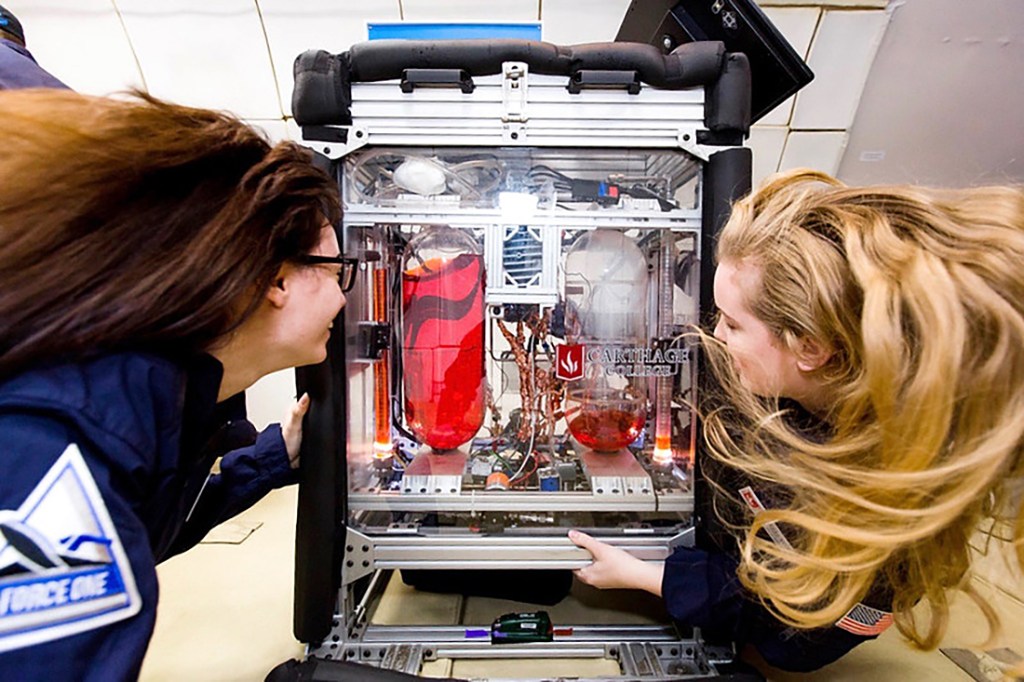
Parabolic Flight
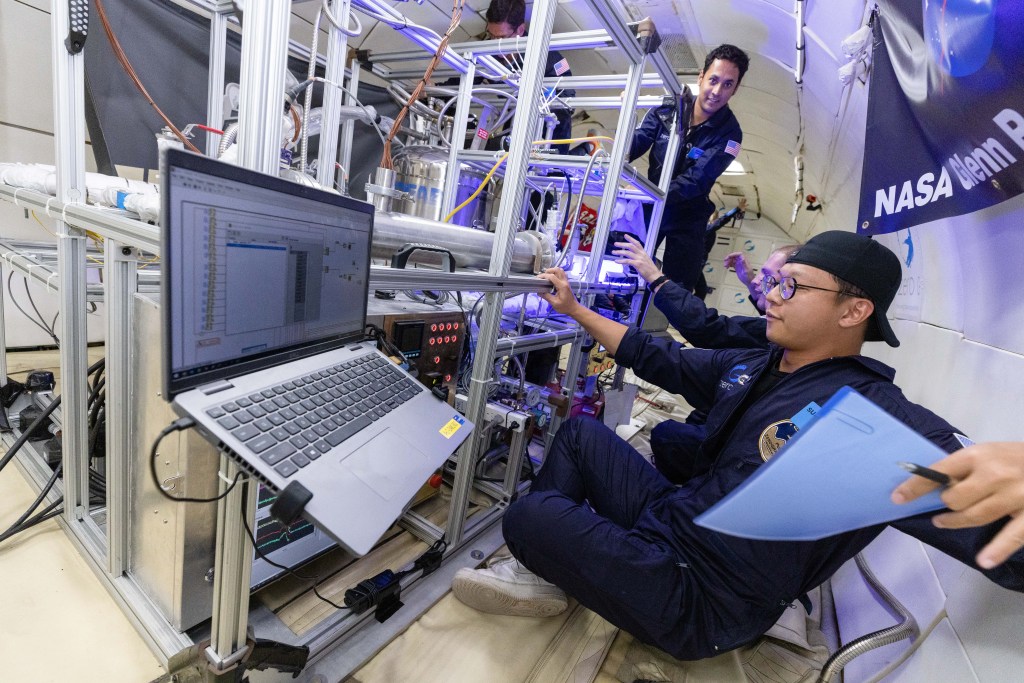
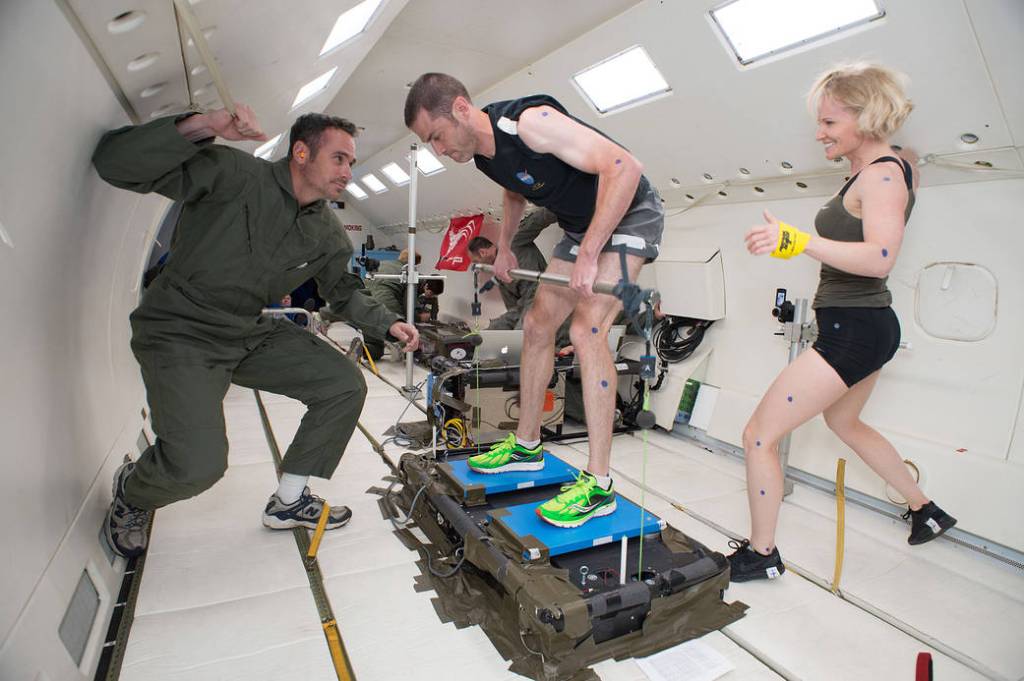
From a stabilized level-flight attitude at 20,000 feet, the aircraft increases attitude. During this phase, the weight is 1.8 times greater than normal weight for 24 seconds. The crew then performs a maneuver called “injection”: the aircraft trajectory is piloted to follow a kind of parabola and the power thrust is reduced.
Mission Overview
Location:
Environment: Simulated microgravity
Hazards Tested: Gravity
Description: From a stabilized level-flight attitude at 20,000 feet, the aircraft increases attitude. During this phase, the weight is 1.8 times greater than normal weight for 24 seconds. The crew then performs a maneuver called “injection”: the aircraft trajectory is piloted to follow a kind of parabola and the power thrust is reduced. The vertical load factor goes from 1.8g to zero gravity for about 22 seconds. The first pilot adjusts the control stick tilt to maintain the vertical load factor at zero, while the second pilot maintains the roll angle at zero, and the mechanic adjusts the thrust of the engines to cancel the longitudinal load factor. An exit phase at 1.8 g, symmetrical with the entry phase, is then performed on the descending part of the parabola to return the aircraft to a stabilized altitude level within about 20 seconds.
Research: Parabolic flights are a gateway to weightlessness. They are dedicated to scientific experiments and to space equipment technological testing.
Learn More: http://www.novespace.fr/en,home.html