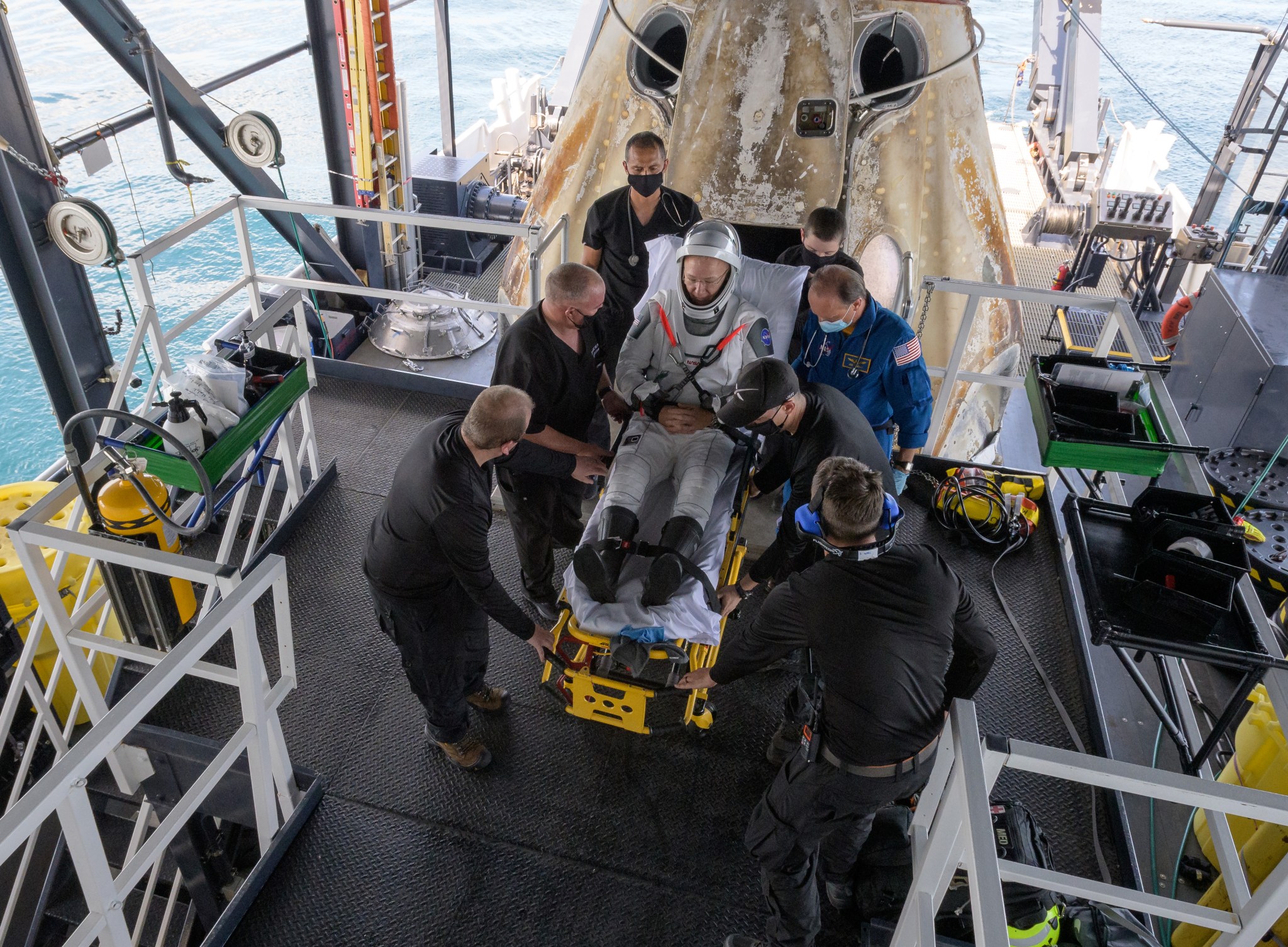
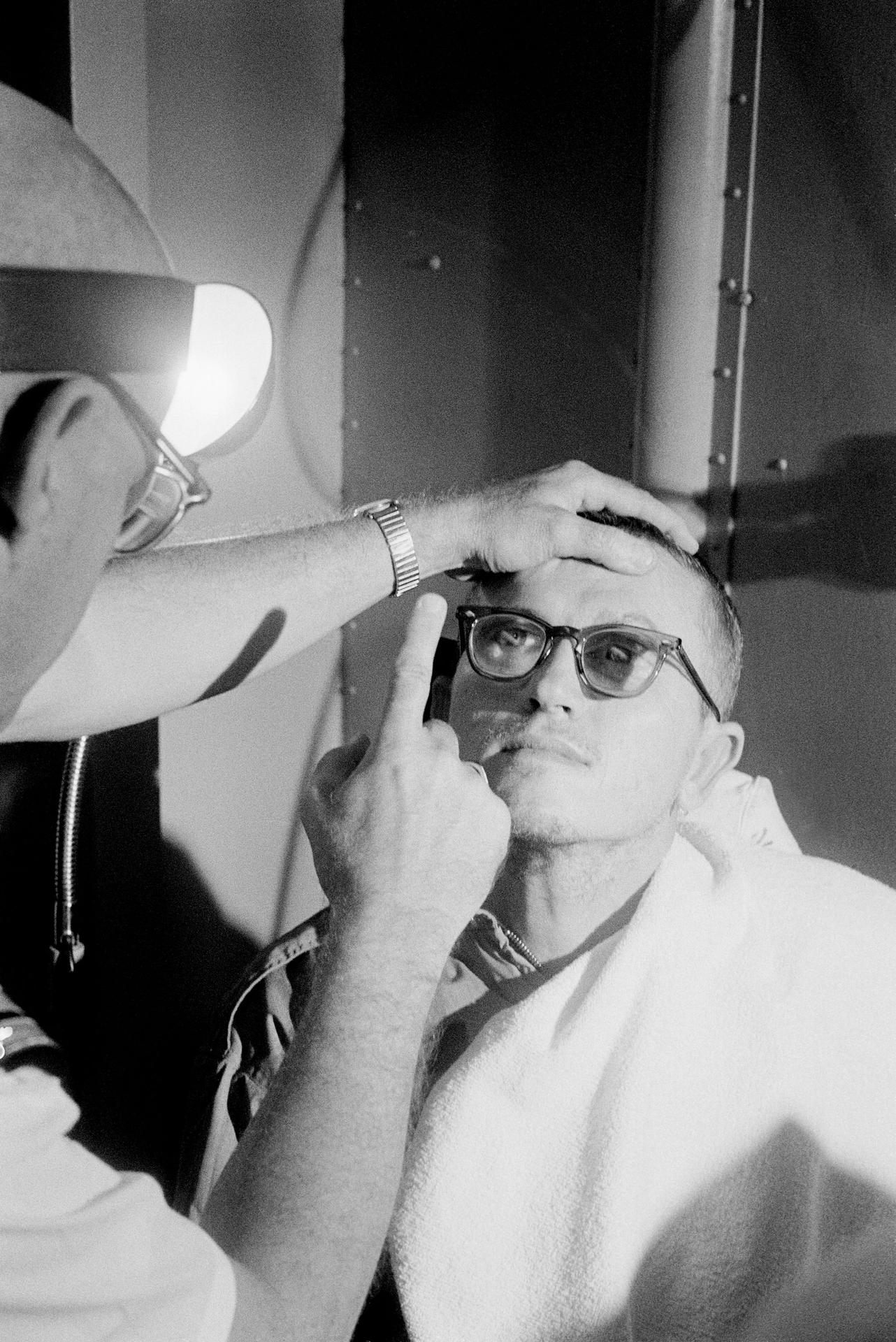
NASA astronaut Douglas Hurley is helped out of the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour spacecraft onboard the SpaceX GO Navigator recovery ship after he and NASA astronaut Robert Behnken landed in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Pensacola, Florida, Sunday, Aug. 2, 2020. The Demo-2 test flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program was the first to deliver astronauts to the International Space Station and return them safely to Earth onboard a commercially built and operated spacecraft. Behnken and Hurley returned after spending 64 days in space. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
NASA
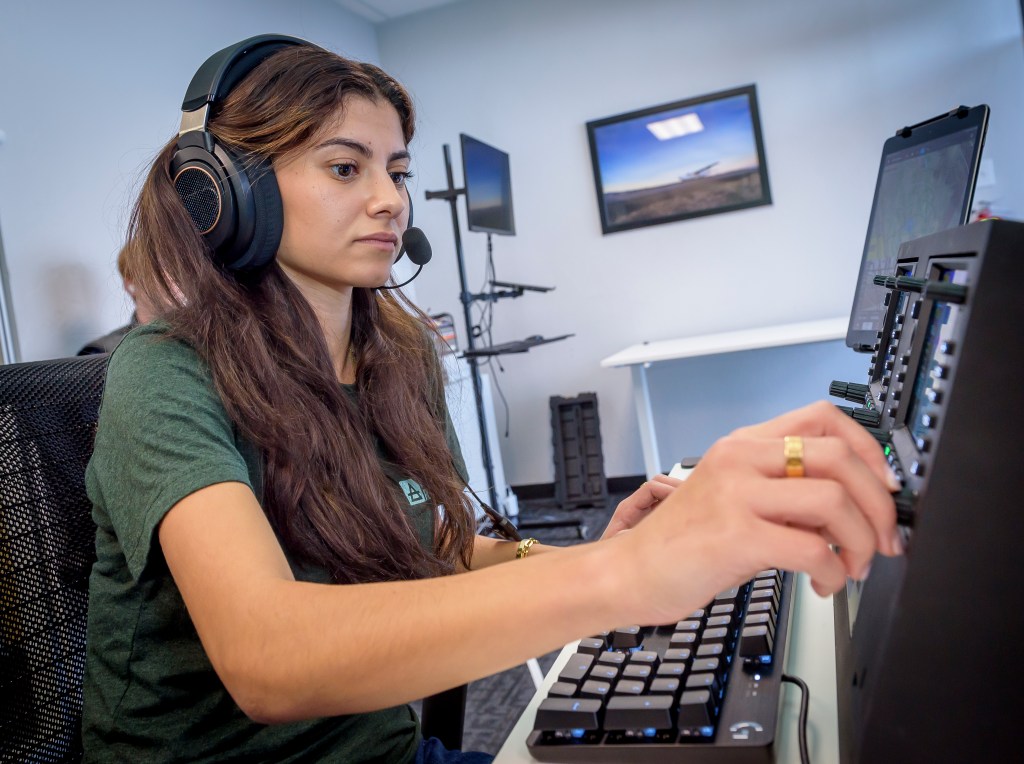
New spacecraft that will transport crews to the Lunar and Martian surfaces and return them to Earth may have diverse landing modalities which will function in different landing environments. Additionally, the crew may be deconditioned on landing, impacting their ability to independently egress the vehicles, perform post-landing tasks in a timely manner, and perform surface EVAs post-landing -including those required for emergencies.
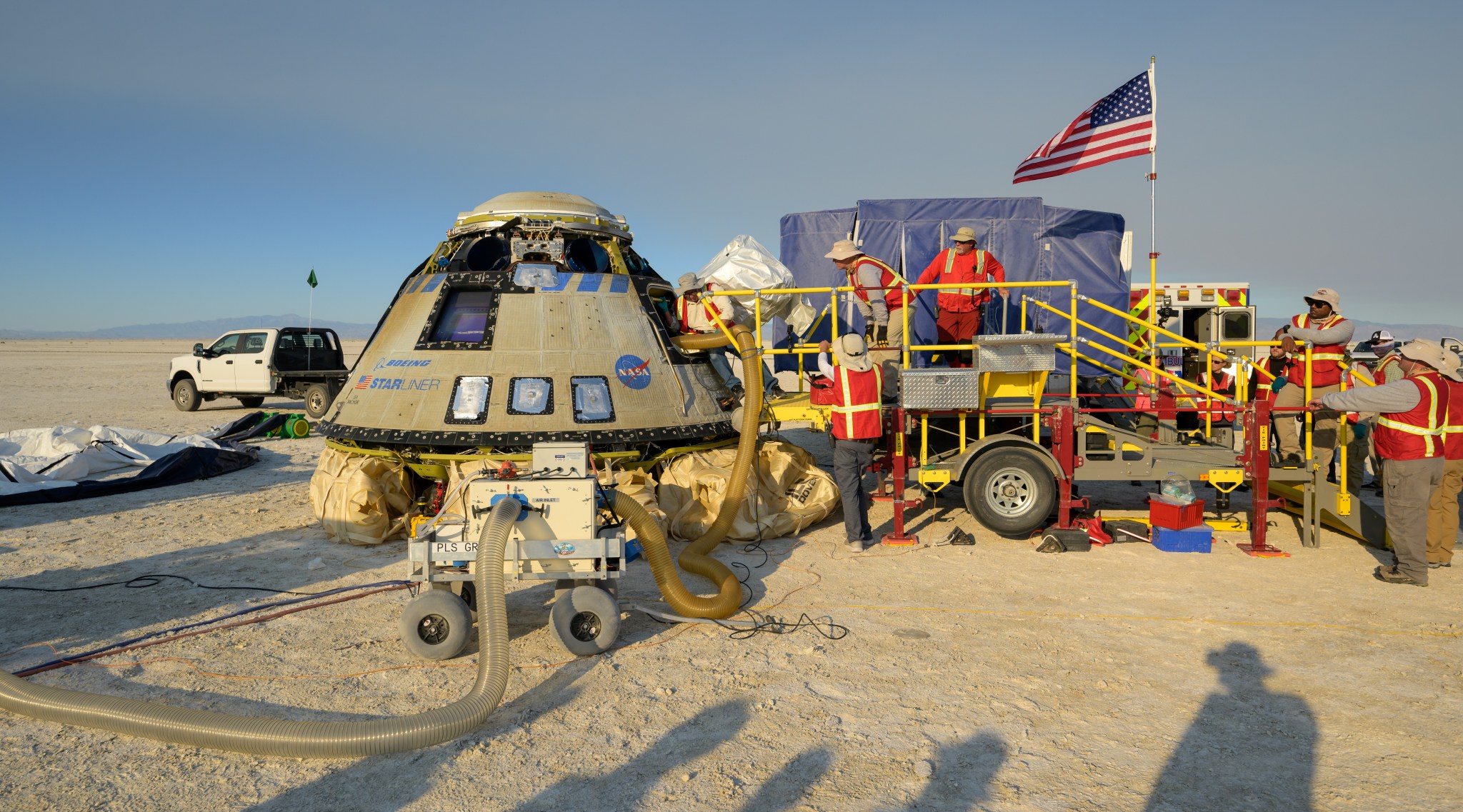

Boeing and NASA teams work around Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft after it landed at White Sands Missile Range’s Space Harbor, Wednesday, May 25, 2022, in New Mexico. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 serves as an end-to-end test of the system’s capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
Directed Acyclic Graph Files
+ DAG File Information (HSRB Home Page)