NASA’s John H. Glenn Research Center comprises two locations–Lewis Field in Cleveland, Ohio and the Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility 60 miles west in Sandusky. The two sites were independently established in 1941 and formally merged in 1963. The names of both locations have changed multiple times over the years.
Lewis Field
The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) established the center in 1941 as the Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory (AERL). During the war years, the laboratory focused its research on aircraft engines, both the traditional piston engines and the emerging turbojets.
In 1947 the NACA updated the site name to the Flight Propulsion Research Laboratory as research expanded to both aircraft and missile propulsion. The facility was rededicated as the Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory in September 1948 to honor the NACA’s former Director of Aeronautical Research, George W. Lewis.
On October 1, 1958, the NACA was incorporated into the new NASA space agency, and the lab was renamed the Lewis Research Center. Lewis was one of three research centers among NASA’s ten sites.
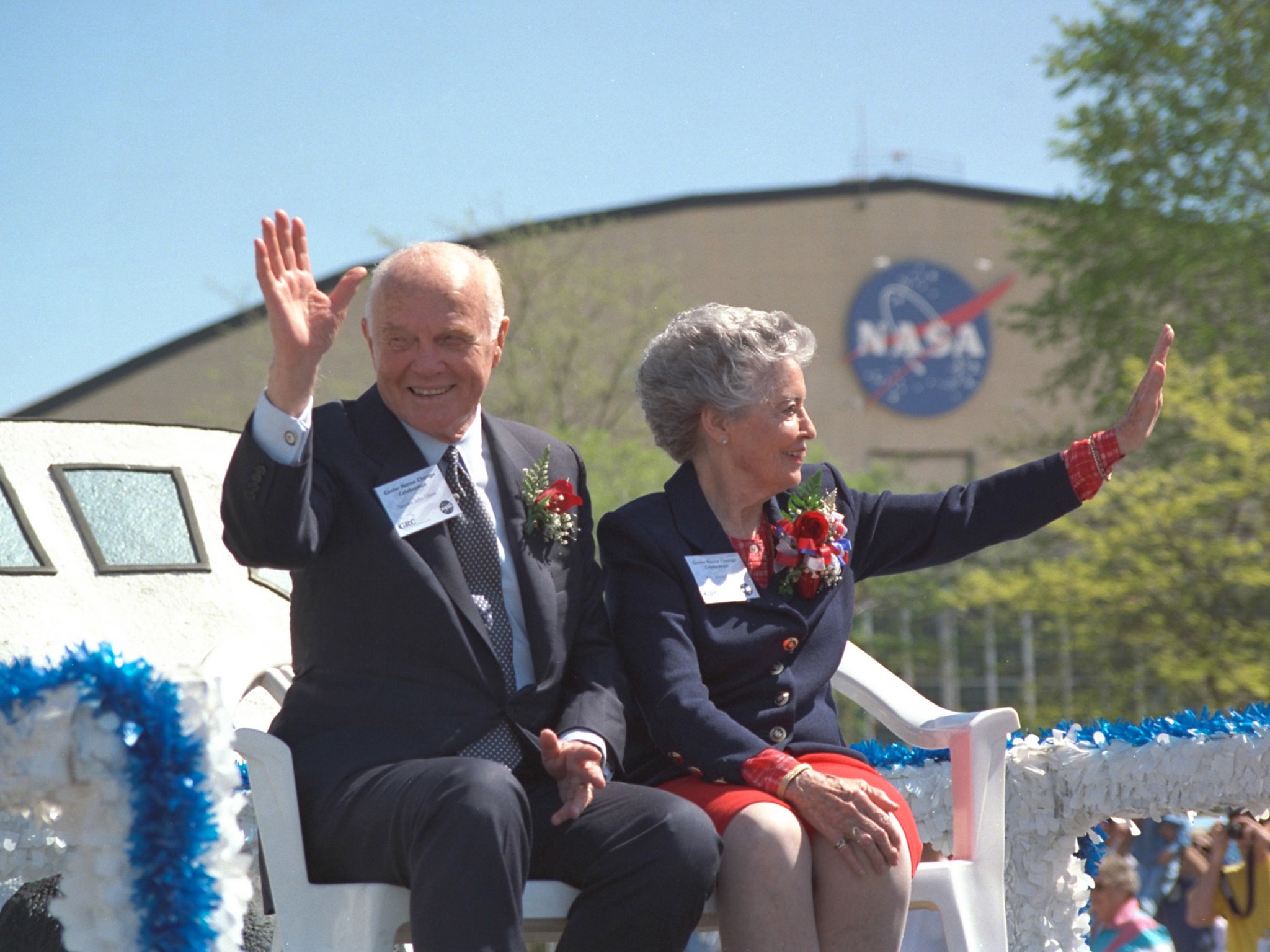
In March 1999 the center was renamed NASA’s John H. Glenn Research Center to honor astronaut and Senator John Glenn, who had recently retired from Congress and returned to space on the shuttle. For the first time, the Cleveland campus was referred to by a different name—Lewis Field–than the center itself.
Armstrong Test Facility
In early 1941, the War Department established the 9,000-acre Plum Brook Ordnance Works (PBOW) near Sandusky, Ohio to manufacture munitions for World War II. The facility was named for one of several streams (the Plum Brook) that run through the property. The PBOW ceased operations in September 1945.
In 1946, 2,800 acres were transferred to the Ravenna Arsenal and renamed the Plum Brook Depot. The remainder of the PBOW property remained vacant as custody shifted from the War Assets Administration (1946) to the General Services Administration (1949) and to the Ravenna Arsenal (1954).
In July 1956, the NACA leased 500 acres at the PBOW to build a test reactor facility. Three years later, NASA leased another 2,725 acres to construct its Rocket Systems Area test sites. NASA initially referred to these remote sites as the Plum Brook Facilities. The name was officially changed to Plum Brook Station in 1962. In March 1963, the military officially transferred both the PBOW and Depot property to NASA.
In 2020, Congress passed legislation changing Plum Brook Station to the Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility.
Glenn Timeline:
1941 – 1947 Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory
1947 – 1948 Flight Propulsion Research Laboratory
1948 – 1958 Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory
1958 – 1999 Lewis Research Center
1999 – present John H. Glenn Research Center
Armstrong Timeline:
1941 – 1963 Plum Brook Ordnance Works
1946 – 1963 Plum Brook Depot
1958 – 1962 Plum Brook Facilities
1963 – 2020 Plum Brook Station
2020 – present Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility
Robert S. Arrighi
NASA’s Glenn Research Center