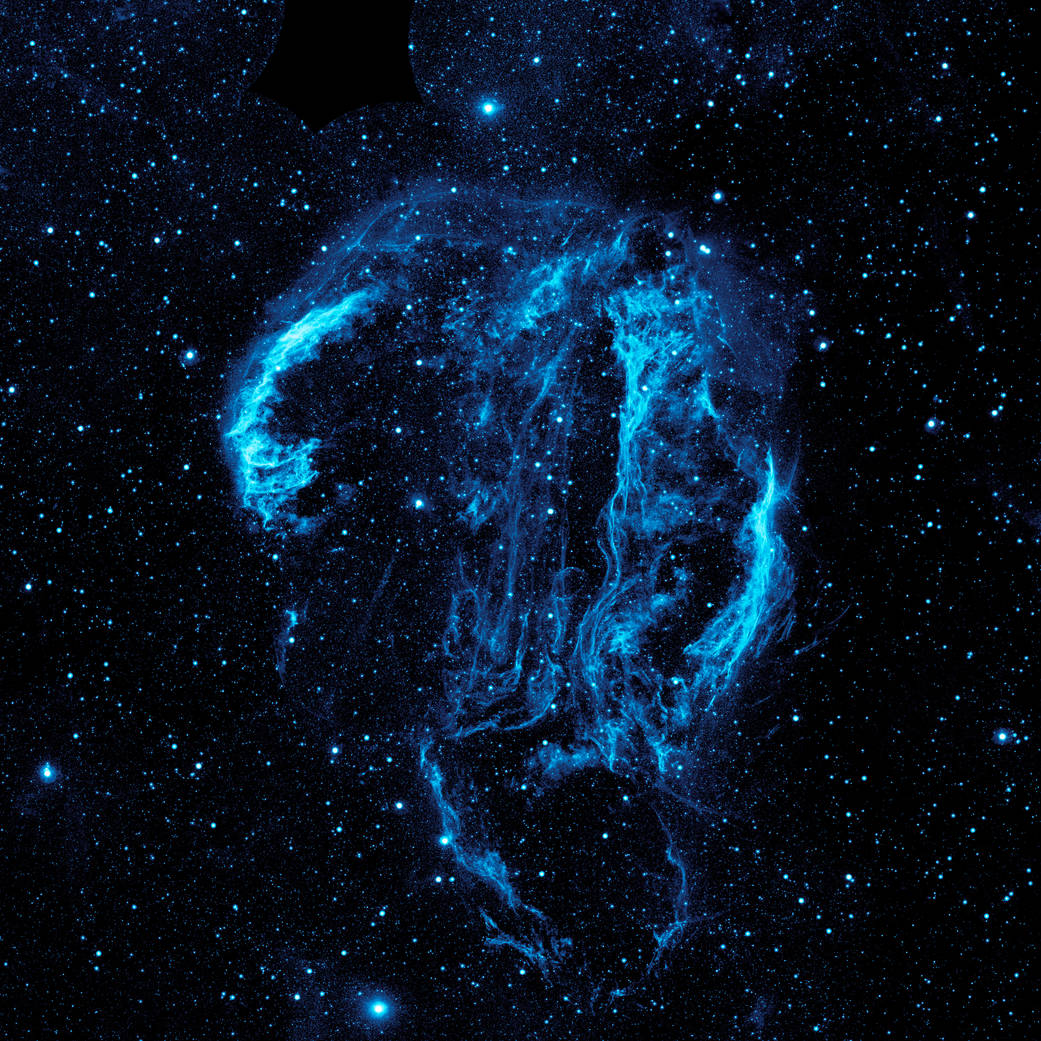
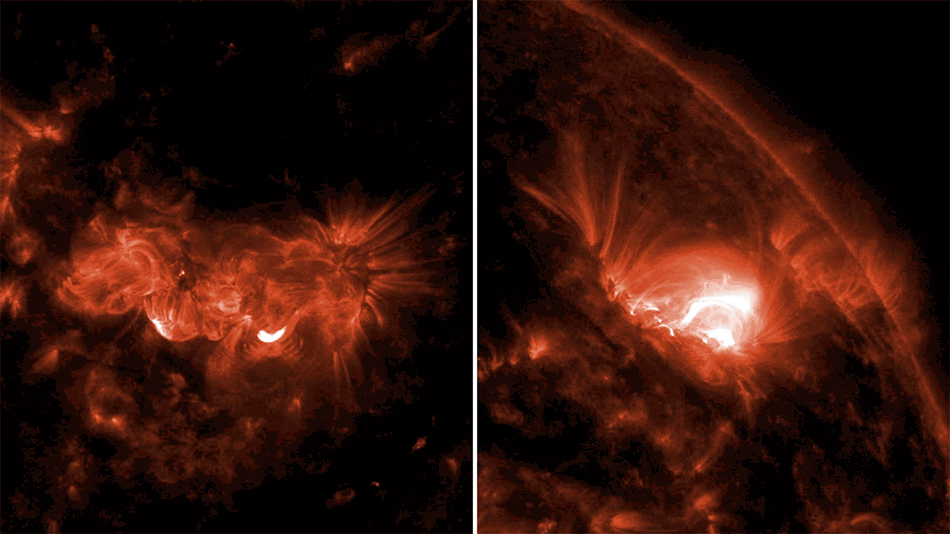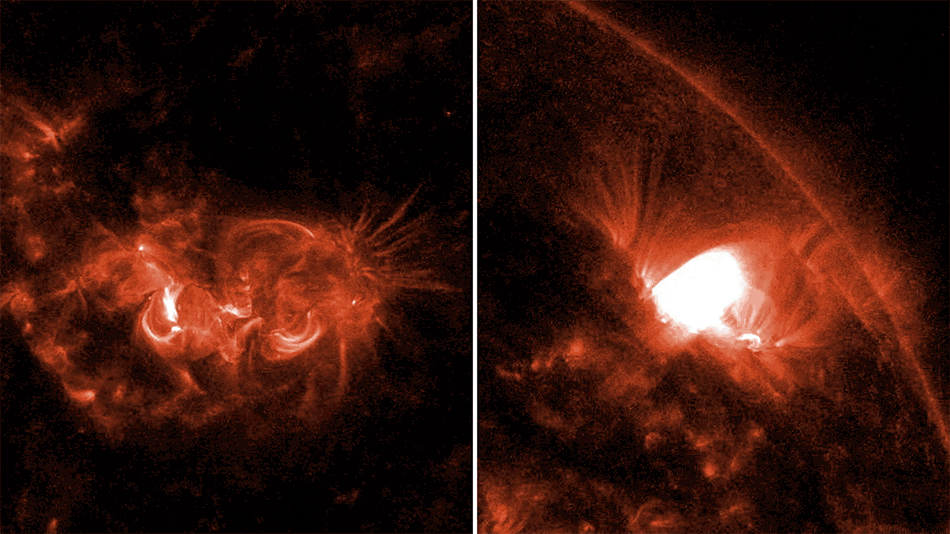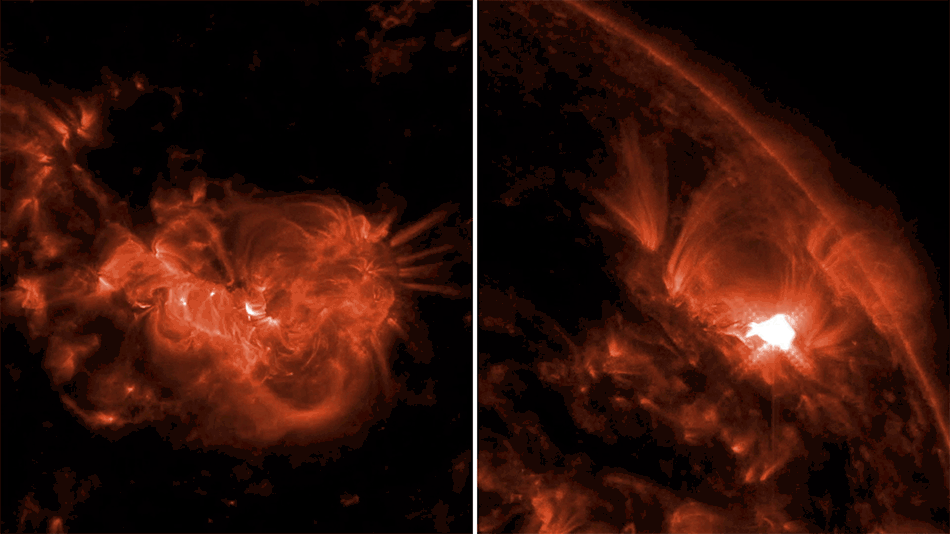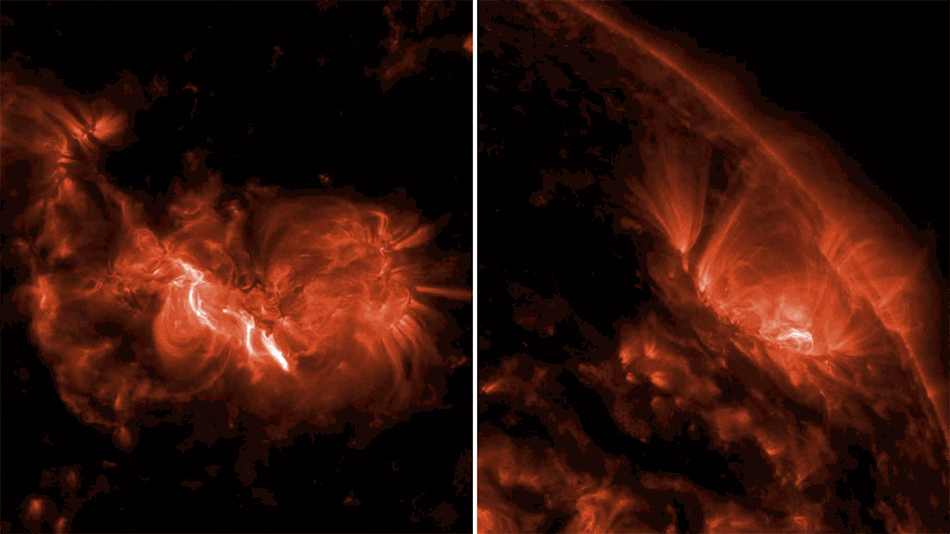
Wispy tendrils of hot dust and gas glow brightly in this ultraviolet image of the Cygnus Loop nebula, taken by NASA’s Galaxy Evolution Explorer. The nebula lies about 1,500 light-years away, and is a supernova remnant, left over from a massive stellar explosion that occurred between 5,000 to 8,000 years ago. The Cygnus Loop extends over three times the size of the full moon in the night sky, and is tucked next to one of the “swan’s wings” in the constellation of Cygnus.
The filaments of gas and dust visible here in ultraviolet light were heated by the shockwave from the supernova, which is still spreading outward from the original explosion. The original supernova would have been bright enough to be seen clearly from Earth with the naked eye.Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech