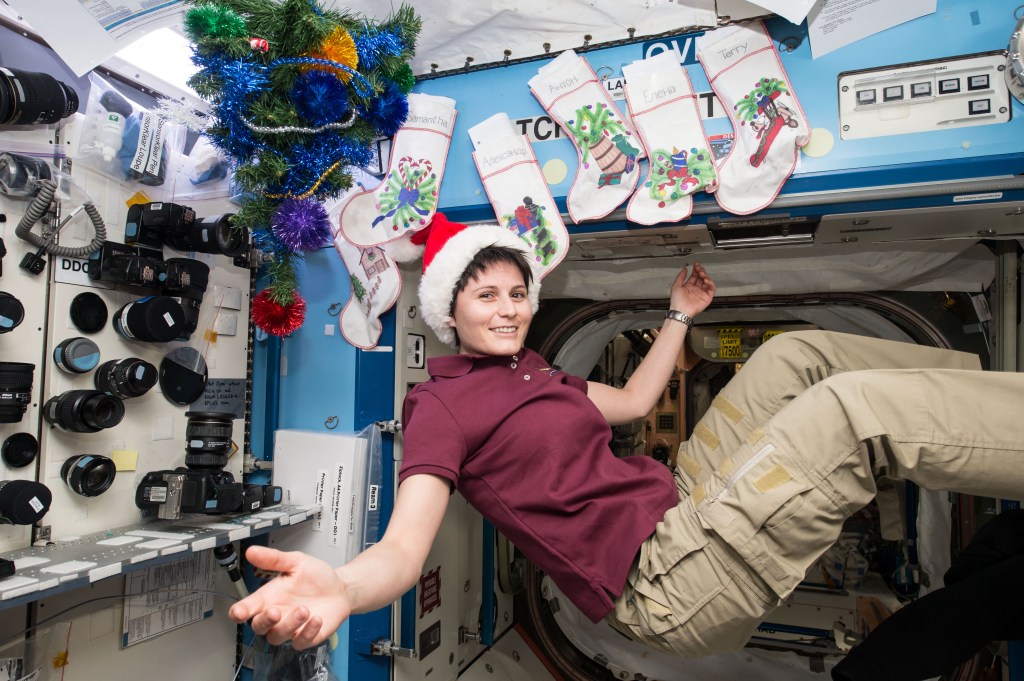
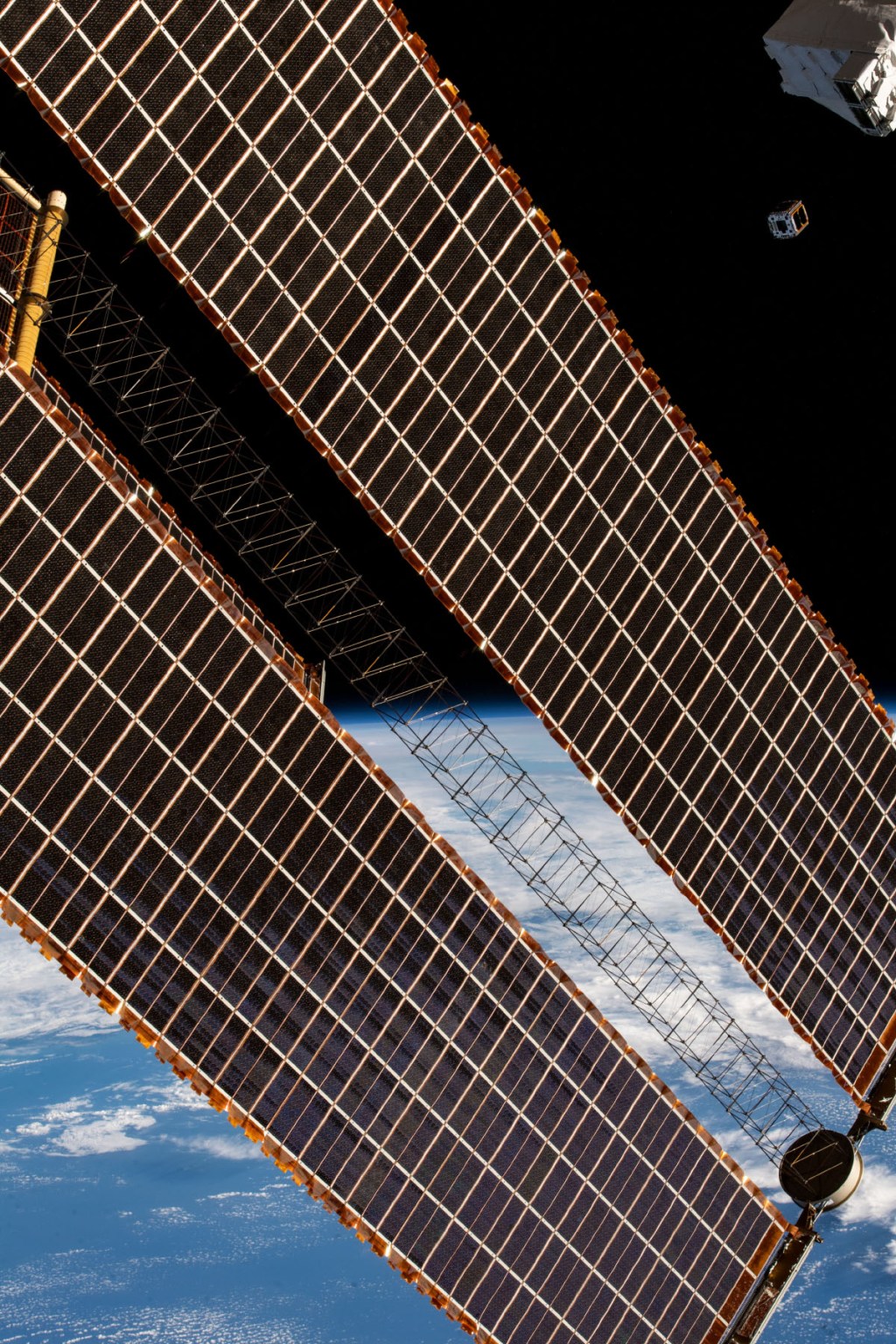
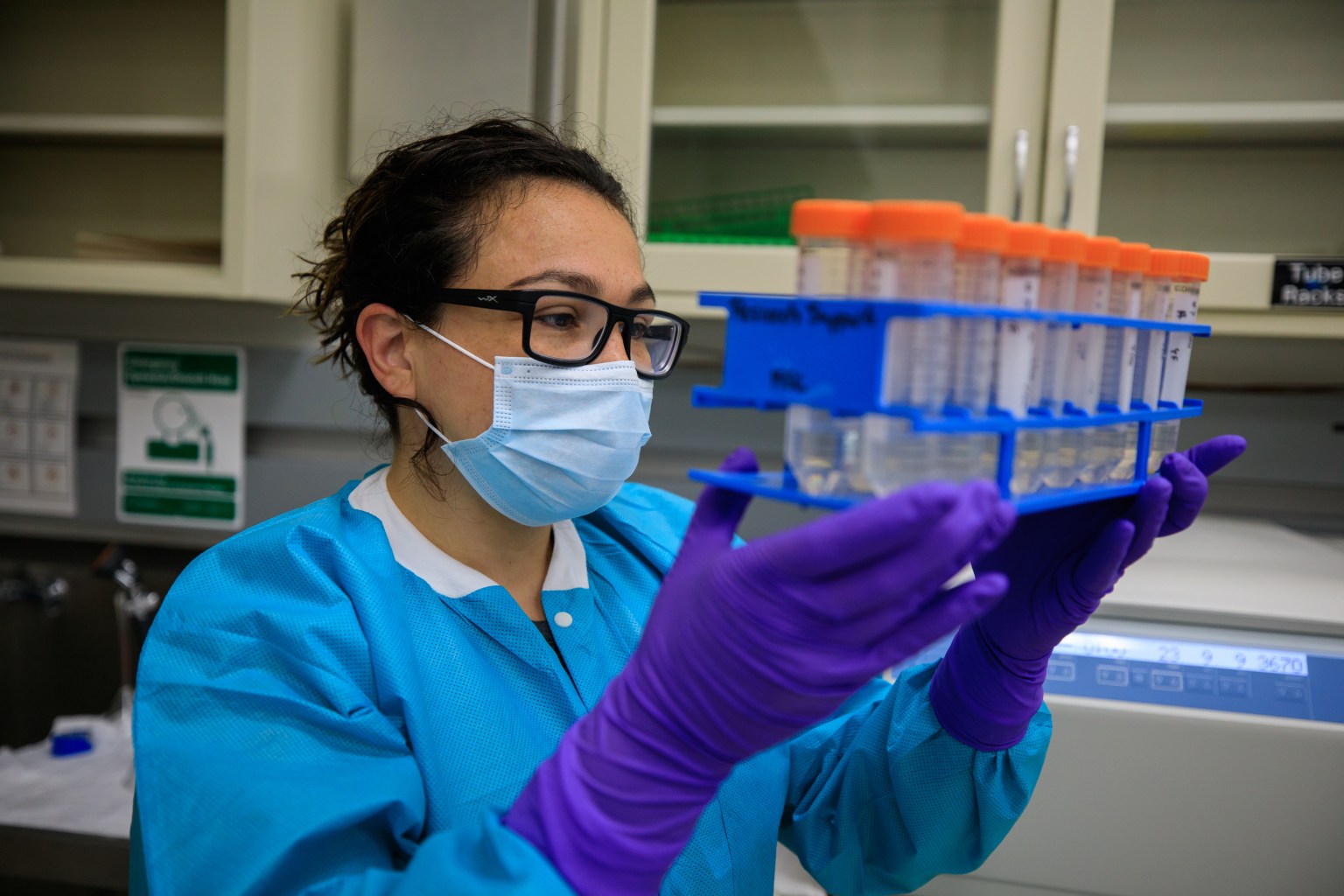
NASA’s BioSentinel Studies Solar Radiation as Earth Watches Aurora
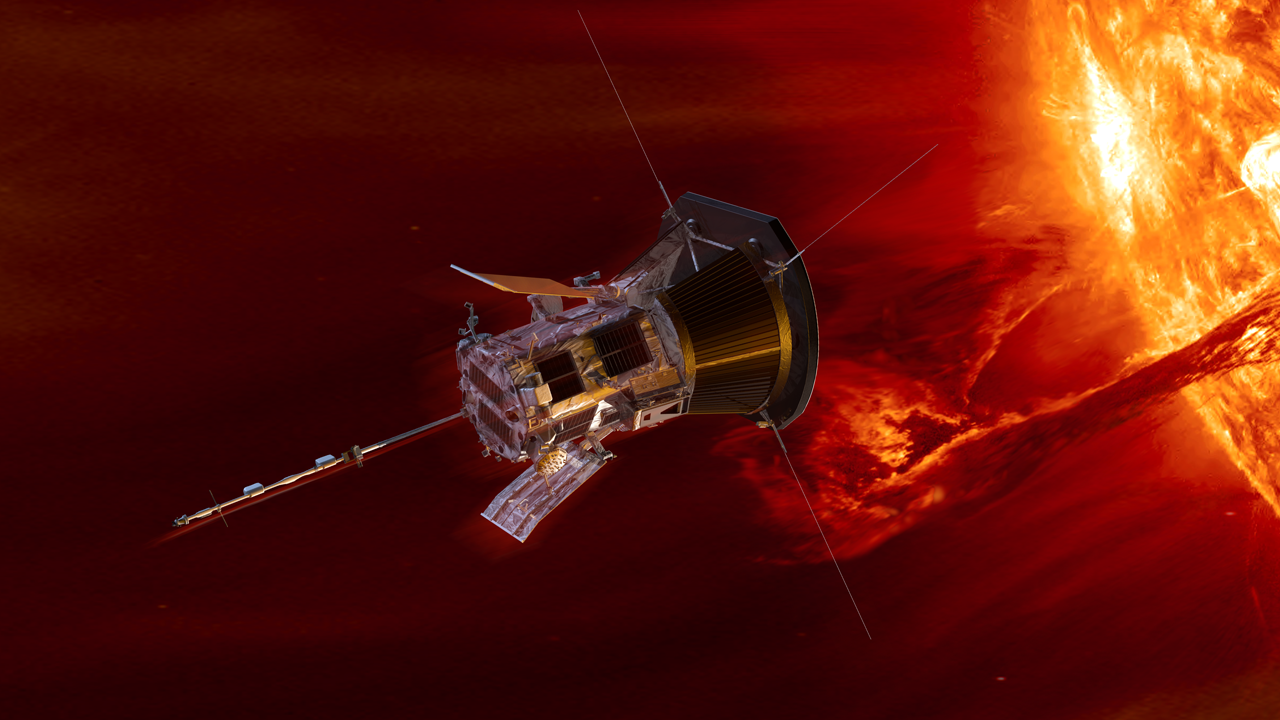
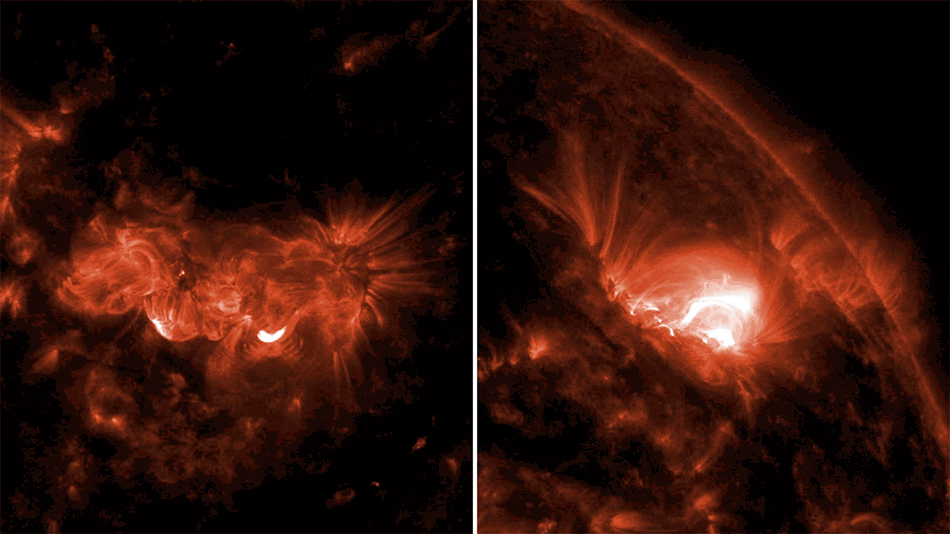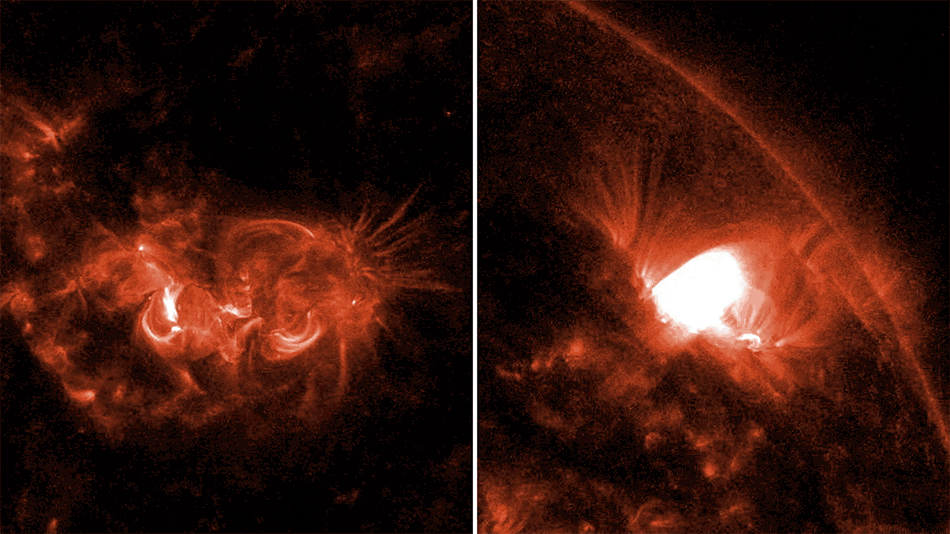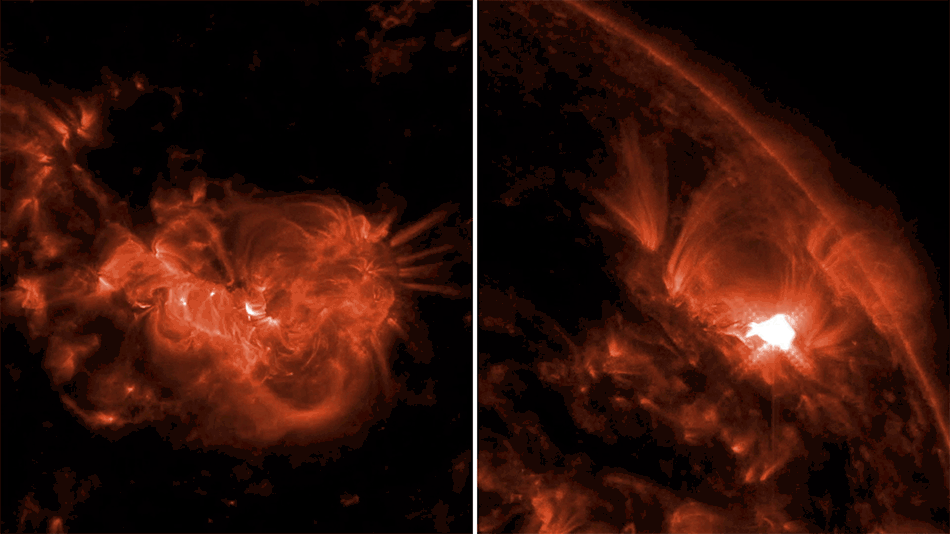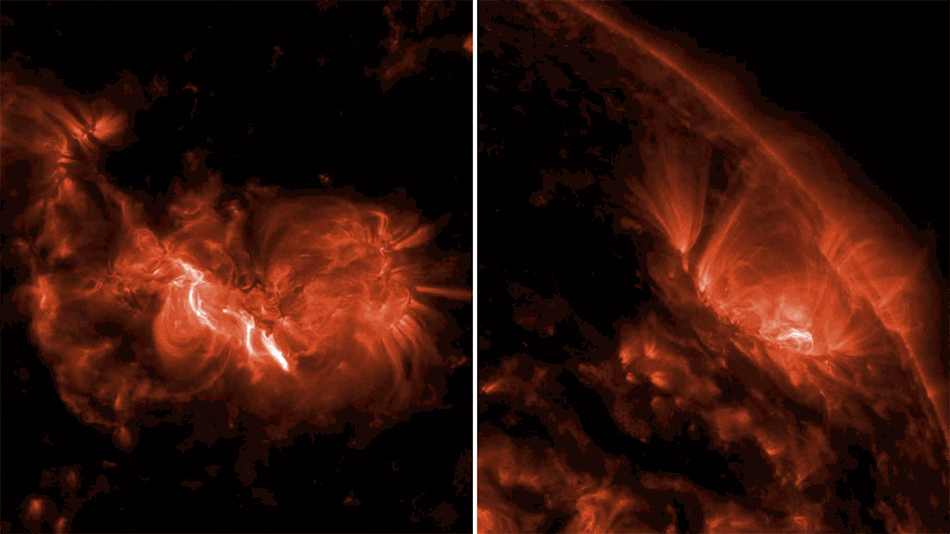
In May 2024, a geomagnetic storm hit Earth, sending auroras across the planet’s skies in a once-in-a-generation light display. These dazzling sights are possible because of the interaction of coronal mass ejections – explosions of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun – with Earth’s magnetic field, which protects us from the radiation the Sun spits out during turbulent storms.
Learn More
Repair Kit for NASA’s NICER Mission Delivered to Space Station
NASA delivered a patch kit for NICER (Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer), an X-ray telescope on the International Space Station, on the agency’s Northrop Grumman 21st commercial resupply mission. Astronauts plan to conduct a spacewalk to complete the repair in early 2025.
Learn More
NASA Seeks Input for Astrobee Free-flying Space Robots
NASA is seeking input from American companies for the operation and use of a system of free-flying robots aboard the International Space Station as the agency continues to foster scientific, educational, and technological developments in low Earth orbit for the benefit of all.
Learn More
New Earth Observation Technology to Expand Insights on Environment
With its unparalleled view of Earth, the International Space Station (ISS) is about to take its environmental monitoring to new heights. An ISS National Laboratory®-sponsored payload, engineered by Airbus U.S. Space and Defense, Inc. for the external hosting Airbus-developed platform Bartolomeo, is set to expand access to the space station’s unprecedented vantage point for research and technology demonstrations.
Learn More
Innovation in Focus: Technology Development
Enter the realm of low Earth orbit, where the International Space Station (ISS) serves as a beacon of innovation and a testament to human ingenuity. The ISS National Laboratory sponsors groundbreaking research and development (R&D) pioneering new technologies.
Learn More
Research Opportunities
The ISS provides the safest, and most efficient capability to test, improve, and qualify advancements in space flight hardware.
Find Opportunities Available