The conclusion of the space shuttle program brought to a close an era that opened in the high desert of Southern California almost a half century earlier when the first of a series of low lift-over-drag wingless lifting bodies made its first free flight.
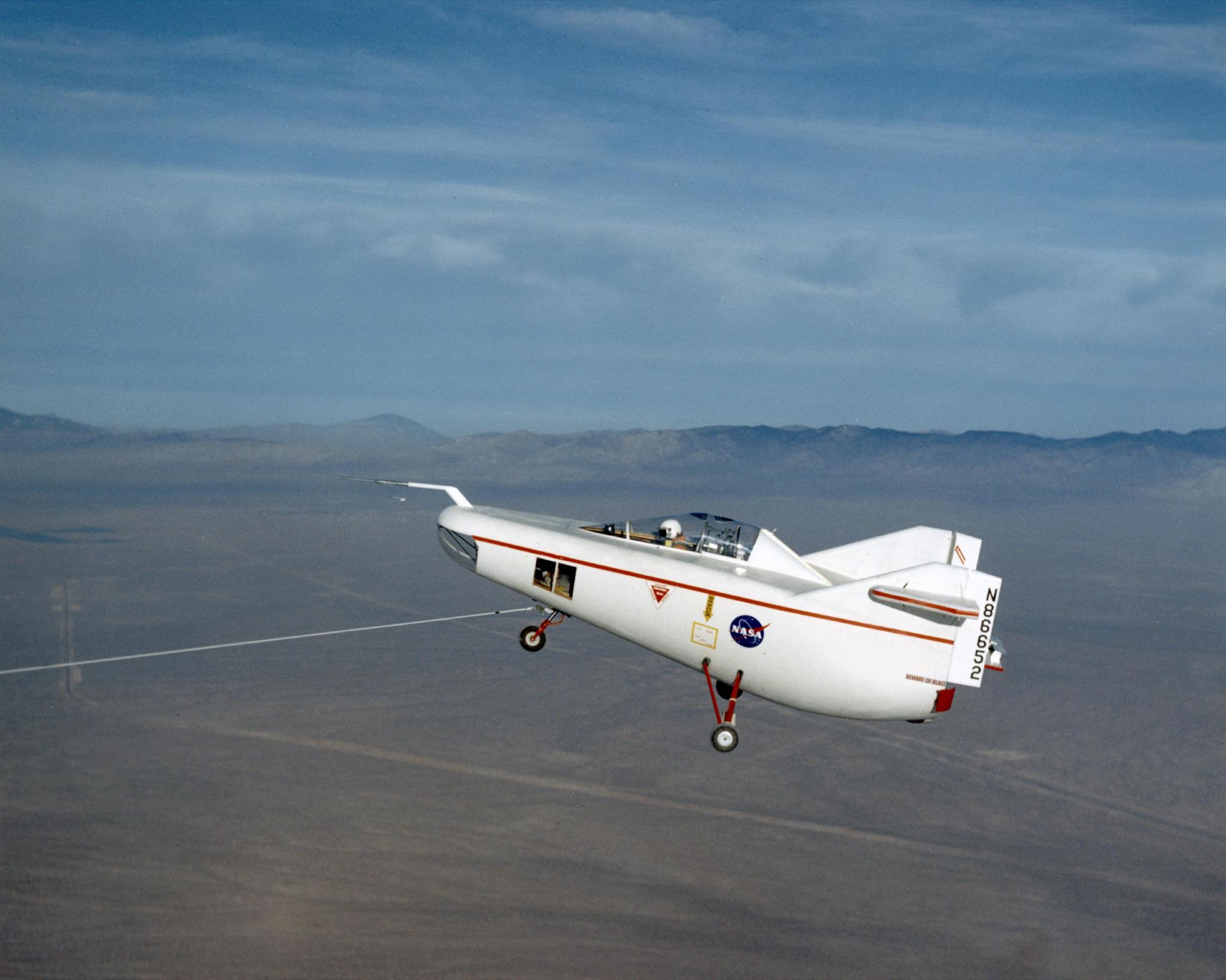
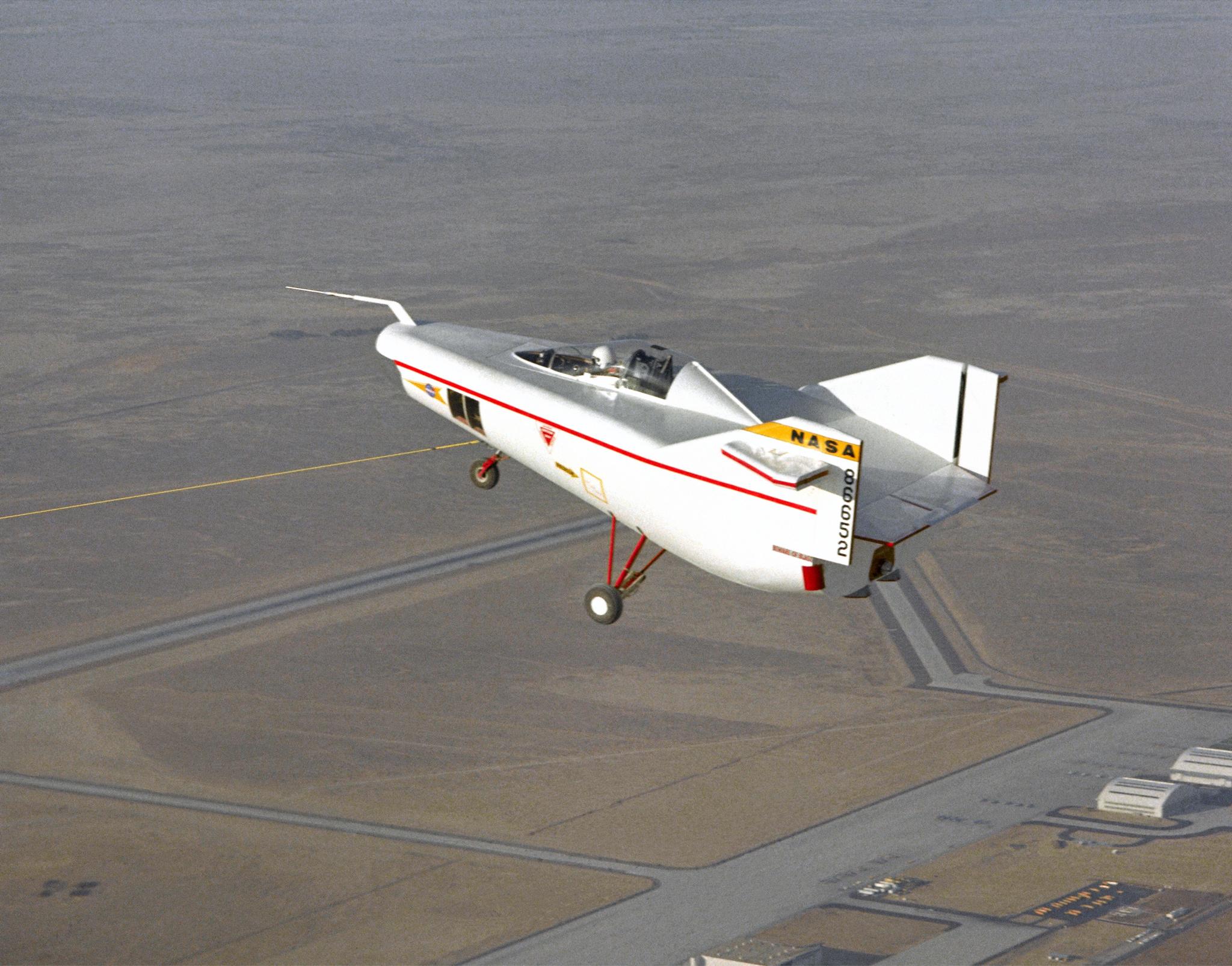
The vehicle that began the era – the M2-F1 – was an unlikely forerunner to the shuttle. The world’s first manned lifting body, the M2-F1 was made of wood, had an internal framework of steel tubes, looked like a bathtub sitting on a tricycle, and had no wings.
Conceived by NASA engineers at the Ames Research Center near San Jose, Calif., the lifting body was intended as an alternative to a capsule spacecraft, which returned to Earth dangling under a parachute. A lifting body was not a conventional winged aircraft but rather used air flowing over its fuselage to generate lift. This design allowed it to re-enter the atmosphere and land on a runway like a conventional airplane.
The idea of an aircraft without wings met with skepticism among engineers. R. Dale Reed of the NASA Flight Research Center – now the Dryden Flight Research Center – was the exception. Reed was excited about the concept and began testing a series of small balsa wood and tissue-paper lifting bodies, which he flew down the hallways of the center’s main office building and off its roof.
Reed was successful in raising interest in the concept, and center director Paul Bikle approved discretionary funding to construct a “homebuilt” lifting body, the M2-F1 (for Manned 2, Flight 1).
Noted sailplane builder Gus Briegleb, who built high-performance wood sailplanes at his facility at the El Mirage Airport some 40 miles from the center, was engaged to build the fuselage. The internal framework was built in a curtained-off section of a hangar with a sign reading “Wright’s Bicycle Shop.” Using volunteer help from center personnel, Reed kept the cost of building the M2-F1 to about $30,000.
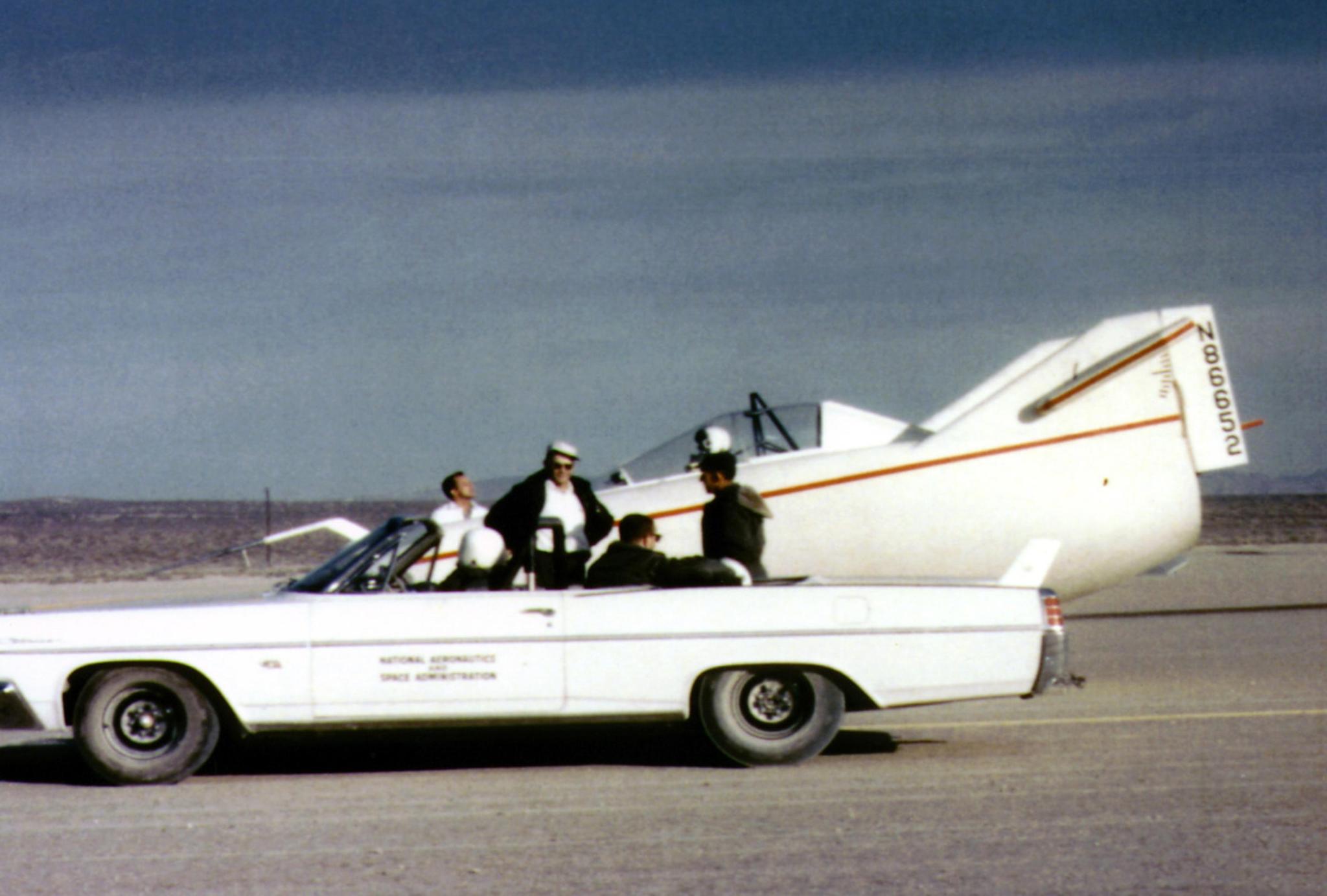
Because the M2-F1 was unpowered, a tow vehicle was required. Walter “Whitey” Whiteside, a hot-rod enthusiast who worked at the center, was sent to purchase a new 1963 Pontiac convertible. Following modification at two race shops, the car was capable of reaching 110 miles per hour with the M2-F1 in tow.
The first car tow attempts were made on March 1, 1963, with NASA research pilot Milton O. “Milt” Thompson in the cockpit. The M2-F1 vehicle bounced back and forth on its main landing gear, and was unable to lift off the lakebed surface. After the poor results, the M2-F1 was taken to the Ames Research Center for wind tunnel testing. The vehicle’s control system was modified based on the data acquired during those tests.
The second attempt to fly came on April 5, 1963. Thompson was able to lift off and remain airborne for longer periods of time while the tow car roared across the lakebed. After several flights, he was able to remain aloft for the entire four miles of the run. During the spring and summer, Thompson made more car-towed flights to higher speeds and altitudes.
The first M2-F1 free flight came on Aug. 16, 1963. A C-47 towed the M2-F1 to an altitude of about 5,200 feet above the lakebed. Thompson released the towline and began a steep descent. The flight lasted under two minutes, with an average descent rate of 4,000 feet per minute. The M2-F1 handled well during the brief flight.
Thompson made several more flights during the summer and fall. By the time the M2-F1 was retired on Aug. 18, 1966, it had made 77 air towed and about 400 car-towed flights.
By this time, the first “heavyweight” lifting body, the M2-F2, had begun flights, launched from the NB-52 mothership. The M2-F2’s design was similar to the M2-F1’s, and had similar flight characteristics during its unpowered phase. This and the subsequent manned lifting bodies, the HL-10, X-24A, M2-F3, and the X-24B, set the stage for construction of the space shuttles.
Although the lifting body concept was ultimately rejected for the shuttle design, the lifting bodies provided extensive data on the aerodynamics and controllability of a low lift-over-drag unpowered vehicle that was directly applicable to the design of the shuttles.
The M2-F1 was restored in the mid-1990s and returned to NASA Dryden in August 1997, where it remains today.