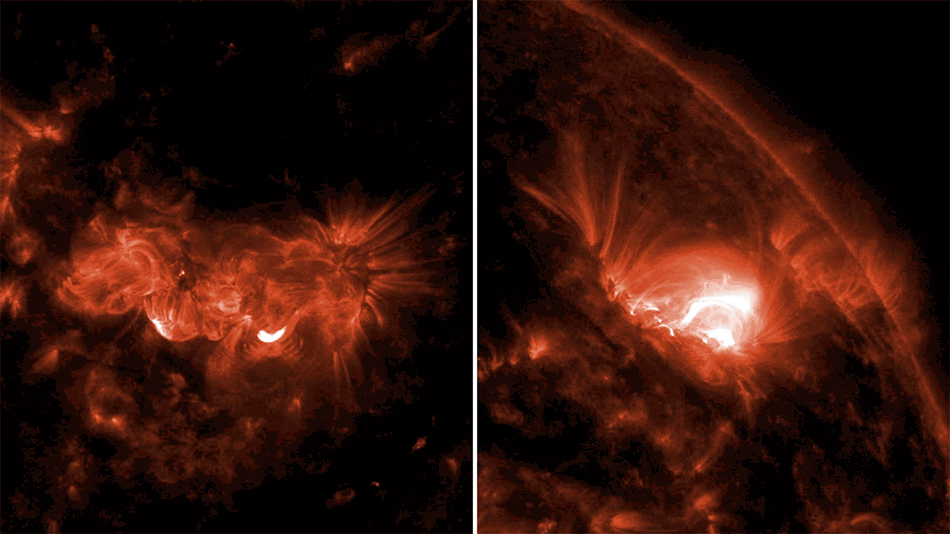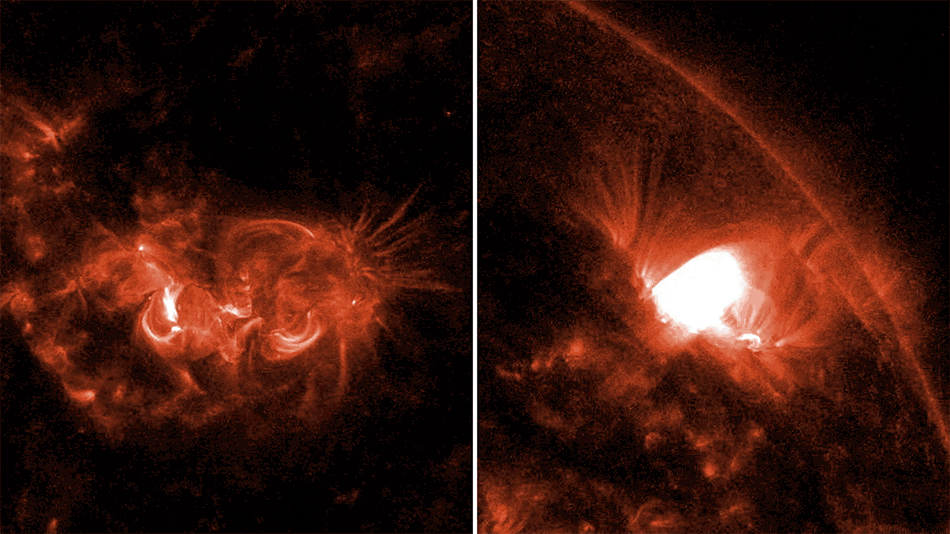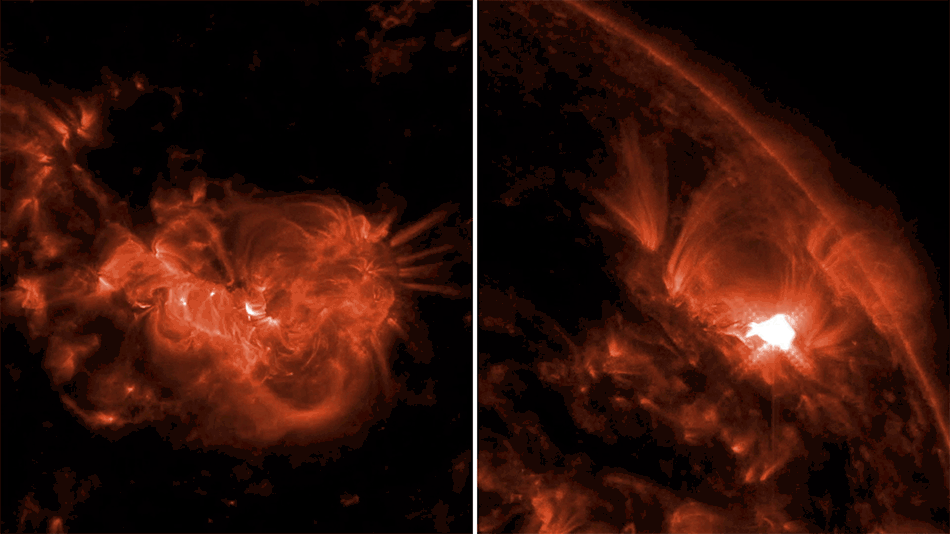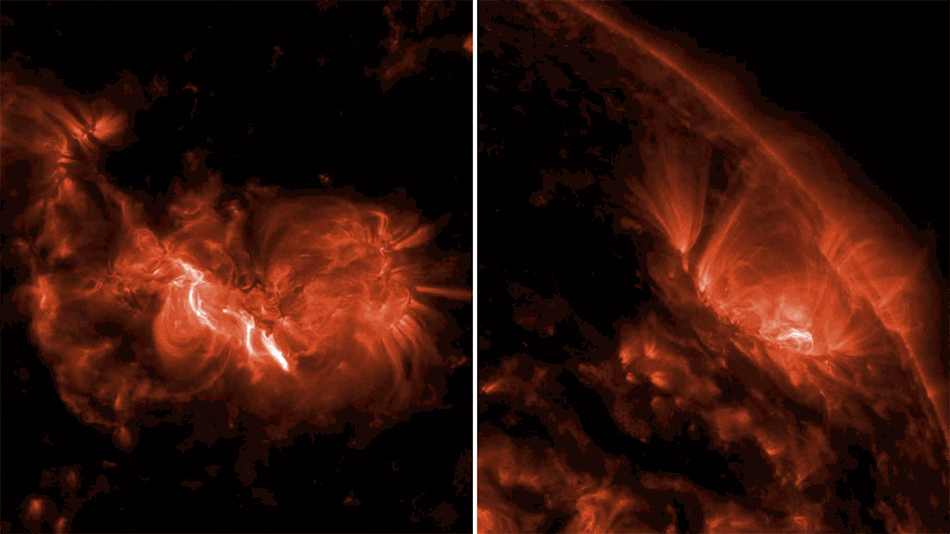
This artist’s rendering shows the tidal disruption event named ASASSN-14li, where a star wandering too close to a 3-million-solar-mass black hole was torn apart. The debris gathered into an accretion disk around the black hole. Data from NASA’s Swift satellite show that the initial formation of the disk was shaped by interactions among incoming and outgoing streams of tidal debris.
More: NASA’s Swift Mission Maps a Star’s ‘Death Spiral’ into a Black Hole
Image Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center