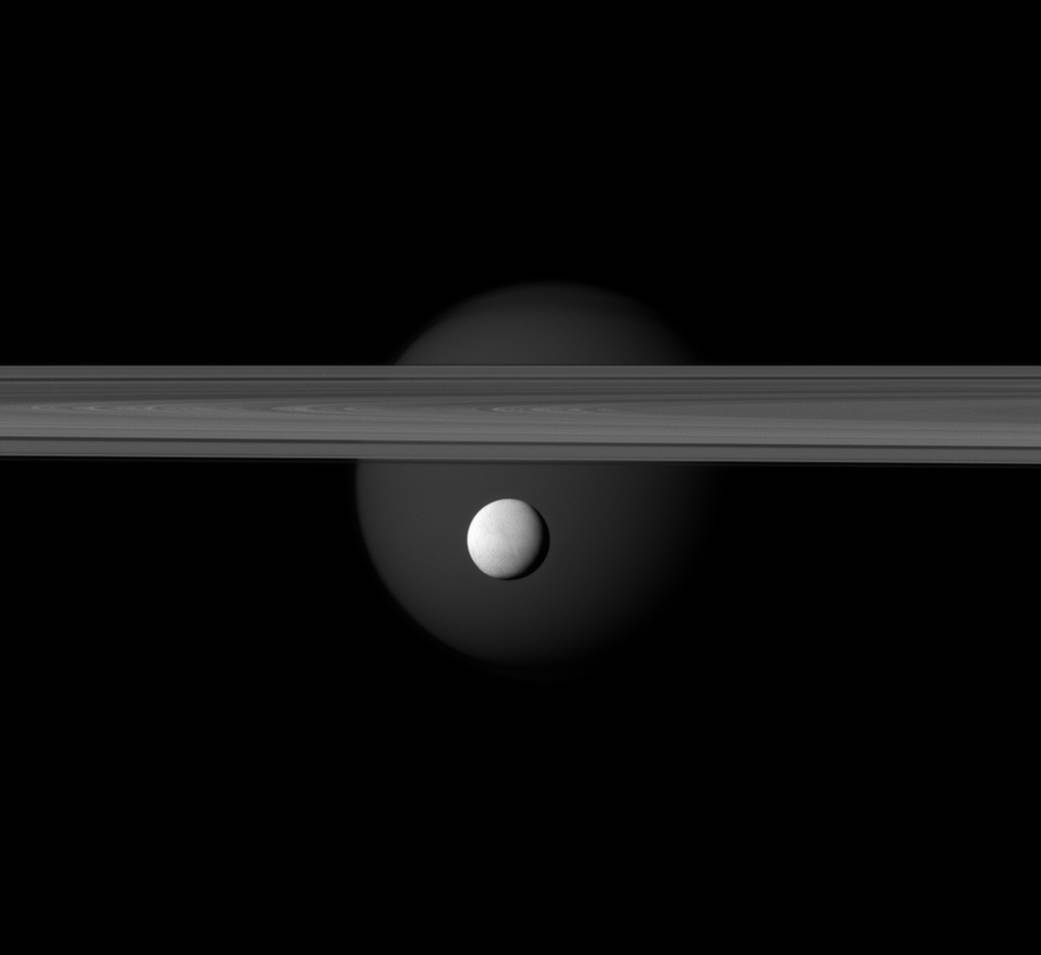
A brightly reflective Enceladus appears before Saturn’s rings, while the planet’s larger moon Titan looms in the distance.
Jets of water ice and vapor emanating from the south pole of Enceladus, which hint at a subsurface sea rich in organics, and liquid hydrocarbons ponding on the surface of Titan make these two of the most fascinating moons in the Saturnian system.
Enceladus (313 miles, or 504 kilometers across) is in the center of the image. Titan (3,200 miles, or 5,150 kilometers across) glows faintly in the background beyond the rings. This view looks toward the anti-Saturn side of Enceladus and the Saturn-facing side of Titan. The northern, sunlit side of the rings is seen from just above the ringplane.
The image was taken in visible green light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on March 12, 2012. The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 600,000 miles (1 million kilometers) from Enceladus and at a Sun-Enceladus-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 36 degrees. Image scale is 4 miles (6 kilometers) per pixel on Enceladus.
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging operations center is based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colo.Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute